Glycyl-l-tyrosine
DEFINITION
Glycyl-l-tyrosine contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 101.5% of glycyl-l-tyrosine (C11H14N2O4), calculated on the anhydrous and solvent-free basis, and excluding glycine and tyrosine.
IDENTIFICATION
• B.
It meets the requirements for Optical Rotation, Specific Rotation  781S
781S in Specific Tests.
in Specific Tests.
ASSAY
• Procedure
Sample:
300 mg
Blank:
Mix 5 mL of formic acid with 50 mL of glacial acetic acid.
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry  541
541 .)
.)
Mode:
Direct titration
Titrant:
0.1 N perchloric acid VS
Endpoint detection:
Potentiometric
Analysis:
Dissolve the Sample in 5 mL of formic acid, add 50 mL of glacial acetic acid, and titrate with the Titrant. Perform the Blank determination, and make any necessary correction.
Calculate the percentage of glycyl-l-tyrosine (C11H14N2O4) in the Sample taken:
Result1 = [(VS 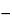 VB) × N × (F/W)] × 100
VB) × N × (F/W)] × 100
| VS | = | = Titrant volume consumed by the Sample (mL) |
| VB | = | = Titrant volume consumed by the Blank (mL) |
| N | = | = actual normality of the Titrant (mEq/mL) |
| F | = | = equivalency factor, 238.2 mg/mEq |
| W | = | = Sample weight (mg) |
Calculate the percentage of glycyl-l-tyrosine (C11H14N2O4) in the Sample taken, excluding glycine and tyrosine:
Result2 = [(Result1 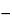 a
a 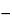 b)]/[(100
b)]/[(100 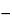 Gly
Gly 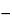 Tyr)] × 100
Tyr)] × 100
a = Gly × (Mr1/Mr2)
b = Tyr × (Mr1/Mr3)
| Gly | = | = percentage of glycine from the Related Compounds test |
| Tyr | = | = percentage of tyrosine from the Related Compounds test |
| Mr1 | = | = molecular weight of glycyl-l-tyrosine, 238.2 |
| Mr2 | = | = molecular weight of glycine, 75.1 |
| Mr3 | = | = molecular weight of tyrosine, 181.2 |
Acceptance criteria:
98.0%–101.5% on the anhydrous and solvent-free basis, and excluding glycine and tyrosine
IMPURITIES
• Residue on Ignition  281
281 :
NMT 0.1%
:
NMT 0.1%
• Chloride and Sulfate, Chloride  221
221
Sample:
0.89 g
Standard solution:
0.50 mL of 0.010 N hydrochloric acid
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 200 µg/g
• Chloride and Sulfate, Sulfate  221
221
Sample:
0.96 g
Standard solution:
0.20 mL of 0.010 N sulfuric acid
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 200 µg/g
• Iron  241
241 :
NMT 10 µg/g
:
NMT 10 µg/g
• Residual Solvents  467
467
Acceptance criteria
Ethanol:
NMT 0.5%
[Note—For the Acceptance criteria for any other residual solvents, see Residual Solvents  467
467 . ]
. ]
• Limit of Ammonium
Standard stock solution:
Dissolve 1.486 g of ammonium chloride in 500.0 mL of water.
Standard calibration solutions:
Transfer 0.01, 0.1, 1.0, and 10.0 mL of Standard stock solution into separate 100-mL volumetric flasks, and dilute with water to volume. The final concentrations are 0.1, 1, 10, and 100 µg/mL of ammonium ions (NH4+), respectively.
Sample solution:
Transfer 1.0 g of Glycyl-l-tyrosine to a 150-mL beaker containing a plastic-coated stirring bar, add 100.0 mL of water, and stir until dissolved.
Electrode system:
Use a gas-sensing, ammonia-specific indicating electrode with internal reference connected to a pH meter capable of measuring potentials with a minimum reproducibility of ±0.1 mV (see pH  791
791 ). Condition the electrode according to the manufacturer's instructions.
). Condition the electrode according to the manufacturer's instructions.
