Add the following:
(fon dap' a rin ux soe' dee um; fon'' da par' in ux soe' dee um).
C31H43N3O49S8Na10
Methyl O-2-deoxy-6-O-sulfo-2-(sulfoamino)-
DEFINITION
Fondaparinux Sodium is the sodium salt of a synthetic sulfated pentasaccharide anticoagulant based on the antithrombin binding moiety of heparin. It is synthesized from a natural source of chirally pure sugars (mono- and di-saccharides). A range of coupling, (de)protection and functionalization reactions leads to crude fondaparinux sodium, which is further purified to yield the drug substance. Fondaparinux Sodium contains NLT 95.0% and NMT 103.0% of fondaparinux sodium, calculated on the anhydrous and solvent-free basis. Fondaparinux Sodium is a white to off-white powder.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. 13C NMR Spectrum
NMR reference:
Standard solution:
Sample solution:
Instrumental conditions
Mode:
Frequency:
Temperature:

System suitability
Sample:
Using a pulsed (Fourier transform) NMR spectrometer operating at NLT 100 MHz for 13C, acquire a free induction decay (FID) using a 90 pulse and a 5-s delay. Record the 13C NMR spectra of the NMR reference at 40
pulse and a 5-s delay. Record the 13C NMR spectra of the NMR reference at 40 , and set the trimethylsilyl resonance to 0.0 ppm. Collect the 13C NMR spectrum with a spectral window of at least 235 to
, and set the trimethylsilyl resonance to 0.0 ppm. Collect the 13C NMR spectrum with a spectral window of at least 235 to 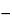 10 ppm with spinning at 20 Hz, using line broadening of NLT 1. The number of transients should be adjusted until the signal-to-noise ratio of the signal for the C-1 in the
10 ppm with spinning at 20 Hz, using line broadening of NLT 1. The number of transients should be adjusted until the signal-to-noise ratio of the signal for the C-1 in the 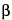 -d-glucopyranosyluronic acid ring of fondaparinux sodium in the Standard solution meets the suitability requirements. The Standard solution shall be run at least daily when the Sample solution is being run. The chemical shift for the C-1 resonance of the
-d-glucopyranosyluronic acid ring of fondaparinux sodium in the Standard solution meets the suitability requirements. The Standard solution shall be run at least daily when the Sample solution is being run. The chemical shift for the C-1 resonance of the 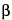 -d-glucopyranosyluronic acid ring of fondaparinux sodium in the Standard solution should be observed at 103.9 ± 0.1 ppm. Record the 13C NMR spectrum of the Sample solution at 40
-d-glucopyranosyluronic acid ring of fondaparinux sodium in the Standard solution should be observed at 103.9 ± 0.1 ppm. Record the 13C NMR spectrum of the Sample solution at 40 using the same conditions.
using the same conditions.
Suitability requirements
Number of transients:
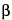 -d-glucopyranosyluronic acid ring of fondaparinux sodium in the Standard solution is at least 20/1 in the region near 103.9 ppm.
-d-glucopyranosyluronic acid ring of fondaparinux sodium in the Standard solution is at least 20/1 in the region near 103.9 ppm.
Chemical shift:
Chemical shifts for system suitability:
Analysis
Sample:
Acceptance criteria:
• B. Chromatographic Identity
Analysis:
Acceptance criteria:
• C. Sodium Determination
Analysis:
Acceptance criteria:
ASSAY
• Procedure
5 mM phosphate solution:
Solution A:
Solution B:
Mobile phase:
[Note—Make adjustments to Solution A as necessary, and degas the Mobile phase and the sample before use. Dissolved gas in the injected solution may lead to baseline interference. Degassing of the Mobile phase is critical to obtain a suitable signal-to-noise ratio and higher sensitivity. An eluant generator1 installed between the injector and the column may reduce the baseline interference.
Table 1
| Time (min) |
Solution A (%) |
Solution B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 |
50 |
50 |
| 5 |
50 |
50 |
| 25 |
5 |
95 |
| 30 |
5 |
95 |
| 35 |
50 |
50 |
| 50 |
50 |
50 |
System suitability solution:
Standard solution:
Sensitivity check solution:
Sample solution:
Blank:
Chromatographic system
Mode:
Detector:
Column:
Column temperature:

