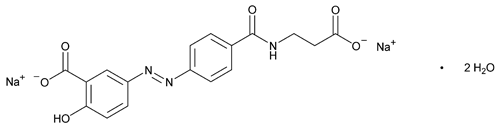
Balsalazide Disodium
C17H13N3Na2O6·2H2O 437.31
Benzoic acid, 5-[[4-[[(2-carboxyethyl)amino]carbonyl]phenyl]azo]-2-hydroxy-, disodium salt, dihydrate, (E)-;
(E)-5-[[p-[(2-Carboxyethyl)carbamoyl]phenyl]azo]salicylic acid, disodium salt, dihydrate

 [150399-21-6].
[150399-21-6].
(bal sal' a zide dye soe' dee um).
C17H13N3Na2O6·2H2O 437.31
Benzoic acid, 5-[[4-[[(2-carboxyethyl)amino]carbonyl]phenyl]azo]-2-hydroxy-, disodium salt, dihydrate, (E)-;
(E)-5-[[p-[(2-Carboxyethyl)carbamoyl]phenyl]azo]salicylic acid, disodium salt, dihydrate
DEFINITION
Balsalazide Disodium contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of C17H13N3Na2O6·2H2O, calculated on the as-is basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• B. Ultraviolet Absorption  197U
197U
Sample solution:
10 µg/mL in water
ASSAY
• Procedure
Sample:
219 mg
Analysis:
Add 80 mL of glacial acetic acid to the Sample, sonicate to dissolve, and titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction (see Titrimetry  541
541 ). Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 21.87 mg of C17H13N3Na2O6·2H2O.
). Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 21.87 mg of C17H13N3Na2O6·2H2O.
Acceptance criteria:
98.0%–102.0% on the as-is basis
IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
• Heavy Metals, Method II  231
231 :
NMT 20 ppm
:
NMT 20 ppm
Organic Impurities
[Note—On the basis of the synthetic route, perform either Procedure 1 or Procedure 2. Procedure 2 is recommended when impurities 1, 2, and 3 listed in Impurity Table 2 may be present. ]
• Procedure 1
Solution A:
Dissolve 2.7 g of monobasic potassium phosphate in 1000 mL of water, and adjust with 10% potassium hydroxide solution to a pH of 6.00 ± 0.1.
Diluent:
Use Solution A.
Solution B:
Use acetonitrile.
Standard solution:
0.5 µg/mL of USP Balsalazide Disodium RS, 0.5 µg/mL of USP Balsalazide Related Compound A RS, 0.5 µg/mL of USP Balsalazide Related Compound B RS, and 0.5 µg/mL of USP Salicylic Acid RS in Diluent. If needed, a small amount of acetonitrile may be added to facilitate dissolution. [Note—USP Balsalazide Related Compound A RS is the disodium salt of (E)-5-[(p-carboxyphenyl)azo]-2-salicylic acid. Use the correction factor stated on the label of the USP Reference Standard to calculate the concentration, as appropriate. ]
Sample solution:
1 mg/mL of Balsalazide Disodium in Diluent
Mobile phase:
See the gradient table below.
| Time (min) |
Solution A (%) |
Solution B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 90 | 10 |
| 4 | 90 | 10 |
| 40 | 75 | 25 |
| 47 | 75 | 25 |
| 55 | 50 | 50 |
| 60 | 50 | 50 |
| 60.1 | 90 | 10 |
| 70 | 90 | 10 |
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 238 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Column temperature:
45
Flow rate:
1 mL/min
Injection size:
30 µL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 5 between balsalazide and balsalazide related compound B
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 5% for each peak
Tailing factor:
NMT 1.8 for the balsalazide peak
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each individual impurity in the portion of Balsalazide Disodium taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response for each individual impurity from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response for the corresponding impurity from the Standard solution. [Note—For unspecified impurities, rS is the peak response for the balsalazide peak from the Standard solution. ] |
| CS | = | = concentration of the corresponding impurity in the Standard solution (mg/mL). [Note—For unspecified impurities, CS is the concentration of balsalazide disodium in the Standard solution. ] |
| CU | = | = concentration of Balsalazide Disodium in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria
Individual impurities:
See Impurity Table 1.
Reporting level for impurities:
0.03%
Total impurities:
NMT 1.0%
Impurity Table 1
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Salicylic acid | 0.37 | 0.05 |
| Balsalazide related compound Aa | 0.70 | 0.05 |
| Balsalazide | 1.00 | — |
| Balsalazide related compound Bb | 1.2 | 0.05 |
| Any other individual unspecified impurity | — | 0.05 |
|
a
(E)-5-[(p-Carboxyphenyl)azo]-2-salicylic acid.
b
(E)-5-({m-[(2-Carboxyethyl)carbamoyl]phenyl}azo)-2-salicylic acid.
|
||
• Procedure 2
Solution A:
Prepare 50 mM monobasic potassium phosphate buffer as follows: Dissolve 6.8 g of monobasic potassium phosphate in 1000 mL of water, and adjust with 2 N potassium hydroxide solution to a pH of 6.8–7.0. [Note—To ensure proper identification of impurity 1, the pH must be maintained between 6.8 and 7.0. ]
Solution B:
Acetonitrile, methanol and Solution A (5:1:14)
Solution C:
Acetonitrile, methanol and Solution A (9:1:10)
Diluent:
Use Solution B.
