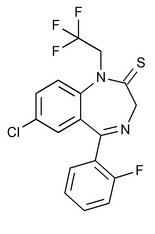
Quazepam
(kwaz' e pam).
2H-1,4-Benzodiazepine-2-thione, 7-chloro-5-(2-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-.
7-Chloro-5-(o-fluorophenyl)-1,3-dihydro-1-(2,2,2-trifluoroethyl)-2H-1,4-benzodiazepine-2-thione
» Quazepam contains not less than 98.5 percent and not more than 101.5 percent of C17H11ClF4N2S, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed containers.
Identification—
B:
The RF value of the principal spot in the chromatogram of the Test solution obtained in the test for Related compounds corresponds to that in the chromatogram of Standard solution A.
Melting range  741
741 :
between 146
:
between 146 and 151
and 151 , but the range between beginning and end of melting does not exceed 2
, but the range between beginning and end of melting does not exceed 2 .
.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 105
—
Dry it at 105 for 4 hours: it loses not more than 0.5% of its weight.
for 4 hours: it loses not more than 0.5% of its weight.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.2%.
:
not more than 0.2%.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
not more than 20 µg per g.
:
not more than 20 µg per g.
Related compounds—
Test solution—
Prepare a solution of Quazepam in methylene chloride containing 20 mg per mL.
Standard solution A—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Quazepam RS in methylene chloride to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 20 mg per mL.
Standard solution B—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Quazepam RS in methylene chloride to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.04 mg per mL (0.2%).
Standard solution C—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Quazepam Related Compound A RS in methylene chloride to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.2 mg per mL (1%).
Procedure—
Separately apply 5 µL of the Test solution and 5 µL of each of the Standard solutions to a thin-layer chromatographic plate (see Chromatography  621
621 ) coated with a 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel. Allow the spots to dry, and develop the chromatogram in a solvent system consisting of a mixture of cyclohexane, ethyl acetate, and ether (170:40:25) in a paper-lined tank until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the developing chamber, mark the solvent front, allow to air-dry, and examine the plate under short-wavelength UV light. Compare the intensity of the secondary spot in the chromatogram of the Test solution having the same RF value as that of the primary spot of Standard solution C: the spot is not larger or more intense than the principal spot in the chromatogram of Standard solution C. Compare the intensities of any additional secondary spots observed in the chromatogram of the Test solution with that of the principal spot in the chromatogram of Standard solution B: the sum of the intensities of the additional secondary spots obtained from the Test solution corresponds to not more than 0.2%.
) coated with a 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel. Allow the spots to dry, and develop the chromatogram in a solvent system consisting of a mixture of cyclohexane, ethyl acetate, and ether (170:40:25) in a paper-lined tank until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the developing chamber, mark the solvent front, allow to air-dry, and examine the plate under short-wavelength UV light. Compare the intensity of the secondary spot in the chromatogram of the Test solution having the same RF value as that of the primary spot of Standard solution C: the spot is not larger or more intense than the principal spot in the chromatogram of Standard solution C. Compare the intensities of any additional secondary spots observed in the chromatogram of the Test solution with that of the principal spot in the chromatogram of Standard solution B: the sum of the intensities of the additional secondary spots obtained from the Test solution corresponds to not more than 0.2%.
Assay—
Dissolve about 500 mg of Quazepam, accurately weighed, in 150 mL of acetic anhydride. Titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically, using a glass-calomel electrode system. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 38.68 mg of C17H11ClF4N2S.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Hariram Ramanathan, M.S.
Associate Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8313 |
(SM42010) Monographs - Small Molecules 4 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 4498