Flow rate:
Injection volume:
System suitability
Samples:
Inject the Blank in duplicate, the Sensitivity check solution, and the System suitability solution. Inject the Standard solution at least six times consecutively.
Suitability requirements
Specificity and baseline drift
The chromatogram of the second Blank injection shows a baseline drift between 0.00 and 0.02 AU over 30 min. If necessary, adjust the DMSO content of the Mobile phase until an acceptable baseline is achieved.
The chromatogram of the second Blank injection does not contain peaks between 3.00 and 30.00 min.
Signal-to-noise ratio:
Chromatogram similarity:
Relative standard deviation:
Analysis
Samples:
Inject the Standard solution at least six times consecutively and the Sample solution in duplicate. Record the chromatograms and measure the retention times and areas for the major peaks (excluding peaks before 3.00 and after 30.00 min).
For each injection of the Standard solution, calculate a response factor (FR):
FR = (CS/rS)
| CS | = | = concentration of fondaparinux sodium in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| rS | = | = peak response of fondaparinux sodium from the Standard solution |
Calculate the mean response factor (FM) for each duplicate injection, and determine the % RSD for the peak areas of fondaparinux sodium (rS) for six consecutive injections of the Standard solution.
Using the mean response factor, calculate the percentage of fondaparinux in the portion of sample taken:
Result (% w/w) = (FM × rU × D × 100)/W
| FM | = | = mean response factor for each duplicate injection |
| rU | = | = peak response of fondaparinux sodium in the Sample solution |
| D | = | = dilution factor for the sample (mL) |
| W | = | = weight of fondaparinux sodium taken to prepare the Sample solution (mg) |
Acceptance criteria:
OTHER COMPONENTS
• Sodium Determination
2% Nitric acid solution:
Sodium solution:
Standard solutions:
Sample solution:
Analysis:
Acceptance criteria:
IMPURITIES
• Free Sulfate and Residual Chloride Determination
Mobile phase:
Standard solution 1:
Standard solution 2:
Standard solution 3:
Standard solution 4:
Calibration standard solutions:
Table 2
| Concentration |
Volume of Sulfate Solution (mL) |
Volume of Chloride Solution (mL) |
Final Volume (mL) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 ppm SO4 |
5.0, Standard solution 4
|
10.0, Standard solution 3
|
100.0 |
| 2.5 ppm SO4 |
0.50, Standard solution 2
|
0.50, Standard solution 1
|
200.0 |
| 5.0 ppm SO4 |
0.50, Standard solution 2
|
0.50, Standard solution 1
|
100.0 |
| 20.0 ppm SO4 |
2.0, Standard solution 2
|
2.0, Standard solution 1
|
100.0 |
| 50.0 ppm SO4 |
5.0, Standard solution 2
|
5.0, Standard solution 1
|
100.0 |
Resolution solution:
Sample solution:
Chromatographic system
Mode:
Detector:
Column:
Regenerating solvent for the suppressor:
Column temperature:
Flow rate:
Injection volume:
Run time:
System suitability
Samples:
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
Response stability:
Relative standard deviation:
Analysis
Sample:
[Note—Regenerate the anion-exchange column for 15 min with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide after each injection of fondaparinux sample, followed by equilibration with Mobile phase for 21 min.
Inject 50 µL of each of the Calibration standard solutions and 50 µL of the Sample solution in triplicate. The peak area responses for the chloride and sulfate ion peaks in the chromatograms obtained with the Calibration standard solutions show two peaks corresponding respectively to chloride ions at a retention time of approximately 3.6 min and to sulfate ions at a retention time of approximately 14.1 min. The Calibration standard solutions and the corresponding standard concentrations are used to construct five-point calibration curves for both chloride and sulfate ions. The concentrations of sulfate and chloride ions in the Sample solutions are calculated using the standard curves.
Calculations:
Result = CS × F × (1/CU) × 100
| CS | = | = concentration of the ion calculated from the quadratic calibration equation (µg/mL) |
| F | = | = conversion factor (µg/mL to mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Fondaparinux Sodium in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Report the average of the triplicate determinations.
Acceptance criteria:
• Organic Impurities
Analysis:
Samples:
Calculate the percentage of each individual impurity in the portion of Fondaparinux Sodium taken:
Result (% area/area) = [rU/(rS + rT)] × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of each impurity from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of fondaparinux sodium from the Sample solution |
| rT | = | = sum of all peak responses for impurities from the Sample solution |
The total impurities content (% area/area) is the sum of all mean unrounded contents of an individual impurity that are NLT 0.200%.
Acceptance criteria:
Table 3
| Name |
Relative Retention Time |
Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Impurity peak Aa
|
0.93 |
0.8 (a/a) |
| Impurity peak Ba
|
1.2b
|
0.6 (a/a) |
| Any unspecified impurity |
— |
0.3 |
| Total impurities |
— |
NMT 2.0% |
|
a
Impurity peak A contains two structures: Methyl (2-deoxy-2-sodium sulfoamino-6-O-sodium sulfonato-
b
Impurity peak B can appear as a complex set of peaks and not fully resolved. In such a case, the integration should be performed such that all such peaks are combined.
|
||
• Pyridine and Ethanol Determination
(See Residual Solvents  467
467 .)
.)
Pyridine standard solution:
Internal standard solution:
Standard solution 1:
Standard solution 2:
Sample stock solution:
Sample solution:
Blank:
Sample preparation:
Chromatographic system
Mode:
Detector:
Column:
Temperatures
[Note—At initial temperature NLT 3 min between injections.
Injector:

