Heparin Sodium
(hep' a rin soe' dee um).
DEFINITION
Heparin Sodium is the sodium salt of sulfated glycosaminoglycans present as a mixture of heterogeneous molecules varying in molecular weights that retains a combination of activities against different factors of the blood clotting cascade. It is present in mammalian tissues and is usually obtained from the intestinal mucosa or other suitable tissues of domestic mammals used for food by man. The sourcing of heparin material must be specified in compliance with applicable regulatory requirements. The manufacturing process should be validated to demonstrate clearance and inactivation of relevant infectious and adventitious agents (e.g., viruses, TSE agents). See Viral Safety Evaluation of Biotechnology Products Derived from Cell Lines of Human or Animal Origin  1050
1050 for general guidance on viral safety evaluation. It is composed of polymers of alternating derivatives of
for general guidance on viral safety evaluation. It is composed of polymers of alternating derivatives of 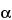 -d-glucosamido (N-sulfated, O-sulfated, or N-acetylated) and O-sulfated uronic acid (
-d-glucosamido (N-sulfated, O-sulfated, or N-acetylated) and O-sulfated uronic acid (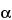 -l-iduronic acid or
-l-iduronic acid or 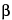 -d-glucuronic acid). The component activities of the mixture are in ratios corresponding to those shown by USP Heparin Sodium for Assays RS. Some of these components have the property of prolonging the clotting time of blood. This occurs mainly through the formation of a complex of each component with the plasma proteins antithrombin and heparin cofactor II to potentiate the inactivation of thrombin (factor IIa). Other coagulation proteases in the clotting sequence, such as activated factor X (factor Xa), are also inhibited. The ratio of anti-factor Xa activity to anti-factor IIa potency is between 0.9 and 1.1. The potency of Heparin Sodium, calculated on the dried basis, is NLT 180 USP Heparin Units in each mg.
-d-glucuronic acid). The component activities of the mixture are in ratios corresponding to those shown by USP Heparin Sodium for Assays RS. Some of these components have the property of prolonging the clotting time of blood. This occurs mainly through the formation of a complex of each component with the plasma proteins antithrombin and heparin cofactor II to potentiate the inactivation of thrombin (factor IIa). Other coagulation proteases in the clotting sequence, such as activated factor X (factor Xa), are also inhibited. The ratio of anti-factor Xa activity to anti-factor IIa potency is between 0.9 and 1.1. The potency of Heparin Sodium, calculated on the dried basis, is NLT 180 USP Heparin Units in each mg.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. 1H NMR spectrum
Standard solution:
NLT 20 mg/mL of USP Heparin Sodium Identification RS in deuterium oxide with 0.02%(w/v) deuterated trimethylsilylpropionic (TSP) acid sodium salt
System suitability solution:
Prepare 1% (w/w) USP Oversulfated Chondroitin Sulfate RS in Standard solution.
