Add the following:
(in' su lin glar' jeen).
C267H404N72O78S6
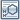
Insulin (human), 21A-glycine-30Ba-l-arginine-30Bb-l-arginine
DEFINITION
Insulin Glargine is a two-chain peptide containing 53 amino acids. The A-chain is composed of 21 amino acids, and the B-chain is composed of 32 amino acids. It is identical to the primary structure of Human Insulin except for position A21 which has Gly rather than Asn as in Human Insulin and two additional amino acids at the C terminal of the B-chain Arg (B31) and Arg (B32). Insulin Glargine is produced by methods based on recombinant DNA technology. Residual host cell protein (HCP) content is determined by a validated method and is NMT 10 ppm (ng HCP per mg of Insulin Glargine). Insulin Glargine contains NLT 94.0% and NMT 105.0% of insulin glargine (C267H404N72O78S6), calculated on the anhydrous basis.
[Note—One USP Insulin Glargine Unit is equivalent to 0.0364 mg of pure Insulin Glargine.
IDENTIFICATION
• A.
• B. Peptide Mapping
Phosphate/perchlorate buffer:
Solution A:
Solution B:
Mobile phase:
Table 1
| Time (min) |
Solution A (%) |
Solution B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 |
90 |
10 |
| 30 |
20 |
80 |
| 35 |
20 |
80 |
| 36 |
90 |
10 |
Tris buffer solution:
Enzyme solution:
Standard solution:
 for 2–3 h. Quench the digestion by adding 2 µL of phosphoric acid.
for 2–3 h. Quench the digestion by adding 2 µL of phosphoric acid.
Sample solution:
 for 2–3 h. Quench the digestion by adding 2 µL of phosphoric acid.
for 2–3 h. Quench the digestion by adding 2 µL of phosphoric acid.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
Detector:
Column:
Column temperature:

Flow rate:
Injection volume:
System suitability
Sample:
Suitability requirements:
Resolution:
Tailing factor:
Analysis
Samples:
Run a blank, and record the chromatograms.
Acceptance criteria:
ASSAY
• Procedure
Buffer:
Solution A:
Solution B:
Mobile phase:
Table 2
| Time (min) |
Solution A (%) |
Solution B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 |
96 |
4 |
| 20 |
83 |
17 |
| 30 |
63 |
37 |
| 33 |
96 |
4 |
[Note—Adjust the Mobile phase composition and the gradient by a parallel shift to obtain a retention time of 18–23 min for the insulin glargine main peak.
System suitability solution:
Standard solution:
Sample solution:
Chromatographic system
Mode:
Detector:
Column:
Column temperature:

Flow rate:
Injection volume:
System suitability
Samples:
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
Tailing factor:
Relative standard deviation:
Analysis
Samples:
Calculate the potency, in percent, of insulin glargine (C267H404N72O78S6) in the portion of Insulin Glargine taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of insulin glargine from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of insulin glargine from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Insulin Glargine RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of the Sample solution (corrected for the water content) (mg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
OTHER COMPONENTS
• Zinc Determination
Standard stock solution:
Standard solutions:
Sample solution:
Blank solution:
Instrumental conditions
Mode:
Analytical wavelength:
Flame:
Lamp:
System suitability
Sample:
Using the Standard solutions and Blank solution, construct a calibration curve by plotting the absorbances of the Standard solutions versus their concentrations, and draw the straight line best fitting the three plotted points.
Suitability requirements
Correlation coefficient:
Analysis
Samples:
Determine the concentration, C, in µg/mL of zinc in the Sample solution using the calibration curve.
Calculate the percentage of zinc in the portion of Insulin Glargine taken:
Result = [C × F1 × V × (F2/W)] × 100
| C | = | = concentration of zinc in the Sample solution (µg/mL) |
| F1 | = | = conversion factor from µg/mL to mg/mL, 0.001 |
| V | = | = volume of the Sample solution, 100 mL |
| F2 | = | = sampling factor, 5 |
| W | = | = weight of Insulin Glargine taken (mg) |
Acceptance criteria:
IMPURITIES
• Related Proteins
Mobile phase, System suitability solution, Standard solution, Sample solution, Chromatographic system, and System suitability:
Analysis
Sample:
Calculate the percentage of each individual insulin related protein (%ix) in the portion of Insulin Glargine taken:
Result = (ri/rT) × 100
| ri | = | = peak response of the insulin related protein |
| rT | = | = sum of the responses for all of the peaks |
Calculate the total percentage of insulin related proteins in the portion of Insulin Glargine taken:
Result = S%ix
Acceptance criteria:
• Limit of High Molecular Weight Proteins
Mobile phase:
System suitability solution:
 for 1.5–3 h.
for 1.5–3 h.
Sample solution:
Chromatographic system
Mode:
Detector:
Column:
Column temperature:
Flow rate:
Injection volume:
System suitability
Sample:
[Note—The retention time for the insulin monomer is about 35 min, and the high molecular weight proteins elute earlier.
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
Tailing factor:
Analysis
Sample:
Measure the areas of the peak responses, disregarding any peaks having retention times greater than that of the insulin monomer.
Calculate the percentage of high molecular weight proteins in the portion of Insulin Glargine taken:
Result = [SrH/(SrH + rM)] × 100
| SrH | = | = sum of the responses for all peaks having retention times less than that of insulin glargine |
| rM | = | = peak response of insulin glargine |
Acceptance criteria:
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Insulin Assays, Bioidentity Test  121
121 :
:
• Bacterial Endotoxins Test  85
85 :
:
• Microbial Enumeration Tests  61
61 and Tests For Specified Microorganisms
and Tests For Specified Microorganisms  62
62 :
:
• Water Determination, Method Ic  921
921 :
:
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
• Labeling:
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Endotoxin RS
USP Insulin Glargine for Peak Identification RS
Contains insulin glargine and 0A-Arg-insulin glargine.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Edith Chang, Ph.D.
Scientific Liaison (301) 816-8392 |
(BIO12010) Monographs - Biologics and Biotechnology 1 |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison (301) 816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison (301) 816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison (301) 816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP38–NF33 Page 3874
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 39(4)