Psyllium Hemicellulose
(sil' ee um hem'' ee sel' ue lose).
DEFINITION
Psyllium Hemicellulose is the alkali soluble fraction of the husk from Plantago ovata Forssk. It consists of a combination of highly substituted arabinoxylan polysaccharides. These polysaccharides are linear chains of xylose units (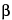 -(1®4)-xylan) to which are attached single units of arabinose and additional xylose. Rhamnose, galactose, glucose, and rhamnosyluronic acid residues are also present as minor constituents. It contains NLT 75.0% of dietary soluble fiber, calculated on the dried basis.
-(1®4)-xylan) to which are attached single units of arabinose and additional xylose. Rhamnose, galactose, glucose, and rhamnosyluronic acid residues are also present as minor constituents. It contains NLT 75.0% of dietary soluble fiber, calculated on the dried basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• A.
The powdered mucilage stains red with ruthenium red TS and lead acetate TS.
• B.
It meets the requirements in Specific Tests for Swell Volume.
COMPOSITION
• Content of Soluble Dietary Fiber
Alcohol solution:
Transfer 82.0 mL of alcohol to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Buffer solution A:
Dissolve 1.95 g of 2-(N-morpholino)-ethanesulfonic acid and 1.22 g of tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane in 170 mL of water. Adjust with 6 N sodium hydroxide to a pH of 8.2, and dilute with water to 200 mL. [Note—It is important to adjust the pH to 8.2 at 24 . If the Buffer solution temperature is 20
. If the Buffer solution temperature is 20 , adjust the pH to 8.3; if the temperature is 28
, adjust the pH to 8.3; if the temperature is 28 , adjust the pH to 8.1. For deviations at 20
, adjust the pH to 8.1. For deviations at 20 –28
–28 , adjust by interpolation. ]
, adjust by interpolation. ]
Acid solution:
Prepare 0.561 N hydrochloric acid by mixing 9.35 mL of 6 N hydrochloric acid in 70 mL of water. Dilute with water to 100.0 mL.
Buffer solution B:
Prepare a pH 6.0 phosphate buffer (see Reagents, Indicators, and Solutions—Buffer Solutions).
Protease solution:
Dissolve 5 mg of protease in 0.1 mL of Buffer solution B
Enzyme purity:
To ensure the absence of undesirable enzymatic activities and the presence of desirable enzymatic activities, proceed as directed for Sample solution and Analysis using the substrates listed in Table 1 in place of Psyllium Hemicellulose.
Table 1
| Substrate | Weight (g) |
Activity Tested |
|---|---|---|
| Pectin | 0.2 | Pectinase |
| Arabinogalactan | 0.2 | Hemicellulase |
| 0.2 | ||
| Wheat starch | 1.0 | amyloglucosidase |
| Corn starch | 1.0 | amyloglucosidase |
| Casein | 0.3 | Protease |
The enzyme preparation is suitable if more than 90% of the original weight of pectin, arabinogalactan, and 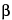 -glucan is recovered; NMT 2% of the original weight of casein and corn starch is recovered; and NMT 1% of the original weight of wheat starch is recovered. [Note—Test the enzyme purity of every new lot of enzyme and at 6-month intervals thereafter. ]
-glucan is recovered; NMT 2% of the original weight of casein and corn starch is recovered; and NMT 1% of the original weight of wheat starch is recovered. [Note—Test the enzyme purity of every new lot of enzyme and at 6-month intervals thereafter. ]
Blank solution:
Using two 400-mL tall-form beakers, appropriately labeled, proceed as directed for Analysis without Psyllium Hemicellulose.
Sample solution:
Weigh, in duplicate, approximately 0.2 g of Psyllium Hemicellulose, previously milled to a very fine powder. [Note—Duplicates should differ by less than 1 mg in weight. ] Transfer duplicate samples to appropriately labeled tall-form 400-mL beakers, and proceed as directed for Analysis.
