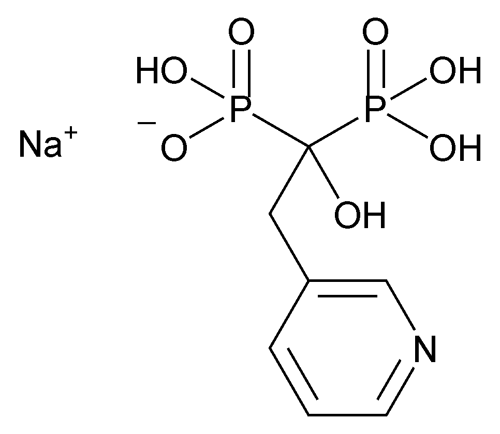
Risedronate Sodium
C7H10NNaO7P2 305.09
C7H10NNaO7P2·H2O 323.12
C7H10NNaO7P2·2.5 H2O 350.13
Phosphonic acid, [1-hydroxy-2-(3-pyridinyl)ethylidene]bis-, monosodium salt;
Sodium trihydrogen [1-hydroxy-2-(3-pyridyl)ethylidene]diphosphonate;
Hemi-pentahydrate

 [329003-65-8].
[329003-65-8].
Monohydrate

 [353228-19-0].
[353228-19-0].
(ris'' e droe' nate soe' dee um).
C7H10NNaO7P2 305.09
C7H10NNaO7P2·H2O 323.12
C7H10NNaO7P2·2.5 H2O 350.13
Phosphonic acid, [1-hydroxy-2-(3-pyridinyl)ethylidene]bis-, monosodium salt;
Sodium trihydrogen [1-hydroxy-2-(3-pyridyl)ethylidene]diphosphonate;
Hemi-pentahydrate
Monohydrate
DEFINITION
Risedronate Sodium contains one or two and one-half molecules of hydration. The monohydrate form contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of C7H10NNaO7P2, calculated on the dried basis. The hemi-pentahydrate form contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of C7H10NNaO7P2, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Infrared Absorption  197
197 :
The spectra of trifluorovinyl chloride polymer and mineral oil dispersions of it, separately prepared from a test specimen, exhibit maxima in the regions of 4000 to 1350 cm–1 and 1350 to 450 cm–1, respectively, only at the same wavelengths as those of similar preparations of USP Risedronate Sodium RS. [Note—If a difference appears in the infrared spectra of the analyte and the standard, dissolve equal portions of the test specimen and the USP Reference Standard in equal volumes of water containing about 50 mg/mL of potassium bromide. Evaporate the solutions to dryness at 105
:
The spectra of trifluorovinyl chloride polymer and mineral oil dispersions of it, separately prepared from a test specimen, exhibit maxima in the regions of 4000 to 1350 cm–1 and 1350 to 450 cm–1, respectively, only at the same wavelengths as those of similar preparations of USP Risedronate Sodium RS. [Note—If a difference appears in the infrared spectra of the analyte and the standard, dissolve equal portions of the test specimen and the USP Reference Standard in equal volumes of water containing about 50 mg/mL of potassium bromide. Evaporate the solutions to dryness at 105 for 120 min. Repeat the test on the residues. ]
for 120 min. Repeat the test on the residues. ]
• B. Identification Tests—General, Sodium  191
191 :
It meets the requirements of the flame test.
:
It meets the requirements of the flame test.
ASSAY
• Procedure
Mobile phase:
1.8 g/L of edetate disodium in water. Adjust with 1 N sodium hydroxide to a pH of 9.5 ± 0.1.
Standard solution:
Dissolve USP Risedronate Sodium RS and USP Risedronate Related Compound A RS in Mobile phase to obtain a solution containing 1.0 mg/mL of anhydrous risedronate sodium and 0.1 mg/mL of risedronate related compound A.
Sample solution:
1.1 mg/mL of Risedronate Sodium in Mobile phase
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 263 nm
Column:
4.0-mm × 25-cm; 10-µm packing L48
Flow rate:
0.8 mL/min
Injection size:
20 µL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 2.3 between risedronate and risedronate related compound A
Tailing factor:
NMT 1.6 for the risedronate peak
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 1.0% for the risedronate peak from three replicate injections
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of risedronate sodium (C7H10NNaO7P2) in the portion of Risedronate Sodium taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Risedronate Sodium RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Risedronate Sodium in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
98.0%–102.0% on the dried basis for the monohydrate form or on the anhydrous basis for the hemi-pentahydrate form
IMPURITIES
• Heavy Metals
Lead nitrate solution:
Add 1 mL of nitric acid to 100 mL of water. Dissolve 100 mg of lead nitrate in it, and dilute with water to 1000 mL.