Sample solution:
NLT 20 mg/mL of Heparin Sodium in deuterium oxide with 0.02% (w/v) deuterated TSP
Spectrometric conditions
Mode:
NMR, pulsed (Fourier transform)
Frequency:
NLT 500 MHz (for 1H)
Temperature:
25
System suitability
Samples:
Standard solution and System suitability solution
Using a pulsed (Fourier transform) NMR spectrometer operating at NLT 500 MHz for 1H, acquire a free induction decay (FID) using NLT 16 scans using a 90 pulse and 20-s delay. Record the 1H NMR spectra of the Standard solution and System suitability solution at 25
pulse and 20-s delay. Record the 1H NMR spectra of the Standard solution and System suitability solution at 25 . Collect the 1H NMR spectrum with a spectral window of at least 10 to
. Collect the 1H NMR spectrum with a spectral window of at least 10 to  2 ppm and without spinning. The number of transients should be adjusted until the signal-to-noise ratio of the N-acetyl heparin signal in the Standard solution is at least 1000/1 in the region near 2 ppm. The Standard solution shall be run at least daily when Sample solutions are being run. For all samples, the TSP methyl signal should be set to 0.00 ppm. The chemical shift for the N-acetyl resonance of heparin and oversulfated chondroitin sulfate in the System suitability solution should be observed at 2.05 ± 0.02 and 2.16 ± 0.03 ppm, respectively. Record the 1H NMR spectrum of the Sample solution at 25
2 ppm and without spinning. The number of transients should be adjusted until the signal-to-noise ratio of the N-acetyl heparin signal in the Standard solution is at least 1000/1 in the region near 2 ppm. The Standard solution shall be run at least daily when Sample solutions are being run. For all samples, the TSP methyl signal should be set to 0.00 ppm. The chemical shift for the N-acetyl resonance of heparin and oversulfated chondroitin sulfate in the System suitability solution should be observed at 2.05 ± 0.02 and 2.16 ± 0.03 ppm, respectively. Record the 1H NMR spectrum of the Sample solution at 25 . Draw a baseline from 8.00 ppm to 0.10 ppm. The ppm values for H1 of GlcNAc/GlcNS, 6S (signal 1), H1 of IdoA2S (signal 2), the H2 of GlcNS (signal 3), and the methyl of GlcNAc (signal 4) of heparin are present at 5.42, 5.21, 3.28 (doublet centered at 3.28 ppm), and 2.05 ppm, respectively.1 The ppm values of these signals do not differ by more than ±0.03 ppm. Measure the signal heights above the baseline of signal 1 and signal 2, and calculate the mean of these signal heights. Other signals of variable heights and ppm values, attributable to heparin and HOD, may be seen between signal 2 and 4.55 ppm. Residual solvent signals may be observed in the 0.10–3.00 range. Heparin Sodium must meet the requirements stated in Residual Solvents
. Draw a baseline from 8.00 ppm to 0.10 ppm. The ppm values for H1 of GlcNAc/GlcNS, 6S (signal 1), H1 of IdoA2S (signal 2), the H2 of GlcNS (signal 3), and the methyl of GlcNAc (signal 4) of heparin are present at 5.42, 5.21, 3.28 (doublet centered at 3.28 ppm), and 2.05 ppm, respectively.1 The ppm values of these signals do not differ by more than ±0.03 ppm. Measure the signal heights above the baseline of signal 1 and signal 2, and calculate the mean of these signal heights. Other signals of variable heights and ppm values, attributable to heparin and HOD, may be seen between signal 2 and 4.55 ppm. Residual solvent signals may be observed in the 0.10–3.00 range. Heparin Sodium must meet the requirements stated in Residual Solvents  467
467 .
.
Suitability requirements
Number of transients:
Adjust until the signal-to-noise ratio of the N-acetyl heparin signal in the Standard solution is at least 1000/1 in the region near 2 ppm.
Chemical shift:
The TSP methyl signal should be set to 0.00 ppm for all samples.
Chemical shifts (for the N-acetyl resonance of heparin and oversulfated chondroitin sulfate):
Should be observed at 2.05 ± 0.02 and 2.16 ± 0.03 ppm, respectively, System suitability solution
Analysis
Sample:
Sample solution
Acceptance criteria:
No unidentified signals greater than 4% of the mean of signal height of 1 and 2 are present in the following ranges: 0.10–2.00, 2.10–3.20, and 5.70–8.00 ppm. No signals greater than 200% signal height of the mean of the signal height of 1 and 2 are present in the 3.35–4.55 ppm for porcine heparin.
• B. Chromatographic Identity
Solution A:
Dissolve 0.8 g of monobasic sodium phosphate dihydrate in 2 L of water and adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 3.0. Pass the solution through a filter membrane with pore sizes of 0.45 µm and degas before use.
Solution B:
Dissolve 0.8 g of monobasic sodium phosphate dihydrate and 280 g of sodium perchlorate monohydrate in 2 L of water and adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 3.0. Pass the solution through a filter membrane with pore sizes of 0.45 µm and degas before use.
