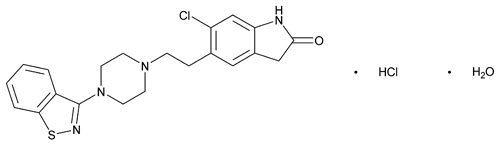
Ziprasidone Hydrochloride
C21H21ClN4OS·HCl·H2O 467.41
2H-Indol-2-one, 5-[2-[4-(1,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]-6-chloro-1,3-dihydro-, monohydrochloride, monohydrate;
5-[2-[4-(1,2-Benzisothiazol-3-yl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]-6-chloro-2-indolinone monohydrochloride, monohydrate

 [138982-67-9].
[138982-67-9].
(zi pras' i done hye'' droe klor' ide).
C21H21ClN4OS·HCl·H2O 467.41
2H-Indol-2-one, 5-[2-[4-(1,2-benzisothiazol-3-yl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]-6-chloro-1,3-dihydro-, monohydrochloride, monohydrate;
5-[2-[4-(1,2-Benzisothiazol-3-yl)-1-piperazinyl]ethyl]-6-chloro-2-indolinone monohydrochloride, monohydrate
DEFINITION
Ziprasidone Hydrochloride contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of C21H21ClN4OS·HCl, calculated on the anhydrous and solvent-free basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• B.
The retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution, as obtained in the Assay.
• C. Identification Tests—General, Chloride  191
191 :
Meets the requirements
:
Meets the requirements
ASSAY
• Procedure
Buffer:
6.8 g/L of monobasic potassium phosphate in water. Adjust with 85% phosphoric acid to a pH of 3.0.
Mobile phase:
Methanol and Buffer (2:3)
Diluent:
Methanol and water (3:2)
Standard solution:
0.23 mg/mL of USP Ziprasidone Hydrochloride RS in Diluent
Sample solution:
0.23 mg/mL of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride in Diluent
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 229 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 15-cm; 5-µm packing L7
Column temperature:
40
Flow rate:
1.5 mL/min
Injection size:
20 µL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Tailing factor:
NMT 2.0
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 2.0%
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of C21H21ClN4OS·HCl in the portion of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Ziprasidone Hydrochloride RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
98.0%–102.0% on the anhydrous and solvent-free basis
IMPURITIES
Organic Impurities
• Procedure 1: Limit of Tetrahydrofuran
Standard solution:
0.05 mg/mL in dimethyl sulfoxide. Transfer 4 mL of this solution to a 20-mL headspace vial, and seal.
Sample solution:
Transfer 40 mg of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride and 4.0 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide to a 20-mL headspace vial, seal, and mix.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
GC with headspace injector
Detector:
Flame ionization
Column:
30-m × 0.32-mm fused silica column coated with a 1.8-µm film of phase G43
Temperature
Injection port:
180
Detector:
260
Column:
See the temperature program table below.