Sodium bicarbonate solution:
Transfer 0.840 g of sodium bicarbonate to a 1000-mL volumetric flask containing about 950 mL of water. Dissolve in and dilute with water to volume. Adjust with 0.1 N sodium hydroxide or 0.1 N hydrochloric acid, as necessary, to a pH of 4.40 ± 0.02.
Hydrogen sulfide solution:
Transfer 200 mL of Sodium bicarbonate solution to a suitable conical flask, and bubble hydrogen sulfide gas through the solution until it turns a strip of lead acetate test paper black (see Reagents, Indicators, and Solution—Indicator and Test Papers).
Standard solutions:
Transfer 500 mg of Risedronate Sodium to each of three separate beakers. Add 41 mL of water to each beaker, and stir to dissolve. Adjust with 0.1 N sodium hydroxide or 0.1 N hydrochloric acid, as necessary, to a pH of 4.40 ± 0.02. Label the first beaker as Standard solution 1. Add 200 µL of Lead nitrate solution to the second beaker (Standard solution 2) and 400 µL to the third beaker (Standard solution 3). These solutions contain the equivalent of 0, 12.5, and 25 µg of lead (representing 0, 10, and 20 ppm, respectively).
Sample solution:
Transfer 1.75 g of Risedronate Sodium to a suitable beaker. Add 41 mL of water, and stir to dissolve. Adjust with 0.1 N sodium hydroxide or 0.1 N hydrochloric acid, as necessary, to a pH of 4.40 ± 0.02.
Analysis:
Add 7 mL of Hydrogen sulfide solution to each of the beakers containing the Standard solutions and the Sample solution. Allow the solutions to stand for at least 5 min. Add 60 µL of 1 N hydrochloric acid to each of the beakers containing the Standard solutions, add 200 µL of 1 N hydrochloric acid to the beaker containing the Sample solution, and stir. Transfer the solutions into 50-mL color-comparison tubes, and view downward over a white surface.
Acceptance criteria:
The color of the solution obtained from the Sample solution is not darker than that of the solution from Standard solution 3 (NMT 20 ppm).
• Organic Impurities, Procedure 1
[Note—Perform both Procedure 1 and Procedure 2. ]
Mobile phase, Standard solution, Sample solution, and Chromatographic system:
Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Diluted standard solution:
Dilute a portion of the Standard solution with Mobile phase to obtain a solution containing 5 µg/mL of anhydrous risedronate sodium and about 0.5 µg/mL of risedronate related compound A.
System suitability
Samples:
Standard solution and Diluted standard solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 2.3 between risedronate related compound A and risedronate, Standard solution
Tailing factor:
NMT 1.6 for the risedronate peak, Standard solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 1.0% for the risedronate peak from three replicate injections, Standard solution; NMT 15% for the risedronate related compound A peak from three replicate injections, Diluted standard solution
Analysis
Samples:
Sample solution and Diluted standard solution
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Risedronate Sodium taken:
Result= (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (1/F) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of each impurity from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of risedronate from the Diluted standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Risedronate Sodium RS in the Diluted standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Risedronate Sodium in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
| F | = | = relative response factor (see Table 1) |
Table 1
| Name | Relative Response Factor |
Relative Retention Time |
|---|---|---|
| 3-Pyridyl acetic acid | 1.65 | 0.22 |
| 2-Pyridinyl isomer (USP Risedronate Related Compound A RS) |
1.0 | 0.84 |
| Risedronate sodium | — | 1.0 |
Acceptance criteria
Any individual impurity:
NMT 0.10%
[Note—Disregard the peak due to the sodium ion, eluting at about 1.6 min, and any peak observed in the blank. The reporting level for impurities is 0.05%. ]
• Organic Impurities, Procedure 2
Mobile phase:
Transfer 16.15 g of dibasic potassium phosphate and 0.46 g of edetate disodium to a 1-L beaker, and dissolve in about 400 mL of water. Add 1 vial of commercially available tetrabutylammonium dihydrogen phosphate buffered solution in methanol1 and 1 mL of hydrochloric acid. Adjust with 1 N sodium hydroxide or 1 N hydrochloric acid, as necessary, to a pH of 7.5 ± 0.1, and dilute with water to 480 mL. Add 20 mL of methanol, mix well, pass the solution through a nylon filter of 0.45-µm pore size, and degas.