Mobile phase:
See the gradient table below.
| Time (min) |
Solution A (%) |
Solution B (%) |
Elution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 80 | 20 | Equilibration |
| 60 | 10 | 90 | Linear gradient |
| 61 | 80 | 20 | Linear gradient |
| 75 | 80 | 20 | Re-equilibration |
Standard solution:
NLT 20 mg/mL of USP Heparin Sodium Identification RS in water
System suitability solution:
Prepare 1% (w/w) USP Oversulfated Chondroitin Sulfate RS and 1% (w/w) USP Dermatan Sulfate RS in Standard solution.
Sample solution:
NLT 20 mg/mL of Heparin Sodium in water
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 202 nm
Column:
2-mm × 25-cm; packing L61
Guard column:
2-mm × 50-mm; packing L61
Column temperature:
Maintain columns at 40
Flow rate:
0.22 mL/min
Injection size:
10 µL
System suitability
Sample:
System suitability solution
[Note—The retention times for dermatan sulfate, heparin, and oversulfated chondroitin sulfate are about 20, 30, and 50 min, respectively. ]
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 1.0 between the dermatan sulfate and the heparin peaks, and NLT 1.5 between the heparin and the oversulfated chondroitin sulfate
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 2% for the heparin peak determined from three replicate injections
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution Record the chromatograms, and measure the retention times for the major peaks.
Acceptance criteria:
The retention time of the major peak from the Sample solution corresponds to that from the Standard solution.
• C. Anti-Factor Xa to Anti-Factor IIa Ratio
Anti-factor Xa activity
pH 8.4 buffer:
Dissolve amounts of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, edetic acid, and sodium chloride in water containing 0.1% of polyethylene glycol 6000 to obtain a solution having concentrations of 0.050, 0.0075, and 0.175 M, respectively. Adjust, if necessary, with hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide solution to a pH of 8.4.
Antithrombin solution:
Reconstitute a vial of antithrombin (see Reagents, Indicators, and Solutions—Reagent Specifications) as directed by the manufacturer, and further dilute with pH 8.4 buffer to obtain a solution having a concentration of 1.0 Antithrombin IU/mL.
Factor Xa solution:
Reconstitute bovine factor Xa as directed by the manufacturer (see Factor Xa in Reagents, Indicators, and Solutions—Reagent Specifications), and further dilute in pH 8.4 buffer to obtain a solution that gives an absorbance value between 0.65 and 1.25 at 405 nm when assayed as described below but using 30 µL of pH 8.4 buffer instead of 30 µL of the Standard solutions or the Sample solutions. [Note—Factor Xa solution contains about 3 nanokatalytic units/mL, but can vary depending upon the manufacturer of factor Xa or the substrate used. ]
Chromogenic substrate solution:
Prepare a solution of a suitable chromogenic substrate for amidolytic test (see Reagents, Indicators, and Solutions—Reagent Specifications) specific for factor Xa in water to obtain a concentration of 1 mM.
Stopping solution:
20% (v/v) solution of acetic acid
Standard solutions:
Reconstitute the entire contents of an ampule of USP Heparin Sodium for Assays RS with water, and dilute with pH 8.4 buffer to obtain at least five dilutions in the concentration range between 0.03 and 0.375 USP Heparin Units/mL.
Sample solutions:
Dissolve or dilute a measured quantity of Heparin Sodium in pH 8.4 buffer, and dilute with the same buffer to obtain solutions having activities approximately equal to those of the Standard solutions.