| Initial Temperature ( |
Temperature Ramp ( |
Final Temperature ( |
Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 0 | 40 | 5 |
| 40 | 2 | 90 | 0 |
| 90 | 30 | 225 | 2 |
Injector split ratio:
30:1
Carrier gas:
Helium
Flow rate:
1.6 mL/min
Injection size:
2 mL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 5%
Analysis:
[Note—The headspace vials are maintained at 105 for 60 min prior to headspace injection. ]
for 60 min prior to headspace injection. ]
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of tetrahydrofuran in the portion of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of tetrahydrofuran from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of tetrahydrofuran from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of tetrahydrofuran in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria
Tetrahydrofuran:
NMT 0.4%
• Procedure 2: Limit of Early-Eluting Impurities
Mobile phase and Chromatographic system:
Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Diluent A:
Methanol, water, and hydrochloric acid (20:5:0.01)
Diluent B:
Methanol and water (3:2)
Standard solution A:
0.5 µg/mL of USP Ziprasidone Related Compound A RS and 0.8 µg/mL of USP Ziprasidone Related Compound B RS in Diluent A
Standard solution B:
0.4 µg/mL of USP Ziprasidone Related Compound B RS in Diluent A
System suitability solution:
0.24 mg/mL of USP Ziprasidone Hydrochloride RS in Standard solution A
Sample solution A:
0.4 mg/mL of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride in Diluent A
Sample solution B:
0.2 mg/mL of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride in Diluent B
System suitability
Sample:
System suitability solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 1.5 between the ziprasidone related compound B and ziprasidone peaks
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 10% for the ziprasidone related compound B peak
Analysis:
[Note—Run the Sample solution NLT 7 times the ziprasidone retention time in Sample solution A. ]
Samples:
Standard solution A and Sample solution A
Calculate the percentages of ziprasidone related compounds A and B relative to the content of ziprasidone free base in the portion of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (Mr2/Mr1) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of the ziprasidone related compound from Sample solution A |
| rS | = | = peak response of the ziprasidone related compound from Standard solution A |
| CS | = | = concentration of the ziprasidone related compound in Standard solution A (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride in Sample solution A (mg/mL) |
| Mr1 | = | = molecular weight of ziprasidone free base, 412.94 |
| Mr2 | = | = molecular weight of ziprasidone hydrochloride, 467.41 |
Samples:
Standard solution B and Sample solution B
Calculate the percentage of ziprasidone open ring relative to the content of ziprasidone free base in the portion of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (Mr2/Mr1) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of ziprasidone open ring from Sample solution B |
| rS | = | = peak response of ziprasidone related compound B from Standard solution B |
| CS | = | = concentration of ziprasidone related compound B in Standard solution B (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride in Sample solution B (mg/mL) |
| Mr1 | = | = molecular weight of ziprasidone free base, 412.94 |
| Mr2 | = | = molecular weight of ziprasidone hydrochloride, 467.41 |
Samples:
Diluent A, Diluent B, Standard solution B, and Sample solution A
Calculate the percentage of unspecified impurity eluting before ziprasidone relative to the content of ziprasidone free base in the portion of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (Mr2/Mr1) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of each unspecified impurity from Sample solution A |
| rS | = | = peak response of ziprasidone related compound B from Standard solution B |
| CS | = | = concentration of ziprasidone related compound B in Standard solution B (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride in Sample solution A (mg/mL) |
| Mr1 | = | = molecular weight of ziprasidone free base, 412.94 |
| Mr2 | = | = molecular weight of ziprasidone hydrochloride, 467.41 |
[Note—Disregard the peaks in the injections of Diluent A and Diluent B. ]
Acceptance criteria
Individual impurities:
See Impurity Table 1.
Impurity Table 1
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Ziprasidone related compound A | 0.4 | 0.1 | |
| Ziprasidone related compound B | 0.8 | 0.2 | |
| Ziprasidone open ringa | 0.9 | 0.2 | |
| Ziprasidone | 1.0 | — | |
| Any individual unspecified impurity eluting before ziprasidone | — | 0.1 | |
|
a
2-(2-Amino-5-(2-(4-(benzo[d]isothiazol-3-yl)piperazin-1-yl)ethyl)-4-chlorophenyl)acetic acid.
|
|||
• Procedure 3: Limit of Late-Eluting Impurities
Buffer:
6.8 g/L of monobasic potassium phosphate in water. Adjust with 5 N potassium hydroxide to a pH of 6.0.
