Oil-Soluble Vitamins Capsules
DEFINITION
Oil-Soluble Vitamins Capsules contain two or more of the following oil-soluble vitamins: Vitamin A, Vitamin D as Ergocalciferol (Vitamin D2) or Cholecalciferol (Vitamin D3), Vitamin E, Phytonadione (Vitamin K1), and Beta Carotene. Capsules contain NLT 90.0% and NMT 165.0% of the labeled amounts of vitamin A (C20H30O) as retinol or esters of retinol in the form of retinyl acetate (C22H32O2) or retinyl palmitate (C36H60O2); vitamin D as cholecalciferol (C27H44O) or ergocalciferol (C28H44O); vitamin E as alpha tocopherol (C29H50O2), alpha tocopheryl acetate (C31H52O3), or alpha tocopheryl acid succinate (C33H54O5); phytonadione (C31H46O2); and beta carotene (C40H56).
Oil-Soluble Vitamins Capsules contain no other vitamins or any minerals. They may contain other labeled added substances that are generally recognized as safe, in amounts that are unobjectionable.
STRENGTH
[Note—In the following assays, where more than one assay method is given for an individual ingredient, the requirements may be met by following any one of the specified methods, the method used being stated in the labeling only if Method 1 is not used. ]
• Vitamin A, Method 1
[Note—Where the use of a vitamin A ester (retinyl acetate or retinyl palmitate) is specified in the following procedure, use the chemical form present in the formulation. USP Vitamin A RS is retinyl acetate. It is to be used where USP Vitamin A RS is specified. Use low-actinic glassware throughout this procedure. ]
Mobile phase:
n-Hexane
Standard solution:
15 µg/mL of retinyl acetate from USP Vitamin A RS in n-hexane
System suitability stock solution:
15 µg/mL of retinyl palmitate in n-hexane
System suitability solution:
Mix equal volumes of the System suitability stock solution and the Standard solution to obtain concentrations of 7.5 µg/mL each of retinyl acetate and retinyl palmitate.
Sample solution:
Transfer the contents of NLT 20 Capsules to a suitable container, mix, and weigh. Transfer a portion of the mixture, equivalent to 5 Capsules, to a container having a polytef-lined screw cap. [Note—For hard gelatin Capsules, remove, as completely as possible, the contents of NLT 20 Capsules by cutting open the Capsule shells, transferring the shells and their contents to a suitable container, and triturating to a homogeneous mass. Transfer a portion of the mass, equivalent to 5 Capsules, to a container having a polytef-lined screw cap. ] Add 10 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide and 15 mL of n-hexane, and shake for 45 min on a wrist-action shaker in a water bath maintained at 60 . [Note—Set up the wrist-action shaker to ensure that the contents of the container are mixed vigorously and thoroughly. ] Centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 10 min, and transfer the hexane layer by means of a pipet to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 15 mL of n-hexane to the dimethyl sulfoxide layer, shake thoroughly for 5 min, and transfer the hexane layer by means of a pipet to the 100-mL volumetric flask. Repeat this extraction with three additional 15-mL portions of n-hexane. Dilute the extracts in the volumetric flask with n-hexane to volume. Dilute a volume of this solution with n-hexane to obtain a solution with a concentration of 15 µg/mL of vitamin A as retinol (C20H30O).
. [Note—Set up the wrist-action shaker to ensure that the contents of the container are mixed vigorously and thoroughly. ] Centrifuge at 3000 rpm for 10 min, and transfer the hexane layer by means of a pipet to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 15 mL of n-hexane to the dimethyl sulfoxide layer, shake thoroughly for 5 min, and transfer the hexane layer by means of a pipet to the 100-mL volumetric flask. Repeat this extraction with three additional 15-mL portions of n-hexane. Dilute the extracts in the volumetric flask with n-hexane to volume. Dilute a volume of this solution with n-hexane to obtain a solution with a concentration of 15 µg/mL of vitamin A as retinol (C20H30O).
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 325 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 15-cm; 3-µm packing L8
Flow rate:
1 mL/min
Injection size:
40 µL
System suitability
Sample:
System suitability solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 10 between all-trans-retinyl acetate and all-trans-retinyl palmitate
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 3.0%
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Measure the peak area for all-trans-retinyl acetate from the Standard solution and the peak area for all-trans-retinyl acetate or all-trans-retinyl palmitate from the Sample solution. For products containing vitamin A acetate or vitamin A palmitate, calculate the percentage of the labeled amount of vitamin A, as retinol (C20H30O), in the portion of Capsules taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × F × 100
| rU | = | = peak area of the all-trans-retinyl ester from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak area of the all-trans-retinyl ester from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of retinyl acetate (C22H32O2) from USP Vitamin A RS in the Standard solution (µg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of vitamin A, as retinol (C20H30O) in the Sample solution (µg/mL) |
| F | = | = factor used to convert retinyl acetate, the ester form present in USP Vitamin A RS, to retinol, 0.872 |
[Note—The molar responses of retinyl acetate and retinyl palmitate are equivalent. ]
Acceptance criteria:
90.0%–165.0% of the labeled amount of vitamin A, as retinol (C20H30O)
• Vitamin A, Method 2
[Note—Where a vitamin A ester (retinyl acetate or retinyl palmitate) is indicated in the following procedure, use the chemical form present in the formulation. USP Vitamin A RS is retinyl acetate. It is to be used where USP Vitamin A RS is specified. Use low-actinic glassware throughout this procedure. ]
3 N methanolic sulfuric acid solution:
Cautiously add 9 mL of sulfuric acid to 80 mL of methanol in a 100-mL volumetric flask. Cool, and dilute with methanol to volume.
