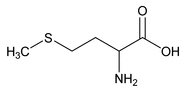
Racemethionine
(rayse'' e me thye' oh neen).
DEFINITION
Racemethionine contains NLT 99.0% and NMT 101.0% of C5H11NO2S, as dl-methionine, calculated on the dried basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Infrared Absorption  197K
197K
Sample:
Dry the substances at 105 .
.
Acceptance criteria:
Meets the requirements
• B.
The principal spot from Sample solution B is similar in size, color, and position to the principal spot from Standard solution A, as obtained in the test for Organic Impurities, Related Substances.
• C. Optical Rotation, Angular Rotation  781A
781A
Sample:
50 mg/mL in 1 M hydrochloric acid
Acceptance criteria:
 0.05
0.05 to +0.05
to +0.05
• D. Procedure
Analysis:
Dissolve 0.1 g of Racemethionine and 0.1 g of glycine in 4.5 mL of dilute sodium hydroxide solution (85 mg/mL). Add 1 mL of sodium nitroferricyanide solution (25 mg/mL). Heat to 40 for 10 min. Allow to cool, and add 2 mL of a mixture of hydrochloric acid and phosphoric acid (90:10).
for 10 min. Allow to cool, and add 2 mL of a mixture of hydrochloric acid and phosphoric acid (90:10).
Acceptance criteria:
A deep red color develops.
ASSAY
• Procedure
Sample:
140 mg of Racemethionine
Analysis:
Dissolve the Sample in a mixture of 3 mL of formic acid and 50 mL of glacial acetic acid. Titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary corrections (see Titrimetry  541
541 ). Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 14.92 mg of C5H11NO2S.
). Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 14.92 mg of C5H11NO2S.
Acceptance criteria:
99.0%–101.0% on the dried basis
IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
• Residue on Ignition  281
281 :
NMT 0.1%, determined on 1.0 g
:
NMT 0.1%, determined on 1.0 g
• Chloride and Sulfate, Chloride  221
221 :
[Note—Prepare the Sample solution and the Standard solution at the same time. ]
:
[Note—Prepare the Sample solution and the Standard solution at the same time. ]
Chloride standard solution (5 ppm Cl):
0.824 mg/mL of NaCl. Just before use, dilute 1 mL of this solution with water to 100 mL.
Standard solution:
To 10 mL of Chloride standard solution add 10 mL of 0.1 N silver nitrate and 25 mL of water, and mix.
Sample solution:
Dissolve 0.25 g in 35 mL of water. Add 5 mL of dilute nitric acid and 10 mL of 0.1 N silver nitrate. Allow to stand protected from light for 5 min.
Analysis:
Examine the Sample solution and Standard solution laterally against a black background.
Acceptance criteria:
Any opalescence in the Sample solution is not more intense than that in the Standard solution (200 ppm).
• Chloride and Sulfate, Sulfate  221
221 :
[Note—Prepare the Sample solution and the Control solution at the same time. ]
:
[Note—Prepare the Sample solution and the Control solution at the same time. ]
Barium chloride solution:
250 mg/mL
Sulfate standard solution (10 ppm SO4):
1.81 mg/mL of potassium sulfate in 30% alcohol (v/v). Just before use, dilute 1 mL of this solution with 30% alcohol (v/v) to 100 mL.
Standard solution:
Mix 3 mL of the Barium chloride solution and 4.5 mL of the Sulfate standard solution, and allow to stand for 1 min.
Sample stock solution:
50.0 mg/mL, heated to 60 . Cool to 10
. Cool to 10 , and filter.
, and filter.
Sample solution:
To 2.5 mL of the Standard solution add 15 mL of the Sample stock solution and 0.5 mL of 5 N acetic acid.
Control solution:
To 2.5 mL of the Standard solution add 15 mL of the Sulfate standard solution and 0.5 mL of 5 N acetic acid.
Analysis
Samples:
Sample solution and Control solution
Acceptance criteria:
After 5 min, any opalescence in the Sample solution is not more intense than that in the Control solution (200 ppm).
• Heavy Metals
Sodium sulfide solution:
Dissolve 5 g of sodium sulfide in 10 mL of water. Add 30 mL of glycerin.
Standard lead solution:
Prepare as directed for Special Reagents in Heavy Metals  231
231 .
.
Standard solution:
Transfer 1.0 mL of the Standard lead solution to a 10-mL volumetric flask. Add 1 mL of 50% acetic acid and 2 drops of 25% sodium hydroxide, and dilute with water to volume.
Sample solution:
Dissolve 5 g of Racemethionine by adding 5 mL of 16% hydrochloric acid and 5 mL of water. Adjust with 25% sodium hydroxide to a pH of 3.0–4.0. Dilute with water to 50 mL. Shake for approximately 15 min, and filter.
Analysis:
Add 1 drop of Sodium sulfide solution to 10 mL of the Sample solution, and add 1 drop of Sodium sulfide solution to 10 mL of the Standard solution. Let stand for 5 min. View downward over a white surface.
Acceptance criteria:
The color of the solution from the Sample solution is not darker than that of the solution from the Standard solution (NMT 10 ppm).
• Limit of Iron
Standard stock solution (125 ppm):
Dissolve 1.727 g of ferric ammonium sulfate [FeNH4(SO4)2·12H2O] in water. Add 50 mL of 10% hydrochloric acid, dilute with water to 1000 mL, and mix. Dilute 1 mL of this solution with water to 40 mL. Pipet 5 mL of this solution into a 200-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Standard solution:
Transfer 2 mL of the Standard stock solution to a 25-mL volumetric flask. Add 5 mL of 16% hydrochloric acid, 50 mg of ammonium persulfate, and 3 mL of 30% ammonium thiocyanate, and dilute with water to volume.