Analysis:
Treat each solution in the following manner. Add 40 mL of Buffer solution A to the beaker. [Note—For the Sample solution, stir until the Psyllium Hemicellulose is completely dispersed. ]
Add 125 µL of heat-stable 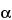 -amylase solution, and stir to ensure uniform mixing. Cover the beaker with aluminum foil, and incubate over a water bath maintained at 95
-amylase solution, and stir to ensure uniform mixing. Cover the beaker with aluminum foil, and incubate over a water bath maintained at 95 –100
–100 for 15 min, with continuous agitation. [Note—Start timing once the water bath temperature reaches 95
for 15 min, with continuous agitation. [Note—Start timing once the water bath temperature reaches 95 . A total time of 35 min is usually sufficient. ]
. A total time of 35 min is usually sufficient. ]
Remove the beaker from the water bath, and cool to 60 . Remove the aluminum foil, scrape any ring from inside the beaker, and disperse any gels in the bottom of the beaker with a spatula. Rinse the walls of the beaker and the spatula with 10 mL of water, collecting the rinsings in the beaker. Add 500 µL of Protease solution. Cover with aluminum foil, and incubate over a water bath maintained at 60 ± 3
. Remove the aluminum foil, scrape any ring from inside the beaker, and disperse any gels in the bottom of the beaker with a spatula. Rinse the walls of the beaker and the spatula with 10 mL of water, collecting the rinsings in the beaker. Add 500 µL of Protease solution. Cover with aluminum foil, and incubate over a water bath maintained at 60 ± 3 for 30 min with continuous agitation. [Note—Start timing when the bath temperature reaches 60
for 30 min with continuous agitation. [Note—Start timing when the bath temperature reaches 60 . ]
. ]
Remove the foil, and transfer 5 mL of Acid solution while stirring. Adjust, if necessary, with 1 N sodium hydroxide or 1 N hydrochloric acid to a pH of 4.28 ± 0.07 at 60 . [Note—It is important to adjust the pH to 4.28 while the solution in the beaker is maintained at 60
. [Note—It is important to adjust the pH to 4.28 while the solution in the beaker is maintained at 60 ; otherwise, the pH will increase at lower temperatures. ]
; otherwise, the pH will increase at lower temperatures. ]
Add 150 µL of amyloglucosidase solution while stirring. Cover with aluminum foil, and incubate over a water bath maintained at 60 ± 3 for 30 min with constant agitation. [Note—Start timing once the water bath reaches 60
for 30 min with constant agitation. [Note—Start timing once the water bath reaches 60 . ]
. ]
Transfer 40 mL of the beaker contents to a 50-mL centrifuge tube, and sonicate the tube contents for 3 min.1 Centrifuge at 10,000–14,000 rpm for 10 min. Carefully pour the supernatant into a labeled 600-mL tared beaker. Do not disturb any pellet in the bottom of the centrifuge tube. Add the remaining sample from the original 400-mL beaker into the centrifuge tube still containing the pellet. Rinse the 400-mL beaker with 15–20 mL of water, and add the rinsing to the 50-mL centrifuge tube. Centrifuge the sample at 10,000–14,000 rpm for 10 min. Carefully pour the supernatant into the 600-mL beaker containing the first supernatant. Add 390 mL (measured before heating) of alcohol at 60 to the 600-mL beaker. Cover the beaker, and allow to stand for at least 1 h to form a precipitate.
to the 600-mL beaker. Cover the beaker, and allow to stand for at least 1 h to form a precipitate.