Analysis
[Note—The procedure can also be performed using alternative platforms. Perform the test with each Standard solution and Sample solution in duplicate. ]
To each of a series of suitable plastic tubes placed in a water bath set at 37 , transfer 120 µL of pH 8.4 buffer. Then separately transfer 30 µL of the different dilutions of the Standard solutions or the Sample solutions to the tubes. Add 150 µL of Antithrombin solution, prewarmed at 37
, transfer 120 µL of pH 8.4 buffer. Then separately transfer 30 µL of the different dilutions of the Standard solutions or the Sample solutions to the tubes. Add 150 µL of Antithrombin solution, prewarmed at 37 for 15 min, to each tube, mix, and incubate for 2 min. Add 300 µL of Factor Xa solution, prewarmed at 37
for 15 min, to each tube, mix, and incubate for 2 min. Add 300 µL of Factor Xa solution, prewarmed at 37 for 15 min, to each tube, mix, and incubate for 2 min. Add 300 µL of Chromogenic substrate solution, prewarmed at 37
for 15 min, to each tube, mix, and incubate for 2 min. Add 300 µL of Chromogenic substrate solution, prewarmed at 37 for 15 min, to each tube, mix, and incubate for exactly 2 min. Add 150 µL of Stopping solution to each tube, and mix. Prepare a blank for zeroing the spectrophotometer by adding the reagents in reverse order, starting with the Stopping solution and ending with the addition of 150 µL of pH 8.4 buffer, and excluding the Standard solutions or the Sample solutions. Record the absorbance at 405 nm against the blank.
for 15 min, to each tube, mix, and incubate for exactly 2 min. Add 150 µL of Stopping solution to each tube, and mix. Prepare a blank for zeroing the spectrophotometer by adding the reagents in reverse order, starting with the Stopping solution and ending with the addition of 150 µL of pH 8.4 buffer, and excluding the Standard solutions or the Sample solutions. Record the absorbance at 405 nm against the blank.
Calculations:
Plot the log of the absorbance values of the Standard solutions and the Sample solutions versus the heparin concentrations in USP Units. Calculate the activity of Heparin Sodium in USP Units/mg using statistical methods for slope ratio assays. Calculate the anti-factor Xa activity of Heparin Sodium:
Result = A × (ST/SS)
| A | = | = potency of USP Heparin Sodium for Assays RS |
| ST | = | = slope of the line for the Sample solutions |
| SS | = | = slope of the line for the Standard solutions |
Express the anti-factor Xa activity of the Sample solution as USP Heparin Units/mg, calculated on the dried basis.
Calculate the ratio of anti-factor Xa activity against anti-factor IIa potency (see the Assay):
Result = anti-factor Xa activity/anti-factor IIa potency
Acceptance criteria:
0.9–1.1
• D. Identification Tests—General, Sodium  191
191 :
It meets the requirements of the flame test for sodium.
:
It meets the requirements of the flame test for sodium.
ASSAY
• Anti-Factor IIa Potency
pH 8.4 buffer:
Dissolve 6.10 g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, 10.20 g of sodium chloride, 2.80 g of edetate sodium, and, if suitable, between 0 and 10.00 g of polyethylene glycol 6000 and/or 2.00 g of bovine serum albumin in 800 mL of water. [Note—2.00 g of human albumin may be substituted for 2.00 g of bovine serum albumin. ] Adjust with hydrochloric acid to a pH of 8.4, and dilute with water to 1000 mL.
Antithrombin solution:
Reconstitute a vial of antithrombin (see Reagents, Indicators, and Solutions—Reagent Specifications) in water to obtain a solution of 5 Antithrombin IU/mL. Dilute this solution with pH 8.4 buffer to obtain a solution having a concentration of 0.125 Antithrombin IU/mL.
Thrombin human solution:
Reconstitute thrombin human (factor IIa) (see Reagents, Indicators, and Solutions—Reagent Specifications) in water to give 20 Thrombin IU/mL, and dilute with pH 8.4 buffer to obtain a solution having a concentration of 5 Thrombin IU/mL. [Note—The thrombin should have a specific activity of NLT 750 IU/mg. ]
Chromogenic substrate solution:
Prepare a solution of a suitable chromogenic thrombin substrate for amidolytic test (see Reagents, Indicators, and Solutions—Reagent Specifications) in water to obtain a concentration of 1.25 mM.
Stopping solution:
20% (v/v) solution of acetic acid
Standard solutions:
Reconstitute the entire contents of an ampule of USP Heparin Sodium for Assays RS with water, and dilute with pH 8.4 buffer to obtain at least four dilutions in the concentration range between 0.005 and 0.03 USP Heparin Unit/mL.
Sample solutions:
Proceed as directed for Standard solutions to obtain concentrations of Heparin Sodium similar to those obtained for the Standard solutions.
