Saw Palmetto Extract
DEFINITION
Saw Palmetto Extract is obtained from comminuted Saw Palmetto by extraction with hydroalcoholic mixtures or solvent hexane, or by supercritical extraction with carbon dioxide. The ratio of starting crude plant material to Extract is from 8.0:1 to 14.3:1. The Extract contains NLT 70.0% and NMT 95.0% of fatty acids and NLT 0.2% and NMT 0.5% of sterols, calculated on the anhydrous basis. The lipophilic Extract contains NLT 0.15% and NMT 0.35% of long-chain alcohols. The hydroalcoholic Extract contains NLT 0.01% and NMT 0.15% of long-chain alcohols. It contains no added substances.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Gas Chromatography
Analysis:
Proceed as directed in Content of Fatty Acids.
Acceptance criteria:
The retention times of the 11 major peaks of the Sample solution correspond to those in the chromatogram of the Standard solution. The ranges for ratios of the concentration of lauric acid to the concentration of the respective fatty acid are in Table 1.
Table 1
| Fatty Acid | Minimum Ratio |
Maximum Ratio |
|---|---|---|
| Capric | 9.0 | 16 |
| Caproic | 8.5 | 24 |
| Caprylic | 8.5 | 17.5 |
| Linoleic | 5.0 | 16 |
| Linolenic | 31.5 | 55 |
| Myristic | 2.2 | 2.8 |
| Oleic | 0.60 | 1.15 |
| Palmitic | 2.8 | 3.9 |
| Stearic | 14 | 26 |
COMPOSITION
• Content of Fatty Acids
Internal standard solution:
12 mg/mL of nonadecane in hexanes
Standard stock solution:
Dissolve quantities of USP Methyl Laurate RS, USP Methyl Oleate RS, USP Methyl Myristate RS, USP Methyl Palmitate RS, USP Methyl Linoleate RS, USP Methyl Caproate RS, USP Methyl Caprylate RS, USP Methyl Caprate RS, USP Methyl Palmitoleate RS, USP Methyl Stearate RS, and USP Methyl Linolenate RS in hexanes to obtain concentrations of each methyl ester as given in the Table 2.
Table 2
| Methyl Ester | Concentration (mg/mL) |
|---|---|
| Methyl laurate | 5 |
| Methyl oleate | 5 |
| Methyl myristate | 2 |
| Methyl palmitate | 2 |
| Methyl linoleate | 1 |
| Methyl caproate | 0.4 |
| Methyl caprylate | 0.4 |
| Methyl caprate | 0.4 |
| Methyl palmitoleate | 0.4 |
| Methyl stearate | 0.4 |
| Methyl linolenate | 0.4 |
Standard solution:
Transfer 1.0 mL of Internal standard solution to 5.0 mL of the Standard stock solution.
Sample solution:
Transfer 100 mg of Extract to a pressure-proof, screw-capped vial, and add 3.0 mL of a solution of sulfuric acid in methanol (5 in 100). Heat at 100 in an oil bath for 2 h, shaking from time to time. Allow to cool, and add 1.0 mL of Internal standard solution, 10.0 mL of water, 1 g of sodium chloride, and 5 mL of hexanes. Shake well, allow the layers to separate completely, and use the hexanes layer. [Note—Store in a refrigerator until ready to use. ]
in an oil bath for 2 h, shaking from time to time. Allow to cool, and add 1.0 mL of Internal standard solution, 10.0 mL of water, 1 g of sodium chloride, and 5 mL of hexanes. Shake well, allow the layers to separate completely, and use the hexanes layer. [Note—Store in a refrigerator until ready to use. ]
Chromatographic system
Mode:
GC
Detector:
Flame ionization
Column:
0.25-mm × 30-m fused silica capillary; 0.25-µm film of phase G16 coating
Temperature
Injector:
250
Detector:
300
Column:
See Table 3.