Sodium ascorbate–pyrogallol solution:
Transfer 10 g of sodium ascorbate and 5 g of pyrogallol to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and add sufficient water to dissolve. Add 1.7 mL of sulfuric acid, and dilute with water to volume.
Lecithin solution:
5 mg/mL of lecithin in 2,2,4-trimethylpentane
Mobile phase:
n-Hexane and ethyl acetate (99.7:0.3)
Standard solution:
15 µg/mL of retinyl acetate from USP Vitamin A RS in 2,2,4-trimethylpentane
System suitability stock solution:
15 µg/mL of retinyl palmitate in 2,2,4-trimethylpentane
System suitability solution:
Mix equal volumes of the System suitability stock solution and the Standard solution to obtain concentrations of 7.5 µg/mL each of retinyl acetate and retinyl palmitate.
Sample solution:
[Note—This preparation is suitable for the determination of vitamin A, vitamin D, and vitamin E, when present in the formulation. ] Weigh NLT 20 Capsules in a tared weighing bottle. Using a sharp blade if necessary, carefully open the Capsules, without loss of shell material, and transfer the contents to a 100-mL beaker. Remove any contents adhering to the empty shells by washing with several portions of ether. Discard the washings, and dry the Capsule shells with the aid of a current of dry air. Weigh the empty Capsule shells in the tared weighing bottle, and calculate the net weight of the Capsule contents. Transfer a portion of the Capsule contents, equivalent to 30 µg of the labeled amount of cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol (vitamin D), to a container with a polytef-lined screw cap. If vitamin D is not present in the formulation, use a portion, equivalent to 90 mg of the labeled amount of vitamin E. If vitamin E is not present in the formulation, use a portion, equivalent to 2.5 mg of the labeled amount of vitamin A, as retinol. Add 0.5 g of sodium bicarbonate, 1.5 mL of Lecithin solution, and 12.5 mL of 2,2,4-trimethylpentane, and disperse on a vortex mixer. Add 6 mL of Sodium ascorbate–pyrogallol solution, shake slowly, and allow the solution to degas. Continue shaking until the evolution of gas has ceased, and then shake for an additional 12 min. Add 6 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide, mix on a vortex mixer to form a suspension, and shake for 12 min. Add 6 mL of 3 N methanolic sulfuric acid solution, mix on a vortex mixer to form a suspension, and shake for 12 min. Add 12.5 mL of 2,2,4-trimethylpentane, mix on a vortex mixer to form a suspension, and shake for 10 min. Centrifuge for 10 min to break up the emulsion and to clarify the supernatant. [Note—The supernatant is used for the determination of vitamin A, and also vitamin D and vitamin E, if present in the formulation. ] If necessary, quantitatively dilute a volume of the supernatant with 2,2,4-trimethylpentane to obtain a concentration close to that of the Standard solution.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 325 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L24
Flow rate:
1.5 mL/min
Injection size:
40 µL
System suitability
Sample:
System suitability solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 8.0 between all-trans-retinyl acetate and all-trans-retinyl palmitate
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 3.0%
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Measure the peak area for all-trans-retinyl acetate from the Standard solution and the peak area of all-trans-retinyl acetate or all-trans-retinyl palmitate from the Sample solution.
Calculate the percentage of the labeled amount of vitamin A, as retinol (C20H30O), in the portion of Capsules taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × F × 100
| rU | = | = peak area of the all-trans-retinyl ester from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak area of the all-trans-retinyl ester from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of retinyl acetate (C22H32O2) from USP Vitamin A RS in the Standard solution (µg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of vitamin A, as retinol (C20H30O) in the Sample solution (µg/mL) |
| F | = | = factor used to convert retinyl acetate, the ester form present in USP Vitamin A RS, to retinol, 0.872 |
[Note—Account for the initial extraction volume of 26.5 mL of 2,2,4-trimethylpentane to calculate the nominal concentration. The molar responses of retinyl acetate and retinyl palmitate are equivalent. ]
Acceptance criteria:
90.0%–165.0% of the labeled amount of vitamin A, as retinol (C20H30O)
• Vitamin A, Method 3
[Note—Where a vitamin A ester (retinyl acetate or retinyl palmitate) is indicated in the following procedure, use the chemical form present in the formulation. USP Vitamin A RS is retinyl acetate. It is to be used where USP Vitamin A RS is specified. Use low-actinic glassware throughout this procedure. ]
Extraction solvent:
n-Hexane and methylene chloride (3:1)
Potassium hydroxide solution:
800 mg/mL of potassium hydroxide in water. [Note—Cautiously add the potassium hydroxide to the water. Mix, and cool. ]
Diluent:
10 mg/mL of pyrogallol in alcohol
Mobile phase:
n-Hexane and isopropyl alcohol (92:8)
Standard stock solution:
30 µg/mL of retinyl acetate from USP Vitamin A RS in Diluent. [Note—This solution may be stored in a refrigerator for 1 week. ]
Standard solution:
Dilute a volume of Standard stock solution with Diluent to obtain a concentration of 1 µg/mL of retinyl acetate from USP Vitamin A RS. Transfer 10.0 mL of this solution to a stoppered 125-mL flask, and add 5 mL of water, 5 mL of Diluent, and 3 mL of Potassium hydroxide solution. Insert the stopper tightly, shake for 15 min over a water bath maintained at 60 ± 5 , and cool to room temperature. Add 7 mL of water and 25.0 mL of Extraction solvent. Insert the stopper tightly, and shake vigorously for 60 s. Rinse the sides of the flask with 60 mL of water, and allow to stand for 10 min until the layers separate. Withdraw a portion of the organic layer for injection into the chromatograph. This Standard solution contains 0.34 µg/mL of retinol.