Mobile phase:
See the gradient table below.
| Time (min) |
Solution A (%) |
Solution B (%) |
Solution C (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 37 | 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 60 | 0 | 0 | 100 |
| 75 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
| 85 | 100 | 0 | 0 |
Standard solution:
0.075 mg/mL of USP Balsalazide Disodium RS in Diluent. [Note—Use sonication to dissolve. ]
Sensitivity solution:
0.375 µg/mL in Diluent, from Standard solution
System suitability solution:
1.5 mg/mL of USP Balsalazide Disodium RS and 1.5 µg/mL of USP Balsalazide Related Compound A RS in Diluent
Sample solution:
1.5 mg/mL of Balsalazide Disodium in Diluent. [Note—Use sonication to dissolve. ]
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 300 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 15-cm; 3-µm packing L1
Column temperature:
25 –27
–27 . [Note—To ensure proper identification of impurity 1, the column temperature must be maintained between 25
. [Note—To ensure proper identification of impurity 1, the column temperature must be maintained between 25 and 27
and 27 . ]
. ]
Flow rate:
1 mL/min
Injection size:
10 µL
System suitability
Samples:
Standard solution, Sensitivity solution, and System suitability solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 8.5 between balsalazide related compound A and balsalazide, from the System suitability solution
Tailing factor:
NMT 3.4 for the balsalazide peak, from the System suitability solution
Signal-to-noise ratio:
NLT 10, from the Sensitivity solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 2.0%, from the Standard solution
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each individual impurity in the portion of Balsalazide Disodium taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) (1/F) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response for each individual impurity from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response for balsalazide from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Balsalazide Disodium RS in the Standard solution |
| CU | = | = concentration of Balsalazide Disodium in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
| F | = | = relative response factor (see Impurity Table 2) |
Acceptance criteria
Individual impurities:
See Impurity Table 2.
Reporting level for impurities:
0.03%
Total impurities:
NMT 0.50%
Impurity Table 2
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
Relative Response Factor |
Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| N-(4-Aminobenzoyl)- |
0.29 | 1.8 | 0.05 |
| Salicylic acid | 0.55 | 1.4 | 0.05 |
| Balsalazide related compound Ab | 0.88 | 1.4 | 0.05 |
| Impurity 1c | 0.91 | 1.9 | 0.05 |
| Impurity 2d | 0.92 | 1.4 | 0.05 |
| Impurity 3e | 0.94 | 0.83 | 0.05 |
| Balsalazide | 1.00 | — | |
| Impurity 4f | 1.35 | 2.1 | 0.05 |
| Impurity 5g | 1.77 | 0.91 | 0.05 |
| Any other individual unspecified impurity | — | — | 0.05 |
|
a
This impurity may be present as two peaks. Use the sum of the two peaks to determine compliance.
b
(E)-5-[(p-Carboxyphenyl)azo]-2-salicylic acid.
c
(E,E)-3,5-di-[4-(2-Carboxyethylcarbamoyl) phenylazo]-salicylic acid.
d
(E)-3-[4-(2-Carboxyethylcarbamoyl) phenylazo]-salicylic acid.
e
(E,E)-5-{{2-[4-(2-Carboxyethylcarbamoyl)phenylazo]-4-[2-carboxyethyl-carbamoyl]}phenylazo}-salicylic acid.
f
(E)-2-[4-(2-Carboxyethylcarbamoyl)phenoxy]-5-{[4-(2-carboxyethyl-carbamoyl)]phenylazo}-benzoic acid
g
(E)-2-Hydroxy-5-[[4-[[(3-isopropoxy-3-oxopropyl)amino]carbonyl]phenyl]azo]benzoic acid
|
|||
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Water Determination, Method Ia  921
921 :
7.8%–9.0%
:
7.8%–9.0%
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight containers. Store at controlled room temperature.
• Labeling:
If a test for Organic Impurities other than Test 1 is used, the labeling states the test with which the article complies.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Balsalazide Related Compound A RS
(E)-5-[(p-Carboxyphenyl)azo]-2-salicylic acid, disodium salt.
C14H8N2O5Na2 330.12
(E)-5-[(p-Carboxyphenyl)azo]-2-salicylic acid, disodium salt.
C14H8N2O5Na2 330.12
USP Balsalazide Related Compound B RS
(E)-5-({m-[(2-Carboxyethyl)carbamoyl]phenyl}azo)-2-salicylic acid.
C17H15N3O6 357.17
(E)-5-({m-[(2-Carboxyethyl)carbamoyl]phenyl}azo)-2-salicylic acid.
C17H15N3O6 357.17
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Elena Gonikberg, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8251 |
(SM32010) Monographs - Small Molecules 3 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 2302
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 35(4) Page 830