Diluent:
Transfer 0.46 g of edetate disodium to a 1-L beaker, and dissolve in 500 mL of water. Adjust with 1 N sodium hydroxide to a pH of 7.5 ± 0.1.
Standard solution:
5 µg/mL of USP Risedronate Related Compound B RS in Diluent
Diluted standard solution:
0.5 µg/mL of USP Risedronate Related Compound B RS in Diluent from the Standard solution
Sample solution:
2 mg/mL of Risedronate Sodium, in Diluent, using sonication if necessary
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 263 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 15-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Flow rate:
1.0 mL/min
Injection size:
10 µL
System suitability
Samples:
Standard solution and Diluted standard solution
Suitability requirements
Capacity factor:
Greater than 2, Standard solution
Tailing factor:
Less than 1.5, Standard solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 5% from three replicate injections, Standard solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 10% from three replicate injections, Diluted standard solution
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
[Note—Disregard any peak eluting before risedronate related compound B. The risedronate peak elutes unretained at the void volume. ]
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Risedronate Sodium taken:
Result= (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (Mr1/Mr2) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of each impurity from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of risedronate related compound B from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Risedronate Related Compound B RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Risedronate Sodium in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
| Mr1 | = | = molecular weight of risedronate related compound B as a free acid, 530.20 |
| Mr2 | = | = molecular weight of risedronate related compound B as a tetrahydrate disodium salt, 646.22 |
Acceptance criteria
Risedronate related compound B:
NMT 0.10%
Individual impurities:
NMT 0.10%
Total impurities:
NMT 0.50%, Procedure 1 and Procedure 2 being combined
[Note—Disregard any peak observed in the blank. The reporting level for impurities is 0.05%. ]
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Water Determination, Method Ic  921
921 (where it is labeled as a hemi-pentahydrate):
11.9%–13.9%. Perform the test by direct introduction of solid sample into the titrator. Alternatively, Method 1a may be used.
(where it is labeled as a hemi-pentahydrate):
11.9%–13.9%. Perform the test by direct introduction of solid sample into the titrator. Alternatively, Method 1a may be used.
• Loss on Drying  731
731 (where it is labeled as a monohydrate)
(where it is labeled as a monohydrate)
(See Thermal Analysis  891
891 .)
.)
Determine the percentage of volatile substances by thermogravimetric analysis on an appropriately calibrated instrument, using 7–15 mg of Risedronate Sodium. Heat the specimen under test at a rate of 10 /min in a stream of nitrogen at a flow rate of about 40 mL/min. Record the thermogram from ambient temperature to 250
/min in a stream of nitrogen at a flow rate of about 40 mL/min. Record the thermogram from ambient temperature to 250 .
.
Acceptance criteria:
It loses between 5.5% and 7.5% of its weight.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Labeling:
Label to indicate whether it is the monohydrate or the hemi-pentahydrate form.
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers. Store at room temperature.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Risedronate Related Compound A RS
2-Pyridinyl isomer [1-hydroxy-2-(2-pyridinyl)ethylidene]bis(phosphonic acid) monohydrate.
C7H11NO7P2 283.12
2-Pyridinyl isomer [1-hydroxy-2-(2-pyridinyl)ethylidene]bis(phosphonic acid) monohydrate.
C7H11NO7P2 283.12
USP Risedronate Related Compound B RS
Cyclic dimer, disodium tetrahydrate salt, [3,6-bis[(3-pyridinyl)methyl]-2,5-dihydroxy-2,5-dioxido-1,4,2,5-dioxadiphosphorinane-3,6-diyl]bis[phosphonic acid] disodium tetrahydrate salt.
C14H16N2O12P4Na2·4H2O 646.22
Cyclic dimer, disodium tetrahydrate salt, [3,6-bis[(3-pyridinyl)methyl]-2,5-dihydroxy-2,5-dioxido-1,4,2,5-dioxadiphosphorinane-3,6-diyl]bis[phosphonic acid] disodium tetrahydrate salt.
C14H16N2O12P4Na2·4H2O 646.22
1
Available from Waters Corp. as Part #85101 (PIC A).
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Elena Gonikberg, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8251 |
(SM32010) Monographs - Small Molecules 3 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 4568
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 37(1)