, and cool to room temperature. Add 7 mL of water and 25.0 mL of Extraction solvent. Insert the stopper tightly, and shake vigorously for 60 s. Rinse the sides of the flask with 60 mL of water, and allow to stand for 10 min until the layers separate. Withdraw a portion of the organic layer for injection into the chromatograph. This Standard solution contains 0.34 µg/mL of retinol.
Sample solution:
Weigh NLT 20 Capsules in a tared weighing bottle. Open the Capsules, without loss of shell material, and transfer the contents to a 100-mL beaker. Remove any contents adhering to the empty shells by washing with several portions of ether. Discard the washings, and dry the Capsule shells with the aid of a current of dry air. Weigh the empty Capsule shells in the tared weighing bottle, and calculate the net weight of the Capsule contents. Transfer a portion of the Capsule contents, equivalent to 1.5 mg of retinyl acetate, to a stoppered 125-mL flask. Add 5 mL of water, 15 mL of Diluent, and 3 mL of Potassium hydroxide solution. Insert the stopper tightly, shake for 15 min over a water bath maintained at 60 ± 5 , and cool to room temperature. Add 7 mL of water and 25.0 mL of Extraction solvent. Insert the stopper tightly, and shake vigorously for 60 s or longer, if necessary, for complete extraction. Rinse the sides of the flask with 60 mL of water, and allow to stand for 10 min until the layers separate. [Note—Do not shake, because an emulsion may form. ] Withdraw a portion of the organic layer, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with Extraction solvent, to obtain a concentration of 0.34 µg/mL of retinol.
, and cool to room temperature. Add 7 mL of water and 25.0 mL of Extraction solvent. Insert the stopper tightly, and shake vigorously for 60 s or longer, if necessary, for complete extraction. Rinse the sides of the flask with 60 mL of water, and allow to stand for 10 min until the layers separate. [Note—Do not shake, because an emulsion may form. ] Withdraw a portion of the organic layer, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with Extraction solvent, to obtain a concentration of 0.34 µg/mL of retinol.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 335 nm
Column:
6.2-mm × 8-cm; packing L3
Column temperature:
40
Flow rate:
4 mL/min
Injection size:
50 µL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
[Note—The relative retention times for 13-cis-retinol and all-trans-retinol are about 0.92 and 1.0, respectively. ]
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 5.0%
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Measure the peak areas for all-trans-retinol and 13-cis-retinol. Calculate the percentage of the labeled amount of vitamin A, as retinol (C20H30O), in the portion of Capsules taken:
Result = (rT1/rT2) × (CS/CU) × F × 100
| rT1 | = | = sum of the areas of the all-trans-retinol and 13-cis-retinol peaks from the Sample solution |
| rT2 | = | = sum of the areas of all-trans-retinol and 13-cis-retinol peaks from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of retinyl acetate (C23H32O2) from USP Vitamin A RS in the Standard solution (µg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of vitamin A, as retinol (C20H30O) in the Sample solution (µg/mL) |
| F | = | = factor used to convert retinyl acetate, the ester form present in USP Vitamin A RS, to retinol, 0.872 |
Acceptance criteria:
90.0%–165.0% of the labeled amount of vitamin A, as retinol (C20H30O)
• Cholecalciferol or Ergocalciferol (Vitamin D), Method 1
[Note—Where vitamin D (cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol) is specified in the following procedure, use the chemical form present in the formulation and the relevant USP Reference Standard. Use low-actinic glassware throughout this procedure. ]
Mobile phase:
n-Hexane and isopropyl alcohol (99:1)
Standard solution:
2 µg/mL of USP Cholecalciferol RS or USP Ergocalciferol RS in n-hexane
System suitability solution:
Heat a volume of the Standard solution at 60 for 1 h to partially isomerize vitamin D (cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol) to its corresponding precursor.
for 1 h to partially isomerize vitamin D (cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol) to its corresponding precursor.
Sample solution:
Proceed as directed for the Sample solution in Vitamin A, Method 1. Transfer NLT 20 mL of this solution retained as specified in the directions for the Sample solution in Vitamin A, Method 1 to a suitable container, and evaporate, if necessary, in vacuum at room temperature to obtain a solution with a concentration of 2 µg/mL of cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 265 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 15-cm; 3-µm packing L8
Flow rate:
1 mL/min
Injection size:
100 µL
System suitability
Samples:
Standard solution and System suitability solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 10 between the vitamin D form present and its corresponding precursor, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 3.0%, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Measure the peak areas for vitamin D. Calculate the percentage of the labeled amount of cholecalciferol (C27H44O) or ergocalciferol (C28H44O) in the portion of Capsules taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × F × 100
| rU | = | = peak area of cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak area of cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Cholecalciferol RS or USP Ergocalciferol RS in the Standard solution (µg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol in the Sample solution (µg/mL) |
| F | = | = correction factor to account for the average amount of previtamin D present in the Sample solution, 1.09 |
Acceptance criteria:
90.0%–165.0% of the labeled amount of vitamin D as cholecalciferol (C27H44O) or ergocalciferol (C28H44O)
• Cholecalciferol or Ergocalciferol (Vitamin D), Method 2
[Note—Where vitamin D (cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol) is specified in the following procedure, use the chemical form present in the formulation and the relevant USP Reference Standard. Use low-actinic glassware throughout this procedure. ]
3 N methanolic sulfuric acid solution, Sodium ascorbate–pyrogallol solution, Lecithin solution, and Sample solution:
Proceed as directed in Vitamin A, Method 2.
