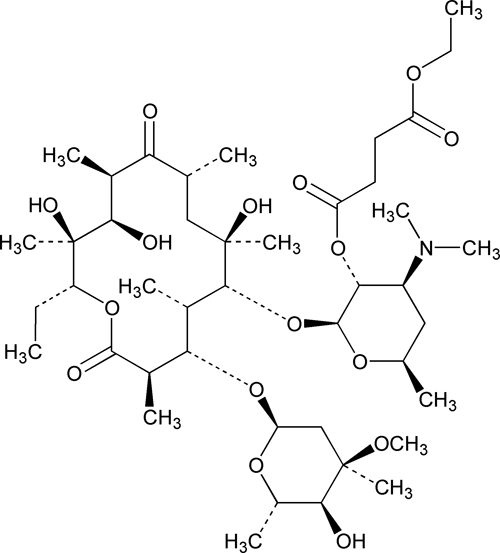
Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate
(e rith'' roe mye' sin eth'' il sux' i nate).
Erythromycin 2¢-(ethyl butanedioate).
Erythromycin 2¢-(ethyl succinate).
» Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate consists primarily of the 2¢-ethylsuccinate ester of erythromycin A. The sum of the percentages of erythromycin A, erythromycin B, and erythromycin C is not less than 76.5 percent, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers.
Labeling—
Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate that is noncrystalline is labeled to indicate that it is amorphous. Any preparation containing the amorphous form of Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate is so labeled.
Identification, Infrared Absorption  197S
197S —
—
Solution:
1 in 100.
Medium:
chloroform.
Cell size:
1.0-mm.
Crystallinity  695
695 :
meets the requirements, except that when it is labeled as being in the amorphous state it does not meet the requirements.
:
meets the requirements, except that when it is labeled as being in the amorphous state it does not meet the requirements.
X-ray diffraction  941
941 —
Where labeled as being in the amorphous state, its X-ray diffraction pattern performed at high sensitivity for angles of diffraction between 2
—
Where labeled as being in the amorphous state, its X-ray diffraction pattern performed at high sensitivity for angles of diffraction between 2 and 20
and 20 exhibits no reflection, and between 7
exhibits no reflection, and between 7 and 10
and 10 exhibits a more intense hachured baseline, creating a halo.
exhibits a more intense hachured baseline, creating a halo.
Water, Method I  921
921 :
not more than 3.0%, 20 mL of methanol containing 10% of imidazole being used in place of methanol in the titration vessel.
:
not more than 3.0%, 20 mL of methanol containing 10% of imidazole being used in place of methanol in the titration vessel.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 1.0% after ignition at 550 ± 50
:
not more than 1.0% after ignition at 550 ± 50 , the charred residue being moistened with 2 mL of nitric acid and 5 drops of sulfuric acid.
, the charred residue being moistened with 2 mL of nitric acid and 5 drops of sulfuric acid.
Related compounds—
Using the chromatograms obtained for the Assay preparation and Standard preparation 2 in the Assay, begin peak integration after the two peaks for succinates that elute just after the solvent front, and calculate the percentage of each related compound having the greatest response, other than erythromycin A, erythromycin B, erythromycin C, erythromycin A enol ether, and erythromycin N-ethylsuccinate (retention time relative to erythromycin A peak is about 1.3), in the portion of Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate taken by the formula:
50(CS2P / W)(ri / rS2)
in which CS2 is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Erythromycin RS in Standard preparation 2; P is the designated percentage of erythromycin A in USP Erythromycin RS; W is the quantity, in mg, of Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate taken to prepare the Assay preparation; ri is the peak response of each related compound, other than erythromycin A, erythromycin B, erythromycin C, erythromycin A enol ether, and erythromycin N-ethylsuccinate, in the chromatogram obtained from the Assay preparation; and rS2 is the erythromycin A peak response in the chromatogram obtained from Standard preparation 2: not more than 3.0% of any individual related compound is found.
Calculate the percentage of erythromycin A enol ether in the portion of Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate taken by the formula:
(50 / 11)(CS2P / W)(rE / rS2)
in which 11 is the response factor for erythromycin A enol ether in relation to that of erythromycin A; rE is the peak response of the erythromycin A enol ether observed in the chromatogram obtained from the Assay preparation; and the other terms are as defined above: not more than 3.0% of erythromycin A enol ether is found.
Calculate the percentage of erythromycin N-ethylsuccinate in the portion of Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate taken by the formula:
(50 / 7.4)(CS2P / W)(rN / rS2)
in which 7.4 is the response factor for erythromycin N-ethylsuccinate in relation to that of erythromycin A; rN is the peak response of the erythromycin N-ethylsuccinate (retention time relative to the erythromycin A peak is about 1.3) observed in the chromatogram obtained from the Assay preparation; and the other terms are as defined above: not more than 3.0% of erythromycin N-ethylsuccinate is found.