Analysis
[Note—The procedure can also be performed using alternative platforms. ]
For each dilution of the Standard solutions and the Sample solutions, at least duplicate samples should be tested. Label a suitable number of tubes, depending on the number of replicates to be tested. For example, if five blanks are to be used: B1, B2, B3, B4, and B5 for the blanks; T1, T2, T3, and T4 each at least in duplicate for the dilutions of the Sample solutions; and S1, S2, S3, and S4 each at least in duplicate for the dilutions of the Standard solutions. Distribute the blanks over the series in such a way that they accurately represent the behavior of the reagents during the experiments. [Note—Treat the tubes in the order B1, S1, S2, S3, S4, B2, T1, T2, T3, T4, B3, T1, T2, T3, T4, B4, S1, S2, S3, S4, B5. ] Note that after each addition of a reagent, the incubation mixture should be mixed without allowing bubbles to form. Add twice the volume (100–200 µL) of Antithrombin solution to each tube containing one volume (50-100 µL) of either the pH 8.4 buffer or an appropriate dilution of the Standard solutions or the Sample solutions. Mix, but do not allow bubbles to form. Incubate at 37 for at least 1 min. Add to each tube 25–50 µL of Thrombin human solution, and incubate for at least 1 min. Add 50–100 µL of Chromogenic substrate solution. Please note that all reagents, Standard solutions, and Sample solutions should be prewarmed to 37
for at least 1 min. Add to each tube 25–50 µL of Thrombin human solution, and incubate for at least 1 min. Add 50–100 µL of Chromogenic substrate solution. Please note that all reagents, Standard solutions, and Sample solutions should be prewarmed to 37 just before use. Two different types of measurements can be recorded:
just before use. Two different types of measurements can be recorded:
-
Endpoint measurement: Stop the reaction after at least 1 min with 50–100 µL of Stopping solution. Measure the absorbance of each solution at 405 nm using a suitable spectrophotometer (see Spectrophotometry and Light-Scattering
 851
851 ). The RSD over the blank readings is less than 10%.
). The RSD over the blank readings is less than 10%.
-
Kinetic measurement: Follow the change in absorbance for each solution over 1 min at 405 nm using a suitable spectrophotometer (see Spectrophotometry and Light-Scattering
 851
851 ). Calculate the change in absorbance/min (DOD/min). The blanks for kinetic measurement are also expressed as DOD/min and should give the highest values because they are carried out in the absence of heparin. The RSD over the blank readings is less than 10%.
). Calculate the change in absorbance/min (DOD/min). The blanks for kinetic measurement are also expressed as DOD/min and should give the highest values because they are carried out in the absence of heparin. The RSD over the blank readings is less than 10%.
Calculations:
The statistical models for Slope ratio assay or Parallel-line assay can be used, depending on which model best describes the correlation between concentration and response.
Parallel-line assay:
For each series, calculate the regression of the absorbance or change in absorbance/min against log concentrations of the Standard solutions and the Sample solutions, and calculate the potency of Heparin Sodium in USP Units/mL using statistical methods for parallel-line assays. Express the potency of Heparin Sodium/mg, calculated on the dried basis.
Slope ratio assay:
For each series, calculate the regression of the log absorbance or the log change in absorbance/min against concentrations of the Standard solutions and the Sample solutions, and calculate the potency of Heparin Sodium in USP Units/mL using statistical methods for slope ratio assays. Express the potency of Heparin Sodium/mg, calculated on the dried basis.
Acceptance criteria:
The potency of Heparin Sodium, calculated on the dried basis, is NLT 180 USP Heparin Units in each mg.