Mobile phase:
n-Hexane and tertiary butyl alcohol (98.75:1.25)
Standard solution:
1 µg/mL of USP Cholecalciferol RS or USP Ergocalciferol RS in 2,2,4-trimethylpentane
System suitability solution:
Heat a volume of the Standard solution at 60 for 1 h to partially isomerize vitamin D (cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol) to its corresponding precursor.
for 1 h to partially isomerize vitamin D (cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol) to its corresponding precursor.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 265 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L24
Flow rate:
1 mL/min
Injection size:
40 µL
System suitability
Samples:
Standard solution and System suitability solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 4.0 between the vitamin D form present and its corresponding precursor, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 3.0%, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Measure the peak areas for vitamin D. Calculate the percentage of the labeled amount of cholecalciferol (C27H44O) or ergocalciferol (C28H44O) in the portion of Capsules taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak area of cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak area of cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Cholecalciferol RS or USP Ergocalciferol RS in the Standard solution (µg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol in the Sample solution (µg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
90.0%–165.0% of the labeled amount of vitamin D as cholecalciferol (C27H44O) or ergocalciferol (C28H44O)
• Cholecalciferol or Ergocalciferol (Vitamin D), Method 3
[Note—Where vitamin D (cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol) is specified in the following procedure, use the chemical form present in the formulation and the relevant USP Reference Standard. Use low-actinic glassware throughout this procedure. ]
Diluted acetic acid:
Glacial acetic acid solution (1 in 10) in water
Phenolphthalein solution:
10 mg/mL of phenolphthalein in alcohol
Potassium hydroxide solution:
Slowly dissolve 14 g of potassium hydroxide in a mixture of 31 mL of dehydrated alcohol and 5 mL of water. Prepare fresh daily.
Extraction solvent:
Methylene chloride and isopropyl alcohol (99.8:0.2)
Mobile phase:
Acetonitrile and methanol (91:9)
Standard stock solution:
0.2 mg/mL of USP Cholecalciferol RS or USP Ergocalciferol RS in dehydrated alcohol. [Note—Prepare fresh every 4 weeks. Store in a freezer. ]
Standard solution:
[Note—Condition the solid-phase extraction column specified for use in the Standard solution and the Sample solution by initially washing the column with 4.0 mL of a mixture of methylene chloride and isopropyl alcohol (4:1), followed by 5.0 mL of Extraction solvent. Do not allow the column to dry. ]
Dilute a volume of the Standard stock solution with dehydrated alcohol to obtain a concentration of 5 µg/mL of USP Cholecalciferol RS or USP Ergocalciferol RS. Prepare this solution fresh daily. Transfer 2.0 mL of this solution to a stoppered 125-mL flask. Add 15.0 mL of water and 15.0 mL of Potassium hydroxide solution, insert the stopper, and shake for 30 min in a water bath maintained at 60 . Allow to cool to room temperature, and transfer the contents of the flask to a 250-mL separatory funnel. Add 15.0 mL of water to the flask, insert the stopper, shake vigorously, and transfer this solution to the separatory funnel. Rinse the flask with 60 mL of n-hexane, and transfer the rinsing to the separatory funnel. Insert the stopper, shake vigorously for 90 s, and allow to stand for 15 min until the layers separate. Drain and discard the aqueous layer. Add 15.0 mL of water to the hexane layer in the separatory funnel, insert the stopper, and shake vigorously. Allow to stand for 10 min until the layers separate, and discard the aqueous layer. Add 1 drop of Phenolphthalein solution and 15.0 mL of water to the separatory funnel. Add Diluted acetic acid dropwise, with shaking, until the washing is neutral. Allow to stand for 10 min until the layers separate. Drain and discard the aqueous layer. Filter the hexane layer through anhydrous sodium sulfate supported by a small pledget of cotton into a 100-mL round-bottom flask. Rinse the funnel and sodium sulfate with a few mL of n-hexane, and collect the rinsings in the same flask. Evaporate the hexane in the flask on a rotary evaporator at 50
. Allow to cool to room temperature, and transfer the contents of the flask to a 250-mL separatory funnel. Add 15.0 mL of water to the flask, insert the stopper, shake vigorously, and transfer this solution to the separatory funnel. Rinse the flask with 60 mL of n-hexane, and transfer the rinsing to the separatory funnel. Insert the stopper, shake vigorously for 90 s, and allow to stand for 15 min until the layers separate. Drain and discard the aqueous layer. Add 15.0 mL of water to the hexane layer in the separatory funnel, insert the stopper, and shake vigorously. Allow to stand for 10 min until the layers separate, and discard the aqueous layer. Add 1 drop of Phenolphthalein solution and 15.0 mL of water to the separatory funnel. Add Diluted acetic acid dropwise, with shaking, until the washing is neutral. Allow to stand for 10 min until the layers separate. Drain and discard the aqueous layer. Filter the hexane layer through anhydrous sodium sulfate supported by a small pledget of cotton into a 100-mL round-bottom flask. Rinse the funnel and sodium sulfate with a few mL of n-hexane, and collect the rinsings in the same flask. Evaporate the hexane in the flask on a rotary evaporator at 50 to dryness. Immediately add 2.0 mL of Extraction solvent to dissolve the residue. Transfer this solution to a freshly conditioned solid-phase extraction column containing silica packing with a sorbent mass-to-column volume ratio of 500 mg to 2.8 mL or equivalent, rinse the round-bottom flask with 1.0 mL of Extraction solvent, and transfer to the column. Elute the column with 2.0 mL of Extraction solvent, and discard this fraction. Elute the column with 7.0 mL of Extraction solvent, and collect the eluate in a suitable flask. Place the flask in a warm water bath maintained at 42
to dryness. Immediately add 2.0 mL of Extraction solvent to dissolve the residue. Transfer this solution to a freshly conditioned solid-phase extraction column containing silica packing with a sorbent mass-to-column volume ratio of 500 mg to 2.8 mL or equivalent, rinse the round-bottom flask with 1.0 mL of Extraction solvent, and transfer to the column. Elute the column with 2.0 mL of Extraction solvent, and discard this fraction. Elute the column with 7.0 mL of Extraction solvent, and collect the eluate in a suitable flask. Place the flask in a warm water bath maintained at 42 , and evaporate the solvent with the aid of a stream of nitrogen. Immediately add 2.0 mL of acetonitrile to the residue, and use the solution for injection into the chromatograph.