Assay—
Hydrolysis reagent—
Prepare a solution of dibasic potassium phosphate (2 in 100), and adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 8.0.
pH 8.0 Buffer—
Prepare a solution of dibasic potassium phosphate (3.5 in 100), and adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 8.0.
pH 3.5 Buffer—
Adjust 20 mL of pH 8.0 Buffer with phosphoric acid to a pH of 3.5.
Mobile phase—
Mix 50 mL of pH 8.0 Buffer with 400 mL of water, add 175 mL of tertiary butyl alcohol and 30 mL of acetonitrile, dilute with water to 1000 mL, and mix. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
[note—Use the following solutions promptly, or within 1 day if stored in a refrigerator. ]
Standard preparation 1—
Transfer about 50 mg of USP Erythromycin RS, accurately weighed, to a 25-mL volumetric flask, add 12.5 mL of methanol, and swirl to dissolve. Dilute with Hydrolysis reagent to volume, and mix.
Standard preparation 2—
Transfer about 5 mg each of USP Erythromycin B RS and USP Erythromycin C RS, both accurately weighed, to a 50-mL volumetric flask, add 25.0 mL of methanol, and swirl to dissolve. Add 2.5 mL of Standard preparation 1, dilute with Hydrolysis reagent to volume, and mix.
System suitability solution—
Dissolve about 2 mg of USP Erythromycin Related Compound N RS in about 20 mL of Standard preparation 2, and mix.
Erythromycin A enol ether solution—
Dissolve about 10 mg of USP Erythromycin RS in 2 mL of methanol. Add 10 mL of pH 3.5 Buffer, mix, and allow to stand for about 30 minutes. Refrigerate this solution until used, and discard 8 hours after preparation.
Assay preparation—
Transfer about 115 mg of Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate, accurately weighed, to a 50-mL volumetric flask, add 25.0 mL of methanol, and swirl to dissolve. Add about 20 mL of Hydrolysis reagent, mix, and allow to stand at room temperature for about 12 hours to effect hydrolysis. Dilute with Hydrolysis reagent to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system
(see Chromatography  621
621 )—The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 215-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains packing L21 (1000
)—The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 215-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains packing L21 (1000  ) and is maintained at a constant temperature of about 70
) and is maintained at a constant temperature of about 70 . The flow rate is about 2 mL per minute. Chromatograph the System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the order of elution of the components is erythromycin related compound N, erythromycin C, erythromycin A, and erythromycin B; and the resolution, R, between erythromycin related compound N and erythromycin C is not less than 0.8 and between erythromycin related compound N and erythromycin A not less than 5.5. Chromatograph the Erythromycin A enol ether solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: adjust the duration of chromatography to include the erythromycin A enol ether peak, which has a retention time of about 4.3 to 4.7 times that of erythromycin A. Chromatograph Standard preparation 1, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 1.0%.
. The flow rate is about 2 mL per minute. Chromatograph the System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the order of elution of the components is erythromycin related compound N, erythromycin C, erythromycin A, and erythromycin B; and the resolution, R, between erythromycin related compound N and erythromycin C is not less than 0.8 and between erythromycin related compound N and erythromycin A not less than 5.5. Chromatograph the Erythromycin A enol ether solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: adjust the duration of chromatography to include the erythromycin A enol ether peak, which has a retention time of about 4.3 to 4.7 times that of erythromycin A. Chromatograph Standard preparation 1, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 1.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 200 µL) of Standard preparation 1, Standard preparation 2, and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph; record the chromatograms for a period of time that is adequate to include the erythromycin A enol ether peak, if present; and measure the areas of the peak responses. Calculate the percentage of erythromycin A in the portion of Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate taken by the formula:
50(CS1P / W)(rU / rS1)
in which CS1 is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Erythromycin RS in Standard preparation 1; P is the designated percentage of erythromycin A in USP Erythromycin RS; W is the quantity, in mg, of Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate taken to prepare the Assay preparation; and rU and rS1 are the erythromycin A peak responses in the chromatograms obtained from the Assay preparation and Standard preparation 1, respectively.
Calculate the percentage of erythromycin B and erythromycin C in the portion of Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate taken by the formula:
50(CS2P / W)(rU / rS2)
in which CS2 is the concentration, in mg per mL, of the relevant USP Reference Standard in Standard preparation 2; P is the designated percentage of erythromycin B or erythromycin C in the relevant USP Reference Standard; W is the quantity, in mg, of Erythromycin Ethylsuccinate taken to prepare the Assay preparation and rU and rS2 are the peak responses of the relevant analyte in the chromatograms obtained from the Assay preparation and Standard preparation 2, respectively. The percentage of erythromycin B is not more than 12.0%, and the percentage of erythromycin C is not more than 5.0%.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Ahalya Wise, M.S.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8161 |
(SM12010) Monographs - Small Molecules 1 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 3087