OTHER COMPONENTS
• Nitrogen Determination, Method I  461
461 :
1.3%–2.5%, calculated on the dried basis, using the procedure for Nitrates and Nitrites Absent
:
1.3%–2.5%, calculated on the dried basis, using the procedure for Nitrates and Nitrites Absent
IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
• Residue on Ignition  281
281 :
28.0%–41.0%
:
28.0%–41.0%
• Heavy Metals, Method II  231
231 :
NMT 30 ppm
:
NMT 30 ppm
Organic Impurities
• Procedure 1: Limit of Galactosamine in Total Hexosamine (a measure of dermatan sulfate and other galactosamine containing impurities)
Mobile phase:
14 mM potassium hydroxide
Glucosamine standard solution:
1.6 mg/mL of USP Glucosamine Hydrochloride RS in 5 N hydrochloric acid
Galactosamine standard solution:
16 µg/mL of USP Galactosamine Hydrochloride RS in 5 N hydrochloric acid
Standard solution:
Mix equal volumes of Glucosamine standard solution and Galactosamine standard solution.
Hydrolyzed standard solution:
Transfer 5 mL of the Standard solution to a 7-mL screw-cap test tube, cap, and heat for 6 h at 100 . Cool to room temperature, quantitatively transfer the solution to a 500-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
. Cool to room temperature, quantitatively transfer the solution to a 500-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Sample solution:
Transfer 12 mg of Heparin Sodium to a 7-mL screw-cap test tube, dissolve in 5 mL of 5 N hydrochloric acid, and cap.
Hydrolyzed sample solution:
Heat the Sample solution for 6 h at 100 . Cool to room temperature, and dilute with water (1 in 100).
. Cool to room temperature, and dilute with water (1 in 100).
Chromatographic system
Mode:
HPIC
Detector:
Pulsed amperometric detector, set to the following waveform:
| Step | Time (s) |
Potential (V) |
Integration |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.00 | +0.1 | — |
| 2 | 0.20 | +0.1 | Begins |
| 3 | 0.40 | +0.1 | Ends |
| 4 | 0.41 | — | |
| 5 | 0.42 | — | |
| 6 | 0.43 | +0.6 | — |
| 7 | 0.44 | — | |
| 8 | 0.50 | — |
Column:
3-mm × 30-mm amino acid trap column in series with a 3- × 30-mm guard column and a 3-mm × 15-cm column that contains packing L69
Column temperature:
Maintain columns at 30 .
.
Flow rate:
0.5 mL/min
Pre-equilibration:
At least 60 min with Mobile phase
Injection size:
10 µL
Elution:
10 min with Mobile phase
Column cleaning:
At least 10 min with 100 mM potassium hydroxide
Equilibration:
At least 10 min with Mobile phase before each injection
System suitability
Sample:
Hydrolyzed standard solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 2 between the galactosamine and glucosamine peaks
Column efficiency:
NLT 2000 theoretical plates for glucosamine
Tailing factor:
Between 0.8 and 2.0 for the galactosamine and glucosamine peaks
Analysis
Samples:
Hydrolyzed standard solution and Hydrolyzed sample solution
Record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the peaks at the retention time of galactosamine and glucosamine. Calculate the response ratio of galactosamine to glucosamine (GalNR) in the Hydrolyzed standard solution:
Result = (GalNB/GalNW) × (GlcNW/GlcNB)
| GalNB | = | = galactosamine peak area from the Hydrolyzed standard solution |
| GalNW | = | = weight of galactosamine for the Standard solution |
| GluNW | = | = weight of glucosamine for the Standard solution |
| GlcNB | = | = glucosamine peak area from the Hydrolyzed standard solution |
Calculate the percentage of galactosamine in the portion of total hexosamine taken:
Result = {[(GalNU/GalNR)]/[(GalNU/GalNR) + GlcNU]} × 100
| GalNU | = | = galactosamine peak area from the Hydrolyzed sample solution |
| GalNR | = | = galactosamine response ratio |
| GlcNU | = | = glucosamine peak area from the Hydrolyzed sample solution |
Acceptance criteria:
The percent galactosamine peak area of the total hexosamine of the Hydrolyzed sample solution must be NMT 1%.
• Procedure 2: Nucleotidic Impurities
(See Biotechnology-Derived Articles—Total Protein Assay  1057
1057 , Method 1, with the following modifications.)
, Method 1, with the following modifications.)