, and evaporate the solvent with the aid of a stream of nitrogen. Immediately add 2.0 mL of acetonitrile to the residue, and use the solution for injection into the chromatograph.
Sample solution:
Proceed as directed for the Sample solution in Vitamin A, Method 3, through “calculate the net weight of the Capsule contents.” Transfer a portion of the Capsule contents, equivalent to 10 µg of ergocalciferol or cholecalciferol, to a stoppered 125-mL flask, and proceed as directed for the Standard solution, beginning with “Add 15.0 mL of water and 15.0 mL of Potassium hydroxide solution”.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 265 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Column temperature:
27
Flow rate:
0.7 mL/min
Injection size:
15 µL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 4.0%
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Measure the peak areas for vitamin D. Calculate the percentage of the labeled amount of cholecalciferol (C27H44O) or ergocalciferol (C28H44O) in the portion of Capsules taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak area of cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak area of cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Cholecalciferol RS or USP Ergocalciferol RS in the Standard solution (µg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of cholecalciferol or ergocalciferol in the Sample solution (µg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
90.0%–165.0% of the labeled amount of vitamin D as cholecalciferol (C27H44O) or ergocalciferol (C28H44O)
• Vitamin E, Method 1
[Note—Where vitamin E (alpha tocopherol, alpha tocopheryl acetate, or alpha tocopheryl acid succinate) is specified in the following procedure, use the chemical form present in the formulation and the relevant USP Reference Standard. Use low-actinic glassware throughout this procedure. ]
Solution A:
Phosphoric acid solution (1 in 100) in water
Mobile phase:
Methanol and Solution A (19:1)
Standard solution:
2 mg/mL of USP Alpha Tocopherol RS, USP Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate RS, or USP Alpha Tocopheryl Acid Succinate RS in methanol
System suitability solution:
Prepare a 0.65-mg/mL solution of USP Ergocalciferol RS in methanol. Transfer 1.0 mL of this solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask containing 100 mg of USP Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate RS. Dissolve in 30 mL of methanol, with the aid of sonication if necessary, and dilute with methanol to volume. Store this solution in a refrigerator.
Sample solution:
Proceed as directed for the Sample solution in Vitamin A, Method 1. Transfer NLT 20 mL of this solution retained as specified in the directions for the Sample solution in Vitamin A, Method 1 to a suitable container, and evaporate if necessary, in vacuum at room temperature to dryness. Transfer the contents of the flask to a suitable volumetric flask with the aid of methanol, and dilute with methanol to volume, to obtain a concentration of 2 mg/mL of alpha tocopherol, alpha tocopheryl acetate, or alpha tocopheryl acid succinate.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 254 nm
Column:
8-mm × 10-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Flow rate:
2 mL/min
Injection size:
100 µL
System suitability
Samples:
Standard solution and System suitability solution
[Note—The relative retention times for ergocalciferol and alpha tocopheryl acetate are about 0.5 and 1.0, respectively. ]
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 12 between ergocalciferol and alpha tocopheryl acetate, System suitability solution
Tailing factor:
Between 0.8 and 1.2, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 3.0%, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Measure the peak areas. Calculate the percentage of the labeled amount of alpha tocopherol (C29H50O2), alpha tocopheryl acetate (C31H52O3), or alpha tocopheryl acid succinate (C33H54O5) in the portion of Capsules taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak area of the relevant vitamin E form from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak area of the relevant vitamin E form from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of the corresponding USP Reference Standard in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of the corresponding form of vitamin E in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
90.0%–165.0% of the labeled amount of vitamin E as alpha tocopherol (C29H50O2), alpha tocopheryl acetate (C31H52O3), or alpha tocopheryl acid succinate (C33H54O5)
• Vitamin E, Method 2
[Note—Where vitamin E (alpha tocopherol, alpha tocopheryl acetate, or alpha tocopheryl acid succinate) is specified in the following procedure, use the chemical form present in the formulation and the relevant USP Reference Standard. Use low-actinic glassware throughout this procedure. ]
Mobile phase:
Mix 240 mL of methanol with 10 mL of water followed by 0.5 mL of 50% phosphoric acid, and dilute with acetonitrile to 1000 mL.