Sample solution:
Transfer 1 g of Racemethionine to a 25-mL volumetric flask. Add 5 mL of 16% hydrochloric acid, and dissolve. Add 50 mg of ammonium persulfate and 3 mL of 30% ammonium thiocyanate, and dilute with water to volume.
Blank:
Transfer 5 mL of 16% hydrochloric acid to a 25-mL volumetric flask. Add 50 mg of ammonium persulfate and 3 mL of 30% ammonium thiocyanate, and dilute with water to volume.
Spectrometric conditions
Mode:
UV-Vis
Analytical wavelength:
475 nm
Cell:
1 cm
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution, Sample solution, and Blank
Without delay, concomitantly determine the absorbances of each sample, correcting for the Blank.
Acceptance criteria:
The absorbance of the Sample solution is NMT that of the Standard solution (NMT 10 ppm).
• Limit of Ammonium
Standard solution A:
0.297 mg/mL of USP Ammonium Chloride RS. This solution contains 0.1 mg/mL or 100 ppm of NH4+.
Standard solution B:
0.297 µg/mL of USP Ammonium Chloride RS. This solution contains 0.1 µg/mL or 0.1 ppm of NH4+.
Standard solution C:
2.97 µg/mL of USP Ammonium Chloride RS. This solution contains 1.0 µg/mL or 1 ppm of NH4+.
Standard solution D:
29.7 µg/mL of USP Ammonium Chloride RS. This solution contains 10 µg/mL or 10 ppm of NH4+.
Sample solution:
10 mg/mL of Racemethionine
Electrode system:
Use an ammonia-specific,1 ion-indicating electrode connected to a pH meter capable of measuring potentials (see pH  791
791 ).
).
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution A, Standard solution B, Standard solution C, Standard solution D, and Sample solution
Add 100 mL of water to a 150-mL beaker, place the electrode in the beaker, stir, and measure the potential. Add 1 mL of 10 N sodium hydroxide. Stir, and measure the potential after stabilization. [Note—It may take about 5 min. ] The potential difference must be less than 20 mV.
Add 100.0 mL each of Standard solutions A, B, C, and D to four different 150-mL beakers. To each beaker, add 1 mL of 10 N sodium hydroxide. Place the ammonia electrode in the beaker, stir, and concomitantly measure the potential after stabilization. [Note—It may take about 5 min. ] Draw a calibration curve of the potential, in mV, versus, the quantity of ammonium (NH4+), in mg.
Add 100.0 mL of the Sample solution to a 150-mL beaker. Add 1 mL of 10 N sodium hydroxide. Adjust the pH, if necessary, with 10 N sodium hydroxide to a pH of NLT 11. Place the ammonia electrode in the beaker, stir, and measure the potential after stabilization. [Note—It may take about 5 min. ] Obtain the quantity of NH4+, in mg, in the 100 mL of the Sample solution based on the calibration curve.
Calculate the percentage of ammonium (NH4+), in the portion of Racemethionine taken:
Result = (C/W) × F
| C | = | = quantity of ammonium in the Sample solution from the standard curve (mg) |
| W | = | = weight of Racemethionine taken to prepare the Sample solution (mg) |
| F | = | = conversion factor to µg/g (ppm), 1 × 106 |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 200 ppm
Organic Impurities
• Procedure: Related Substances
Standard solution A:
0.40 mg/mL of USP Racemethionine RS
Standard solution B:
40 µg/mL of USP Racemethionine RS
Sample solution A:
20 mg/mL of Racemethionine
Sample solution B:
0.40 mg/mL of Racemethionine
Chromatographic system
Mode:
TLC
Adsorbent:
0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel mixture
Application volume:
5 µL
Developing solvent system:
Butyl alcohol, glacial acetic acid, and water (3:1:1)
Spray reagent:
2 mg/mL of ninhydrin in a mixture of butyl alcohol and 2 N acetic acid (95:5)
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution A, Standard solution B, Sample solution A, and Sample solution B
Develop over a path of 10 cm using the Developing solvent system. After air-drying the plate, spray with Spray reagent, and heat between 100 and 105
and 105 for 15 min. Examine the plate under white light.
for 15 min. Examine the plate under white light.
Acceptance criteria:
Any spot obtained from Sample solution A, apart from the principal spot, is not more intense than the spot obtained from Standard solution B (NMT 0.2%).
SPECIFIC TESTS
• pH  791
791 :
5.4–6.1, in a 20 mg/mL solution
:
5.4–6.1, in a 20 mg/mL solution
• Loss on Drying  731
731 :
Dry a sample at 105
:
Dry a sample at 105 for 3 h: it loses NMT 0.5% of its weight, determined on 1.000 g.
for 3 h: it loses NMT 0.5% of its weight, determined on 1.000 g.
• Transmittance
Sample solution:
10% of Racemethionine in 2 N hydrochloric acid, prepared by sonication
Analysis:
Determine the transmittance in a 1-cm cell at 430 nm with a suitable spectrophotometer.
Acceptance criteria:
Transmittance of NLT 0.98, corresponding to an absorbance of NMT about 0.009
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers, protected from light.
1
Orion 95-12 is suitable.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Robert H. Lafaver, M.S.
Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8335 |
(EXC2010) Monographs - Excipients |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 1939
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 36(5) Page 1236