Analysis:
Dissolve 40 mg of Heparin Sodium in 10 mL of water. Measure the absorbance of this solution at 260 nm using the light-scattering correction procedure of Biotechnology-Derived Articles—Total Protein Assay  1057
1057 , Method 1.
, Method 1.
Acceptance criteria:
The absorbance of this solution at 260 nm is NMT 0.20.
• Procedure 3: Absence of Oversulfated Chondroitin Sulfate
A:
Proceed as directed in Identification test A. No features associated with oversulfated chondroitin sulfate are found between 2.12 and 3.00 ppm.
B:
Proceed as directed in Identification test B. No peaks corresponding to oversulfated chondroitin sulfate should be detected eluting after the heparin peak.
• Procedure 4: Protein Impurities
Standard stock solution:
0.100 mg/mL of bovine serum albumin in water
Standard solutions:
Dilute portions of the Standard stock solution with water to obtain NLT 5 standard solutions having concentrations between 0.005 and 0.100 mg/mL of bovine serum albumin, the concentrations being evenly spaced.
Sample solution:
5 mg/mL of Heparin Sodium in water. Prepare in triplicate.
Blank:
Water
Lowry reagent A:
Prepare a solution of 10 g/L of sodium hydroxide in water and a solution of 50 g/L of sodium carbonate in water. Mix equal volumes (2V:2V) of each solution, and dilute with water to 5V.
Lowry reagent B:
Prepare a solution of 29.8 g/L of disodium tartrate dihydrate in water. Prepare a solution of 12.5 g/L of cupric sulfate in water. Mix equal volumes of both solutions (2V:2V), and dilute with water to 5V.
Lowry reagent C:
Mix 50 volumes of Lowry reagent A with 1 volume of Lowry reagent B.
Diluted Folin–Ciocalteu's phenol reagent:
Dilute Folin–Ciocalteu's phenol reagent 2–4 times with water. The dilution should be chosen such that the pH of the samples (i.e., Standard solution and Sample solution after addition of Lowry reagent C and the Diluted Folin–Ciocalteu's phenol reagent) is 10.25 ± 0.25.
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solutions, Sample solution, and Blank
To 1 mL each of Standard solution, Sample solution, and Blank, add 5 mL of Lowry reagent C. Allow to stand at room temperature for 10 min. Add 0.5 mL of Diluted Folin–Ciocalteu's phenol reagent to each solution, mix immediately, and allow to stand at room temperature for 30 min. Determine the absorbance as directed in Biotechnology-Derived Articles—Total Protein Assay  1057
1057 , Method 2.
, Method 2.
Calculations:
See Biotechnology-Derived Articles—Total Protein Assay  1057
1057 , Method 2.
, Method 2.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 1.0% (w/w) is found.
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Bacterial Endotoxins Test  85
85 :
It contains NMT 0.03 USP Endotoxin Unit/USP Heparin Unit.
:
It contains NMT 0.03 USP Endotoxin Unit/USP Heparin Unit.
• Loss on Drying  731
731 :
Dry a sample in a vacuum at 60
:
Dry a sample in a vacuum at 60 for 3 h: it loses NMT 5.0% of its weight.
for 3 h: it loses NMT 5.0% of its weight.
• pH  791
791 :
5.0–7.5, in a solution (1 in 100)
:
5.0–7.5, in a solution (1 in 100)
• Sterility Tests  71
71 :
Where it is labeled as sterile, it meets the requirements.
:
Where it is labeled as sterile, it meets the requirements.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight containers, and store below 40 , preferably at room temperature.
, preferably at room temperature.
• Labeling:
Label it to indicate the tissue and the animal species from which it is derived.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Dermatan Sulfate RS
USP Endotoxin RS
USP Heparin Sodium Identification RS
USP Oversulfated Chondroitin Sulfate RS
1
GlcNAc, N-acetylated glucosamine; GlcNS, N-sulfated glucosamine; S, sulfate; IdoA, iduronic acid; GlcN, glucosamine; GalN, galactosamine.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Anita Y. Szajek, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8325 |
(BIO12010) Monographs - Biologics and Biotechnology 1 |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 3403
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 35(2) Page 257