System suitability solution:
2 mg/mL each of USP Alpha Tocopherol RS, USP Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate RS, and USP Alpha Tocopheryl Acid Succinate RS in methanol
Standard solution:
2 mg/mL of USP Alpha Tocopherol RS, USP Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate RS, or USP Alpha Tocopheryl Acid Succinate RS in methanol
3 N methanolic sulfuric acid solution:
Cautiously mix sulfuric acid and methanol (9 in 100) in a 100-mL volumetric flask. [Note—Dissolve in a portion of methanol, cool, and then dilute to final volume. ]
Sodium ascorbate–pyrogallol solution:
Transfer 10 g of sodium ascorbate and 5 g of pyrogallol to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add sufficient water to dissolve. Add 1.7 mL of sulfuric acid, and dilute with water to volume.
Lecithin solution:
5 mg/mL of lecithin in 2,2,4-trimethylpentane
Sample solution:
Proceed as directed for the Sample solution in Vitamin A, Method 2, through “calculate the net weight of the Capsule contents.” Transfer a portion of the Capsule contents, equivalent to 55 mg of vitamin E, to a container having a polytef-lined screw cap. Add 0.5 g of sodium bicarbonate, 1.5 mL of Lecithin solution, and 12.5 mL of 2,2,4-trimethylpentane, and disperse on a vortex mixer. Add 6 mL of Sodium ascorbate–pyrogallol solution, shake slowly, and allow the solution to degas. Continue shaking until the evolution of gas has ceased, and then shake for an additional 12 min. Add 6 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide, mix on a vortex mixer to form a suspension, and shake for 12 min. Add 6 mL of 3 N methanolic sulfuric acid solution, mix on a vortex mixer to form a suspension, and shake for 12 min. Add 12.5 mL of 2,2,4-trimethylpentane, mix on a vortex mixer to form a suspension, and shake for 10 min. Centrifuge for 10 min to break up the emulsion and to clarify the supernatant layer. Transfer a volume of the supernatant 2,2,4-trimethylpentane layer to a suitable volumetric flask, the volume of the specimen withdrawn from the 2,2,4-trimethylpentane layer and the size of the volumetric flask being such that the final concentration of the Sample solution is equivalent to that of the Standard solution. Evaporate nearly to dryness, add several mL of methanol, and evaporate the remaining 2,2,4-trimethylpentane. Dilute with methanol to volume.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 280 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Flow rate:
1.5 mL/min
Injection size:
25 µL
System suitability
Samples:
Standard solution and System suitability solution
[Note—The relative retention times for alpha tocopheryl acid succinate, alpha tocopherol, and alpha tocopheryl acetate are about 0.6, 0.8, and 1.0, respectively. ]
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 4.0 between alpha tocopheryl acid succinate and alpha tocopherol and NLT 3.0 between alpha tocopherol and alpha tocopheryl acetate, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 3.0%, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Measure the peak areas. Calculate the percentage of the labeled amount of alpha tocopherol (C29H50O2), alpha tocopheryl acetate (C31H52O3), or alpha tocopheryl acid succinate (C33H54O5) in the portion of Capsules taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak area of the relevant vitamin E form from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak area of the relevant vitamin E form from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of the corresponding USP Reference Standard in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of the corresponding form of vitamin E in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
[Note—Account for the initial extraction volume of 26.5 mL of 2,2,4-trimethylpentane and the dilution factor to exchange the solvent from 2,2,4-trimethylpentane to methanol to calculate the nominal concentration. ]
Acceptance criteria:
90.0%–165.0% of the labeled amount of vitamin E as alpha tocopherol (C29H50O2), alpha tocopheryl acetate (C31H52O3), or alpha tocopheryl acid succinate (C33H54O5)
• Vitamin E, Method 3
[Note—Where vitamin E (alpha tocopherol, alpha tocopheryl acetate, or alpha tocopheryl acid succinate) is specified in the following procedure, use the chemical form present in the formulation and the relevant USP Reference Standard. Use low-actinic glassware throughout this procedure. ]
Diluent:
Acetonitrile and ethyl acetate (1:1)
Mobile phase:
Methanol, acetonitrile, and n-hexane (46.5:46.5:7.0)
Standard solution:
0.3 mg/mL of USP Alpha Tocopherol RS in methanol
Sample solution:
Proceed as directed for the Sample solution in Vitamin A, Method 3 through “calculate the net weight of the Capsule contents“. Transfer a portion of the Capsule contents, equivalent to 8.0 mg of alpha tocopherol, to a glass-stoppered conical flask. Add 25.0 mL of water, 25.0 mL of dehydrated alcohol, and 3.5 g of potassium hydroxide pellets. Shake for 1 h in a water bath maintained at 55 , cool, and transfer with the aid of a minimum volume of water to a 125-mL separatory funnel. Rinse the flask with 50 mL of n-hexane, and add the rinsing to the separatory funnel. Insert the stopper, shake vigorously for 60 s, and allow the layers to separate. Drain the aqueous layer into a second 250-mL separatory funnel, and repeat the extraction with 50 mL of n-hexane. Discard the aqueous layer and combine the hexane extracts. Wash the combined extracts with 25 mL of water, allow the layers to separate, and discard the aqueous layer. Add 3 drops of glacial acetic acid, and repeat the washing procedure two more times. Filter the washed hexane layer through anhydrous sodium sulfate into a 250-mL round-bottom flask. Rinse the funnel and sodium sulfate with a few mL of n-hexane, and add the rinsing to the hexane solution in the flask. Place the flask in a water bath maintained at 50
, cool, and transfer with the aid of a minimum volume of water to a 125-mL separatory funnel. Rinse the flask with 50 mL of n-hexane, and add the rinsing to the separatory funnel. Insert the stopper, shake vigorously for 60 s, and allow the layers to separate. Drain the aqueous layer into a second 250-mL separatory funnel, and repeat the extraction with 50 mL of n-hexane. Discard the aqueous layer and combine the hexane extracts. Wash the combined extracts with 25 mL of water, allow the layers to separate, and discard the aqueous layer. Add 3 drops of glacial acetic acid, and repeat the washing procedure two more times. Filter the washed hexane layer through anhydrous sodium sulfate into a 250-mL round-bottom flask. Rinse the funnel and sodium sulfate with a few mL of n-hexane, and add the rinsing to the hexane solution in the flask. Place the flask in a water bath maintained at 50 , and evaporate the hexane solution with the aid of a rotary evaporator to dryness. Immediately add 25.0 mL of Diluent, and swirl to dissolve the residue.