Place 3 g of chromatographic siliceous earth into a clean air-dried crucible with a fritted disk. Heat the crucible containing chromatographic siliceous earth at 525 in a muffle furnace for at least 4 h. Cool. Pass deionized water through the crucible while applying constant suction. Rinse with acetone, and allow to air-dry. Store the crucible in a convection oven at 130
in a muffle furnace for at least 4 h. Cool. Pass deionized water through the crucible while applying constant suction. Rinse with acetone, and allow to air-dry. Store the crucible in a convection oven at 130 for at least 2 h before use. Weigh the prepared crucible to 0.1 mg before use. Wet the chromatographic siliceous earth in the crucible using a stream of Alcohol solution from a washing bottle, and apply suction to evenly distribute the chromatographic siliceous earth over the fritted disk. Maintaining the suction, transfer the supernatant and precipitate from the beaker to the crucible, and filter. Transfer any solid residue in the beaker with the aid of Alcohol solution. [Note—In some cases, gums may form during filtration, trapping liquid in the residue. If so, break the surface film with a spatula to improve filtration. ]
for at least 2 h before use. Weigh the prepared crucible to 0.1 mg before use. Wet the chromatographic siliceous earth in the crucible using a stream of Alcohol solution from a washing bottle, and apply suction to evenly distribute the chromatographic siliceous earth over the fritted disk. Maintaining the suction, transfer the supernatant and precipitate from the beaker to the crucible, and filter. Transfer any solid residue in the beaker with the aid of Alcohol solution. [Note—In some cases, gums may form during filtration, trapping liquid in the residue. If so, break the surface film with a spatula to improve filtration. ]
Wash the residue in the crucible sequentially with 30 mL of Alcohol solution, 20 mL of alcohol, and 20 mL of acetone. Dry the crucible containing the residue at 100 in a convection oven for at least 4 h, and cool to room temperature in a desiccator.
in a convection oven for at least 4 h, and cool to room temperature in a desiccator.
Determine the weight of the residue (R).
Use one of the duplicate residues from the Sample solution and one of the blank residues from the Blank solution to determine the protein content, in mg, by placing the residue in a 500-mL Kjeldahl flask, and proceeding as directed for Nitrogen Determination  461
461 , Method I. The protein content is determined by multiplying the content of nitrogen found by 6.25. Incinerate the residue from the remaining duplicate of the Sample solution and the Blank solution as directed for Articles of Botanical Origin
, Method I. The protein content is determined by multiplying the content of nitrogen found by 6.25. Incinerate the residue from the remaining duplicate of the Sample solution and the Blank solution as directed for Articles of Botanical Origin  561
561 , Total Ash at a reduced temperature of 525
, Total Ash at a reduced temperature of 525 , and determine the ash content as directed.
, and determine the ash content as directed.
Calculate the corrected average weight of the blank (B), in mg:
B = RB  PB
PB  AB
AB
| RB | = | = weight of the average blank residue for duplicate blank determinations (mg) |
| PB | = | = content found in the test for protein in the blank (mg) |
| AB | = | = content of ash found in the blank (mg) |
Calculate the percentage of soluble dietary fiber:
Result = [(RU  PU
PU  AU
AU  B)/WU] × 100
B)/WU] × 100
| RU | = | = weight of average residue for the duplicate Sample solution (mg) |
| PU | = | = content of protein found in the Psyllium Hemicellulose (mg) |
| AU | = | = content of ash found in the Psyllium Hemicellulose (mg) |
| B | = | = average weight of the blank as calculated above |
| WU | = | = average weight of the Psyllium Hemicellulose taken (mg) |
Acceptance criteria:
NLT 75.0% of dietary soluble fiber on the dried basis
CONTAMINANTS
• Heavy Metals, Method II  231
231 :
NMT 10 µg/g
:
NMT 10 µg/g
• Limit of Alcohol
Internal standard solution:
n-Propyl alcohol and water (1:99)
Standard stock solution:
5.0 mL of absolute alcohol at 20 ± 2 , diluted with water to 500.0 mL
, diluted with water to 500.0 mL
Standard solution:
10.0 mL of Standard stock solution and 10.0 mL of Internal standard solution, diluted with water to 100.0 mL
Sample solution:
0.5 g of Psyllium Hemicellulose in 90 mL of water. Stir rapidly for 3 h using a magnetic stirrer. Add 10.0 mL of the Internal standard solution. Pass the Sample solution through a filter having a 0.45-µm pore size.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
GC
Detector:
Flame ionization
Column:
0.53-mm × 30-m fused silica analytical; coated with 3.0-µm G43 stationary phase. [Note—A 0.53-mm × 2-m fused silica guard column may be used. ]
Temperature:
See Table 2.