Analysis
Standard response line:
Transfer 100 mL of water into a 150-mL beaker containing a plastic-coated stirring bar, insert the electrode into the water, stir, and measure the potential. Add 1 mL of 10 N sodium hydroxide solution, stir, and measure the potential after stabilization (about 3 min). The potential difference must be below 20 mV. Transfer 100.0 mL of each of Standard calibration solutions (0.1, 1, 10, 100 µg/mL of ammonium ions) into separate 150-mL beakers, and add 1 mL of 10 N sodium hydroxide. Insert the electrode into each solution, stir, and measure the potential after stabilization (about 3 min). Plot a curve (four calibration points) of the potential (mV) as function of ammonium ion concentrations (µg/mL).
Sample:
Sample solution
Rinse the electrode, insert it into the Sample solution, add 1 mL of 10 N sodium hydroxide, and stir. Check the pH, which must be above 11; if not, adjust with 10 N sodium hydroxide. After 3 min, measure the potential, and determine the corresponding ammonium ion concentration from the calibration curve.
Calculate the content of ammonium in the portion of the Sample taken:
Result = (V × C)/W
| V | = | = volume of the Sample solution (mL) |
| C | = | = concentration of ammonium ions in the Sample solution determined from the Standard response line (µg/mL) |
| W | = | = weight of Glycyl-l-tyrosine taken to prepare the Sample solution (g) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 200 µg/g
• Related Compounds
Buffer solution:
Dissolve 6.84 g of potassium phosphate in 1000 mL of water.
Mobile phase:
Acetonitrile and Buffer solution (65:35)
System suitability solution:
Transfer 25 mg of USP l-Alanyl-l-glutamine RS and 5 mg of USP l-Alanyl-alanine RS into a 25-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Transfer 1.0 mL of this solution into a 10-mL volumetric flask containing 20 mg of USP Glycyl-l-tyrosine RS, and dilute with Mobile phase to volume.
Standard solution 1:
0.037 mg/mL of USP l-Tyrosine RS in Mobile phase
Standard solution 2:
0.025 mg/mL of USP Glycine RS in Mobile phase
Sample solution:
2.5 mg/mL of Glycyl-l-tyrosine in Mobile phase
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 215 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L8
Flow rate:
0.7 mL/min
Injection volume:
20 µL
System suitability
Sample:
System suitability solution
[Note—The relative retention times for glycyl-l-tyrosine, l-alanyl-l-alanine, and l-alanyl-l-glutamine are 1.0, 1.6, and 1.8, respectively. ]
Suitability requirements
Column efficiency:
NLT 8000 theoretical plates for the l-alanyl-l-glutamine peak
Resolution:
NLT 2.0 between l-alanyl-l-glutamine and l-alanyl-l-alanine
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution 1, Standard solution 2, and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of tyrosine and glycine in the portion of the Sample taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of tyrosine or glycine from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of tyrosine from Standard solution 1 or glycine from Standard solution 2 |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP l-Tyrosine RS in Standard solution 1 (mg/mL) or concentration of USP Glycine RS in Standard solution 2 (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Glycyl-l-tyrosine in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Calculate the percentage of any other specified and unspecified impurities in the portion of the Sample taken:
Result = (rU/rT) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of each individual impurity |
| rT | = | = sum of the responses of all the peaks, excluding peak responses of glycine and tyrosine |
Acceptance criteria:
See Table 1.
Table 1
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Cyclo(gly-tyr) | 0.41 | 0.2 |
| Pivaloyl-l-tyrosine | 0.48 | 0.1 |
| Tyrosine | 0.67 | 1.5 |
| Glycine | 1.15 | 1.0 |
| Gly-gly-tyr | 1.27 | 0.3 |
| Any unspecified impurity | — | 0.1 |
| Total unspecified impurities | — | 0.5 |
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Optical Rotation, Specific Rotation  781S
781S
Sample solution:
20 mg/mL in water. Perform the measurement at 20 .
.
Acceptance criteria:
+46.0 to +50.0
to +50.0 on the anhydrous basis
on the anhydrous basis
• Water Determination, Method Ia  921
921 :
10.0%–16.0%
:
10.0%–16.0%
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed, tight, light-resistant containers.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Alanyl-l-alanine RS
USP l-Alanyl-l-glutamine RS
USP Glycyl-l-tyrosine RS
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Huy T. Dinh, M.S.
Senior Scientific Liaison (301) 816-8594 |
(DS2010) Monographs - Dietary Supplements and Herbal Medicines |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP38–NF33 Page 6083
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 39(4)