, and evaporate the hexane solution with the aid of a rotary evaporator to dryness. Immediately add 25.0 mL of Diluent, and swirl to dissolve the residue.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 291 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 25-cm; packing L1
Column temperature:
40
Flow rate:
3 mL/min
Injection size:
20 µL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 5.0%
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of the labeled amount of vitamin E as alpha tocopherol (C29H50O2) in the portion of Capsules taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak area for alpha tocopherol from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak area for alpha tocopherol from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of alpha tocopherol in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of alpha tocopherol the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
[Note—Calculate the content of alpha tocopheryl acetate (C31H52O3) or alpha tocopheryl acid succinate (C33H54O5) by dividing the content, in mg/Capsule of vitamin E as alpha tocopherol (C29H50O2), by the factor 0.91 or 0.81, respectively. ]
Acceptance criteria:
90.0%–165.0% of the labeled amount of vitamin E as alpha tocopherol (C29H50O2), alpha tocopheryl acetate (C31H52O3) or alpha tocopheryl succinate (C33H54O5)
• Phytonadione
[Note—Use low-actinic glassware throughout this procedure. ]
Mobile phase:
Methanol and water (19:1)
Standard stock solution:
200 µg/mL of USP Phytonadione RS in methanol. Dissolve with the aid of sonication if necessary.
Standard solution:
20 µg/mL of USP Phytonadione RS from the Standard stock solution diluted with methanol
System suitability solution:
0.65 mg/mL of USP Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate RS and 20 µg/mL of USP Phytonadione RS from the Standard stock solution diluted with methanol. [Note—Dissolve USP Alpha Tocopheryl Acetate RS in a portion of methanol, add the Standard stock solution, and then dilute with methanol to volume. ]
Sample solution:
Proceed as directed for the Sample solution in Vitamin A, Method 1. Transfer NLT 20 mL of this solution retained as specified in the directions for the Sample solution in Vitamin A, Method 1 to a suitable container, and evaporate, if necessary, in vacuum at room temperature to dryness. Transfer the contents of the flask to a suitable volumetric flask with the aid of methanol, and dilute with methanol to volume to obtain a concentration of 20 µg/mL of phytonadione.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 254 nm
Column:
8-mm × 10-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Flow rate:
2 mL/min
Injection size:
100 µL
System suitability
Samples:
Standard solution and System suitability solution
[Note—The relative retention times for alpha tocopheryl acetate and phytonadione are about 0.68 and 1.0, respectively. ]
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 5 between alpha tocopheryl acetate and phytonadione, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 3.0%, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Measure the peak areas. Calculate the percentage of the labeled amount of phytonadione (C31H46O2) in the portion of Capsules taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak area of phytonadione from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak area of phytonadione from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Phytonadione RS in the Standard solution (µg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of phytonadione in the Sample solution (µg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
90.0%–165.0% of the labeled amount of phytonadione (C31H46O2)
• Beta Carotene
[Note—Use low-actinic glassware throughout this procedure. ]
Potassium hydroxide solution:
Dissolve 58.8 g of potassium hydroxide in 50 mL of water.
Iodine solution:
Transfer 10 mg of iodine to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in cyclohexane, and dilute with cyclohexane to volume. Dilute 10 mL of this solution with cyclohexane to 100 mL. [Note—Prepare this solution fresh daily. ]
Sample solution A (for preparations containing beta carotene in oil solutions):
Proceed as directed in Vitamin A, Method 1, except use cyclohexane instead of n-hexane as the extraction solvent, and dilute the filtered extracts with cyclohexane to obtain a concentration of 2 µg/mL of beta carotene.