Table 2
| Initial Temperature ( |
Temperature Ramp ( |
Final Temperature ( |
Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | 0 | 40 | 5 |
| 40 | 10 | 230 | 3 |
Injector:
250
Detector:
300
Carrier gas:
Helium
Flow rate:
4 mL/min
Injection size:
0.5 µL
Injection type:
Split flow ratio, 10:1
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 2.0%, for replicate injections
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of alcohol in the portion of Psyllium Hemicellulose taken:
Result = (RU/RS) × CS × (V/W) × 100
| RU | = | = ratio of the peak response of alcohol/peak response of n-propyl alcohol from the Sample solution |
| RS | = | = ratio of the peak response of alcohol/peak response of n-propyl alcohol from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of alcohol in the Standard stock solution (mg/mL) |
| V | = | volume of the Standard stock solution (mL) |
| W | = | weight of Psyllium Hemicellulose taken to prepare the Sample solution (mg) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 12.0% (w/w)
• Microbial Enumeration Tests  61
61 and Tests for Specified Microorganisms
and Tests for Specified Microorganisms  62
62 :
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 103 cfu/g, and the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 102 cfu/g. It meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli.
:
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 103 cfu/g, and the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 102 cfu/g. It meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli.
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Swell Volume
Sample:
0.50 g of Psyllium Hemicellulose
Analysis:
Add the Sample to a glass-stoppered, 100-mL graduated mixing cylinder. To avoid material clumping, hold the cylinder at a 45 angle, and gently rotate it while using a wash bottle to forcefully add 30 mL of water. Add water to bring the total volume to 100 mL, and cap the cylinder. Invert the cylinder several times until a uniform suspension is achieved, and allow to stand. Gently invert the cylinder several times again at 4–8 h after the initial Sample solution preparation, and allow to stand. Allow the gel to settle for 16 h. Determine the volume of the gel.
angle, and gently rotate it while using a wash bottle to forcefully add 30 mL of water. Add water to bring the total volume to 100 mL, and cap the cylinder. Invert the cylinder several times until a uniform suspension is achieved, and allow to stand. Gently invert the cylinder several times again at 4–8 h after the initial Sample solution preparation, and allow to stand. Allow the gel to settle for 16 h. Determine the volume of the gel.
Acceptance criteria:
NLT 80 mL/g of Psyllium Hemicellulose
• Total Acidity:
Transfer 40 mL of the supernatant as obtained in the test for Swell Volume without disturbing the gel. Titrate with 0.03 N sodium hydroxide, using 1 mL of phenolphthalein TS as indicator.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 1.8 mL of 0.03 N sodium hydroxide is consumed
• Loss on Drying  731
731 :
Dry a sample at 105
:
Dry a sample at 105 for 3 h: it loses NMT 12.0% of its weight.
for 3 h: it loses NMT 12.0% of its weight.
• Articles of Botanical Origin, Total Ash  561
561 :
NMT 5.0%
:
NMT 5.0%
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight containers. Store at 25 , excursions permitted between 15
, excursions permitted between 15 and 30
and 30 .
.
1
A suitable sonicator is Sonifier 250 (or equivalent), equipped with a 12-mm tip, from Branson Ultrasonic Corp., Danbury, CT, in which an output control value of 3 and a cycle time of 75% generate a power output of 43 W.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Maged H. Sharaf, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8318 |
(DS2010) Monographs - Dietary Supplements |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology |
USP35–NF30 Page 4481
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 30(1) Page 173