Detector:

Column:
Table 4
| Initial Temperature ( |
Temperature Ramp ( |
Final Temperature ( |
Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 |
— |
40 |
20 |
| 40 |
10 |
240 |
0 |
| 240 |
— |
240 |
5 |
Carrier gas:
Injection type:
Head space autosampler
Sample equilibration temperature:

Sample equilibration time:
Transfer line temperature:

System suitability
Samples:
Assay a water Blank followed by six consecutive samples of Standard solution 2(A), followed by a single injection of Standard solution 2(B).
Suitability requirements
Blank:
Signal-to-noise ratio:
Relative standard deviation:
Analysis
Samples:
Calculations:
Result = CS × (RU/RS) × (V/M) × D
| CS | = | = concentration of Standard solution 2 (µg/mL) |
| RU | = | = peak response ratio of solvent “s” in the Sample solution to solvent “s” in the Internal standard solution |
| RS | = | = peak response ratio of solvent “s” in Standard solution 2 to solvent “s” in the Internal standard solution |
| V | = | = volume of solution used to prepare the Sample solution (mL) |
| M | = | = mass of sample dissolved to prepare the Sample solution (g) |
| D | = | = dilution factor of the Sample solution |
The average of three independent assays constitutes the results.
Acceptance criteria:
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Bacterial Endotoxins Test  85
85 :
:
• pH  791
791 :
:
 –25
–25 (2.5% w/v)
(2.5% w/v)
• Microbial Enumeration Tests  61
61 :
:
• Water Determination, Method Ic  921
921 :
:
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
 in a dry environment.
in a dry environment.
• Labeling:
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Endotoxin RS
USP Fondaparinux Sodium for Assay RS
USP Fondaparinux Sodium Identification RS
USP Fondaparinux Sodium System Suitability Mixture A RS
1
One suitable eluant generator is Dionex DEGAS EG40/50 (12 × 17 cm, thickness 2.2 cm).
2
One suitable suppressor is Dionex ASRS 300 4 mm.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Anita Y. Szajek, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison (301) 816-8325 |
(BIO12010) Monographs - Biologics and Biotechnology 1 |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison (301) 816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison (301) 816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP38–NF33 Page 3603
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 39(5)