Sample solution B (for preparations containing beta carotene in dry powder):
Remove the contents of NLT 20 Capsules by cutting open the Capsules. Mix, and determine the weight of the contents. Transfer a quantity of the Capsule contents, equivalent to 2 mg of beta carotene, to a 500-mL saponification flask. Add 100 mL of alcohol, 6 mL of Potassium hydroxide solution, and a magnetic stirring bar. Attach an air condenser to the flask, and heat under reflux for 45 min with constant stirring. Cool to room temperature. Add 170 mL of solvent hexane, and stir for 30 min. Quantitatively transfer the contents of the flask to a 500-mL separatory funnel with portions of solvent hexane. Allow the layers to separate for 5–10 min, and transfer the upper organic layer to a 500-mL volumetric flask. Transfer the lower aqueous layer into the saponification flask. Add 170 mL of solvent hexane, and stir for an additional 20 min. Quantitatively transfer the contents of the saponification flask to the separatory funnel with the aid of portions of solvent hexane. Allow the layers to separate for 10 min. Drain the lower aqueous layer, and discard. Transfer the organic layer to the volumetric flask containing the previously collected organic layer. Rinse the separatory funnel with small portions of solvent hexane, and transfer the washings to the volumetric flask. Dilute the hexane extracts with solvent hexane to volume. Add 3 g of anhydrous sodium sulfate, shake, and allow to settle. Quantitatively transfer a volume of this solution, equivalent to 100 µg of beta carotene, to a 50-mL volumetric flask. Evaporate under a stream of nitrogen to dryness, and immediately add cyclohexane. Add 2 mL of Iodine solution, and heat for 15 min in a water bath maintained at 65 . Cool rapidly, and dilute with cyclohexane to volume.
. Cool rapidly, and dilute with cyclohexane to volume.
Spectrometric conditions
Mode:
Vis
Analytical wavelength:
452 nm
Blank:
Cyclohexane
Analysis
Sample:
Sample solution A or Sample solution B
Determine the absorbance against the Blank. Calculate the percentage of the labeled amount of beta carotene (C40H56) in the portion of Capsules taken:
Result = (AU/F) × (100/CU)
| AU | = | = absorbance of Sample solution A or Sample solution B |
| F | = | = absorptivity of beta carotene at 452 nm, 223 |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of beta carotene in Sample solution A or Sample solution B (mg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
90.0%–165.0% of the labeled amount of beta carotene (C40H56)
PERFORMANCE TESTS
• Disintegration and Dissolution of Dietary Supplements  2040
2040 :
Meet the requirements
:
Meet the requirements
• Weight Variation of Dietary Supplements  2091
2091 :
Meet the requirements
:
Meet the requirements
CONTAMINANTS
• Microbial Enumeration Tests  2021
2021 :
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 3000 cfu/g, and the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 300 cfu/g.
:
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 3000 cfu/g, and the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 300 cfu/g.
• Absence of Specified Microorganisms  2022
2022 :
Meet the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus.
:
Meet the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species, Escherichia coli, and Staphylococcus aureus.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers.
• Labeling1 :
Label the Capsules to state that the product is Oil-Soluble Vitamins Capsules. The label also states the quantity of each vitamin/dosage unit and, where necessary, the chemical form in which it is present. Where the product contains vitamin E, the label also indicates whether it is the d- or dl- form. Where more than one assay method is given for a particular vitamin, the labeling states the assay method used only if Method 1 is not used.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Cholecalciferol RS 
9,10-Secocholesta-5,7,10(19)-trien-3-ol, (3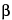 ,5Z,7E)-.
,5Z,7E)-.
Cholecalciferol.
C27H44O 384.64

9,10-Secocholesta-5,7,10(19)-trien-3-ol, (3
Cholecalciferol.
C27H44O 384.64
USP Ergocalciferol RS 
9,10-Secoergosta-5,7,10 (19),22-tetraen-3-ol, (3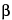 ,5Z,7E,22E)-.
,5Z,7E,22E)-.
Ergocalciferol.
C28H44O 396.65

9,10-Secoergosta-5,7,10 (19),22-tetraen-3-ol, (3
Ergocalciferol.
C28H44O 396.65
1
USP Units of activity for vitamins, where such exist or formerly existed, are equivalent to the corresponding international units, where such formerly existed. The USP Unit for Vitamin E has been discontinued. International units (IU) for vitamins also have been discontinued; however, the use of IU on the labels of vitamin products continues. Where articles are labeled in terms of Units in addition to the required labeling, the relationship of the USP Units or IU to mass is as follows. One USP Vitamin A Unit = 0.3 µg of all-trans-retinol (vitamin A alcohol) or 0.344 µg of all-trans-retinyl acetate (vitamin A acetate) or 0.55 µg of all-trans-retinyl palmitate (vitamin A palmitate), and 1 µg of retinol (3.3 USP Vitamin A Units) = 1 retinol equivalent (RE); 1 IU of beta carotene = 0.6 µg of all-trans-beta carotene; 1 USP Vitamin D Unit = 0.025 µg of ergocalciferol or cholecalciferol; and 1 mg of dl-alpha tocopherol = 1.1 former USP Vitamin E Units, 1 mg of dl-alpha tocopheryl acetate = 1 former USP Vitamin E Unit, 1 mg of dl-alpha tocopheryl acid succinate = 0.89 former USP Vitamin E Unit, 1 mg of d-alpha tocopherol = 1.49 former USP Vitamin E Units, and 1 mg of d-alpha tocopheryl acetate = 1.36 former USP Vitamin E Units, 1 mg of d-alpha tocopheryl acid succinate = 1.21 former USP Vitamin E Units. In terms of d-alpha tocopherol equivalents, 1 mg of d-alpha tocopheryl acetate = 0.91, 1 mg of d-alpha tocopheryl acid succinate = 0.81, 1 mg of dl-alpha tocopherol = 0.74, 1 mg of dl-alpha tocopheryl acetate = 0.67, and 1 mg of dl-alpha tocopheryl acid succinate = 0.60.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Natalia Davydova
Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8328 |
(DS2010) Monographs - Dietary Supplements |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 1468
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 36(1) Page 169