Mobile phase:
Acetonitrile, methanol, and Buffer (11:1:8)
Diluent:
Methanol, water, and hydrochloric acid (20:5:0.01)
Standard solution:
0.8 µg/mL each of USP Ziprasidone Related Compound C RS and USP Ziprasidone Related Compound D RS in Diluent
System suitability solution:
0.24 mg/mL of USP Ziprasidone Hydrochloride RS in the Standard solution
Sample solution:
0.45 mg/mL of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride in Diluent
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 229 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 15-cm; 5-µm packing L7
Column temperature:
35
Flow rate:
1 mL/min
Injection size:
20 µL
System suitability
Sample:
System suitability solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 6.0 between the ziprasidone and ziprasidone related compound C peaks
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 10% for the ziprasidone related compound C peak
Analysis:
[Note—Run the Sample solution NLT 12 times the ziprasidone retention time in the Sample solution. ]
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentages of ziprasidone related compounds C and D relative to the content of ziprasidone free base in the portion of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (Mr2/Mr1) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of the ziprasidone related compound from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of the ziprasidone related compound from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of the ziprasidone related compound in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
| Mr1 | = | = molecular weight of ziprasidone hydrochloride free base, 412.94 |
| Mr2 | = | = molecular weight of ziprasidone hydrochloride, 467.41 |
Samples:
Diluent, Standard solution, and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of unspecified impurity eluting after ziprasidone relative to the content of ziprasidone free base in the portion of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (Mr2/Mr1) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of each unspecified impurity from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of ziprasidone related compound D from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of ziprasidone related compound D in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of Ziprasidone Hydrochloride in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
| Mr1 | = | = molecular weight of ziprasidone hydrochloride free base, 412.94 |
| Mr2 | = | = molecular weight of ziprasidone hydrochloride, 467.41 |
[Note—Disregard the peaks in the injection of the Diluent. ]
Acceptance criteria
Individual impurities:
See Impurity Table 2.
Total impurities:
NMT 0.5%. [Note—The total impurities are the sum of related compounds A, B, C, D, ziprasidone open ring, and all unspecified impurities found in Procedure 2: Limit of Early-Eluting Impurities and Procedure 3: Limit of Late-Eluting Impurities. ]
Impurity Table 2
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Ziprasidone | 1.0 | — | |
| Ziprasidone related compound C | 2.0 | 0.2 | |
| Ziprasidone related compound D | 3.0 | 0.2 | |
| Any individual unspecified impurity eluting after ziprasidone | — | 0.1 | |
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Water Determination, Method I  921
921 :
Between 3.7% and 5.0%
:
Between 3.7% and 5.0%
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers, and store at room temperature.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Ziprasidone Related Compound A RS
3-(Piperazin-1-yl)benzo[d]isothiazole monohydrochloride.
C11H13N3S·HCl 255.77
3-(Piperazin-1-yl)benzo[d]isothiazole monohydrochloride.
C11H13N3S·HCl 255.77
USP Ziprasidone Related Compound B RS
5-(2-(4-(Benzo[d]isothiazol-3-yl)piperazin-1-yl)ethyl)-6-chloroindoline-2,3-dione.
C21H19ClN4O2S 426.92
5-(2-(4-(Benzo[d]isothiazol-3-yl)piperazin-1-yl)ethyl)-6-chloroindoline-2,3-dione.
C21H19ClN4O2S 426.92
USP Ziprasidone Related Compound C RS
5,5¢-Bis(2-(4-(benzo[d]isothiazol-3-yl)piperazin-1-yl)ethyl)-6,6¢-dichloro-3-hydroxy-3,3¢-biindoline-2,2¢-dione.
C42H40Cl2N8O3S2 839.85
5,5¢-Bis(2-(4-(benzo[d]isothiazol-3-yl)piperazin-1-yl)ethyl)-6,6¢-dichloro-3-hydroxy-3,3¢-biindoline-2,2¢-dione.
C42H40Cl2N8O3S2 839.85
USP Ziprasidone Related Compound D RS
3-(Benzo[d]isothiazol-3-yl)-5-(2-(4-(benzo[d]isothiazol-3-yl)piperazin-1-yl)ethyl)-6-chloroindolin-2-one.
C28H24ClN5OS2 546.11
3-(Benzo[d]isothiazol-3-yl)-5-(2-(4-(benzo[d]isothiazol-3-yl)piperazin-1-yl)ethyl)-6-chloroindolin-2-one.
C28H24ClN5OS2 546.11
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Hariram Ramanathan, M.S.
Associate Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8313 |
(SM42010) Monographs - Small Molecules 4 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 5079
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 35(3) Page 592