Table 3
| Initial Temperature ( |
Temperature Ramp ( |
Final Temperature ( |
Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 120 | 0 | 120 | 3 |
| 120 | 50 | 220 | 12 |
Carrier gas:
Helium
Flow rate:
1 mL/min
Injection size:
1 µL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
[Note—See Table 4 for the relative retention times. ]
Table 4
| Methyl Ester | Relative Retention Time |
|---|---|
| Methyl caproate | 0.39 |
| Methyl caprylate | 0.56 |
| Methyl caprate | 0.76 |
| Methyl laurate | 0.94 |
| Nonadecane (internal standard) | 1.0 |
| Methyl myristate | 1.1 |
| Methyl palmitate | 1.3 |
| Methyl palmitoleate | 1.35 |
| Methyl stearate | 1.65 |
| Methyl oleate | 1.7 |
| Methyl linoleate | 1.8 |
| Methyl linolenate | 2.0 |
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 1.5 between methyl stearate and methyl oleate peaks
Tailing factor:
NMT 2.0 for each of the methyl ester peaks
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 5.0% for each of the methyl ester peaks
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each fatty acid in the portion of Extract taken:
Result = (RU/RS) × (CS × V) × (1/W ) × (Mr1/Mr2) × 100
| RU | = | = peak response ratio of the relevant methyl ester to the internal standard from the Sample solution |
| RS | = | = peak response ratio of the relevant methyl ester to the internal standard from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of the respective methyl ester in the Standard stock solution (mg/mL) |
| V | = | = volume of the Standard stock solution used to prepare the Standard solution (mL) |
| W | = | = weight of Extract taken to prepare the Sample solution (mg) |
| Mr1 | = | = molecular weight of the relevant fatty acid |
| Mr2 | = | = molecular weight of the methyl ester of the relevant fatty acid |
Acceptance criteria:
70.0%–95.0% for the sum of the percentages of all the fatty acids.
• Content of Long-Chain Alcohols and Sterols
Derivatizing solution A:
Bis(trimethylsilyl)acetamide, trimethylsilylimidazole, and trimethylchlorosilane (3:3:2)
Derivatizing solution B:
Derivatizing solution A, bis(trimethylsilyl)trifluoroacetamide, and pyridine (1:1:1)
Internal standard solution:
10 mg/mL of eicosanol and 5 mg/mL of cholesterol in chloroform
Standard stock solution:
0.75 mg/mL of USP Hexacosanol RS and 1.4 mg/mL of USP 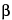 -Sitosterol RS in chloroform
-Sitosterol RS in chloroform
Standard solution:
Mix 5.0 mL of Standard stock solution with 1.0 mL of the Internal standard solution. Evaporate 0.75 mL of this solution to dryness using a stream of nitrogen. Dissolve the residue in 1.0 mL of Derivatizing solution B, and allow to stand for NLT 15 min at room temperature.
Sample solution:
Transfer 3.35 g of Extract into a 50-mL round-bottomed flask. Add 1.0 mL of Internal standard solution, and evaporate under vacuum at a temperature not exceeding 50 . Add 20 mL of a solution prepared by dissolving 130 g of potassium hydroxide in 200 mL of water in a 1000-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with methanol to volume. Attach a condenser, and reflux in a bath at 100
. Add 20 mL of a solution prepared by dissolving 130 g of potassium hydroxide in 200 mL of water in a 1000-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with methanol to volume. Attach a condenser, and reflux in a bath at 100 for 2 h. Quantitatively transfer this solution to a 25-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Transfer a 3-mL portion to a cartridge1 containing diatomaceous earth capable of holding 3 mL of aqueous phase.
for 2 h. Quantitatively transfer this solution to a 25-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Transfer a 3-mL portion to a cartridge1 containing diatomaceous earth capable of holding 3 mL of aqueous phase.
Absorb the solution into the column under vacuum for 20 min until the column is not cold. Elute the analytes from the column with 90 mL of methylene chloride, and evaporate the eluate to dryness. Dissolve the residue in 1.0 mL of Derivatizing solution B, and allow to stand for NLT 15 min at room temperature.
System suitability stock solution A:
2 mg/mL each of tetracosanol, octacosanol, USP Hexacosanol RS, and triacontanol in chloroform
System suitability solution A:
Mix 5.0 mL of System suitability stock solution A with 1.0 mL of Internal standard solution. Evaporate 0.75 mL of this solution to dryness using a stream of nitrogen. Dissolve the residue in 1.0 mL of Derivatizing solution B, and allow to stand for NLT 15 min at room temperature.
System suitability stock solution B:
2 mg/mL each of campesterol, stigmasterol, and USP 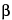 -Sitosterol RS and 0.37 mg/mL of stigmastanol
-Sitosterol RS and 0.37 mg/mL of stigmastanol
System suitability solution B:
Mix 5.0 mL of System suitability stock solution B with 1.0 mL of the Internal standard solution. Evaporate 0.75 mL of this solution to dryness using a stream of nitrogen. Dissolve the residue in 1.0 mL of Derivatizing solution B, and allow to stand for NLT 15 min at room temperature.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
GC
Detector:
Flame ionization
Column:
0.2-mm × 25-m capillary; 0.33-µm thickness of phase G1 coating
Temperature
Injector:
325
Detector:
325
Column:
See Table 5.
Table 5
| Initial Temperature ( |
Temperature Ramp ( |
Final Temperature ( |
Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 200 | 0 | 200 | 3 |
| 200 | 10 | 300 | 35 |
Carrier gas:
Helium
Flow rate:
0.5 mL/min
Make up gas flow:
25 mL/min
Injection size:
1 µL
Injection type:
Split ratio, 1:40
System suitability
Samples:
System suitability solution A and System suitability solution B
[Note—The relative retention times for tetracosanol, hexacosanol, octacosanol, and triacontanol are 0.89, 1.00, 1.15, and 1.36, respectively, System suitability solution A; and the relative retention times for cholesterol, campesterol, stigmasterol, 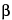 -sitosterol, and stigmastanol are 0.85, 0.92, 0.95, 1.00, and 1.01, respectively, System suitability solution B. ]
-sitosterol, and stigmastanol are 0.85, 0.92, 0.95, 1.00, and 1.01, respectively, System suitability solution B. ]
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 2 between 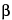 -sistosterol and stigmastanol peaks, System suitability solution B
-sistosterol and stigmastanol peaks, System suitability solution B
Column efficiency:
NLT 200,000 theoretical plates for the eicosanol peak, System suitability solution A; and NLT 150,000 theoretical plates for the cholesterol peak, System suitability solution B
Tailing factor:
NMT 2.0 for each relevant peak, System suitability solution A; and NMT 2.0 for each relevant peak, System suitability solution B
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Identify the signals corresponding to the relevant analytes by comparison with the chromatograms obtained with System suitability solutions A and B.
Separately calculate the percentages of tetracosanol, hexacosanol, octacosanol, and triacontanol, respectively, in the portion of Extract taken:
Result = (RU/RS) × (CS × V) × (1/W ) × 100
| RU | = | = peak response ratio of the relevant long-chain alcohol to the internal standard from the Sample solution |
| RS | = | = peak response ratio of hexacosanol to the internal standard from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of hexacosanol in the Standard stock solution (mg/mL) |
| V | = | = volume of the Standard stock solution used to prepare the Standard solution (mL) |
| W | = | = weight of the Extract taken to prepare the Sample solution (mg) |
Calculate the total content of long-chain alcohols as a percentage by adding the individual percentages.
Separately calculate the percentages of campesterol, stigmasterol, 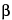 -sitosterol, and stigmastanol, respectively, in the portion of Extract taken:
-sitosterol, and stigmastanol, respectively, in the portion of Extract taken:
Result = (RU/RS) × (CS × V) × (1/W ) × 100
| RU | = | = peak response ratio of the relevant sterol to the internal standard from the Sample solution |
| RS | = | = peak response ratio of |
| CS | = | = concentration of |
| V | = | = volume of the Standard stock solution used to prepare the Standard solution (mL) |
| W | = | = weight of the Extract taken to prepare the Sample solution (mg) |
Calculate the total content of sterols as a percentage by adding the individual percentages.
Acceptance criteria:
0.2%–0.5% of sterols; the lipophilic Extract contains 0.15%–0.35% of long-chain alcohols; and the hydroalcoholic Extract contains 0.01%–0.15% of long-chain alcohols
CONTAMINANTS
• Heavy Metals, Method II  231
231 :
NMT 40 µg/g
:
NMT 40 µg/g
• Botanical Extracts, Pesticide Residues  565
565 :
Meets the requirements
:
Meets the requirements
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Alcohol Determination, Method II  611
611 (if present):
NMT 1%
(if present):
NMT 1%
• Fats and Fixed Oils, Unsaponifiable Matter  401
401 :
1.8%–3.5%
:
1.8%–3.5%
• Water Determination, Method I  921
921 :
NMT 3% is found in the hydroalcoholic Extract.
:
NMT 3% is found in the hydroalcoholic Extract.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Meets the requirements in Botanical Extracts  565
565 , Packaging and Storage
, Packaging and Storage
• Labeling:
The label states the Latin binomial and, following the official name, the part of the plant from which the article was prepared. The label also indicates the content of fatty acids and sterols and the ratio of the starting crude plant material to Extract. It meets the requirements in Botanical Extracts,  565
565 Labeling.
Labeling.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Methyl Caprate RS
USP Methyl Caproate RS
USP Methyl Caprylate RS
USP Methyl Laurate RS
USP Methyl Linoleate RS
USP Methyl Linolenate RS
USP Methyl Myristate RS
USP Methyl Oleate RS
USP Methyl Palmitate RS
USP Methyl Palmitoleate RS
USP Methyl Stearate RS
1
A suitable cartridge is Extrelut NT3, or an equivalent cartridge.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Maged H. Sharaf, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8318 |
(DS2010) Monographs - Dietary Supplements |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 1435
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 28(2) Page 425
