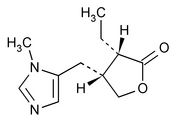
Pilocarpine
(pye'' loe kar' peen).
2(3H)-Furanone, 3-ethyldihydro-4-[(1-methyl-1H-imidazol-5-yl)methyl]-, (3S-cis)-.
Pilocarpine
» Pilocarpine contains not less than 95.0 percent and not more than 100.5 percent of pilocarpine (C11H16N2O2), calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers, in a cold place.
Identification—
Solution:
20 µg per mL.
Medium:
water.
Specific rotation  781S
781S :
between +102
:
between +102 and +107
and +107 .
.
Test solution:
20 mg per mL, in pH 6.0 phosphate buffer.
Refractive index  831
831 :
between 1.5170 and 1.5210 at 25
:
between 1.5170 and 1.5210 at 25 , determined in a liquid specimen. If crystals are present, first warm to about 40
, determined in a liquid specimen. If crystals are present, first warm to about 40 .
.
Water, Method I  921
921 :
not more than 0.5%.
:
not more than 0.5%.
Chloride—
Standard chloride solution—
Transfer 165 mg of sodium chloride to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in and dilute with water to volume. Transfer 25.0 mL of this solution to a 1000-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. This solution contains 25 µg of chloride per mL.
Test solution—
Transfer about 1.0 g of Pilocarpine, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume.
Procedure—
Transfer 5.0 mL of the Test solution to a test tube, add 0.6 mL of diluted nitric acid and 0.3 mL of silver nitrate TS: any opalescence produced is not greater than that produced by an identically treated solution containing 5.0 mL of the Standard chloride solution (0.25%).
Sulfate—
Standard sulfate solution—
Dissolve 148 mg of anhydrous sodium sulfate in water, and dilute with water to 100 mL. Dilute 10.0 mL of this solution with water to 1000 mL. This solution contains 10 µg of sulfate per mL.
Procedure—
To about 1 g of Pilocarpine in a test tube add 1 mL of 6 N hydrochloric acid and 4 mL of water, and mix. For the control, transfer 4.0 mL of Standard sulfate solution to a test tube, add 1 mL of 6 N hydrochloric acid, and mix. Adjust both solutions with pH indicator paper by the dropwise addition of 3 N hydrochloric acid or 6 N ammonium hydroxide, if necessary, to a pH of between 2 and 3. Add water to maintain the same volume in the control and test specimen tubes. To each tube add 1 mL of barium chloride TS, and mix: any turbidity produced in the specimen tube after 10 minutes' standing is not greater than that produced in the control (0.004%).
Limit of nitrate—
Standard preparation—
Prepare a solution of USP Pilocarpine Nitrate RS to contain 43 µg per mL. This solution contains the equivalent of 10 µg of nitrate ion per mL.
Test preparation—
Prepare a solution of Pilocarpine to contain 200 mg per mL.
Procedure—
Transfer 0.5-mL portions of the Test preparation and of the Standard preparation, respectively, to separate test tubes, and to each tube add 1 drop of a 1 in 100 solution of sulfanilic acid in 5 N acetic acid and 1 drop of a 3 in 1000 solution of N-(1-naphthyl)ethylenediamine dihydrochloride in 5 N acetic acid. Adjust the Standard preparation and the Test preparation with pH indicator paper by the dropwise addition of 3 N hydrochloric acid or 1 N ammonium hydroxide, if necessary to a pH of between 2 and 3. To each solution add a few granules of acid-washed, nitrate-free zinc. Heat the test tubes in a water bath at a temperature of about 32 . Allow 5 minutes for the development of a pink color: any pink color observed in the Test preparation is not greater than that observed in the Standard preparation (0.005%).
. Allow 5 minutes for the development of a pink color: any pink color observed in the Test preparation is not greater than that observed in the Standard preparation (0.005%).
Related compounds—
Buffer solution
, Mobile phase, System suitability preparation, and Chromatographic system—Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Standard solution—
Prepare a solution in water of isopilocarpine nitrate to contain 1.5 µg per mL.
Test preparation—
Prepare as directed for Assay preparation in the Assay.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 40 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for all the peaks. Calculate the percentage of isopilocarpine in the portion of Pilocarpine taken by the formula:
(208.26 / 271.27)50(C / W)(rU / rS)
in which 208.26 and 271.27 are the molecular weights of pilocarpine and isopilocarpine nitrate, respectively, C is the concentration, in µg per mL, of isopilocarpine nitrate in the Standard solution, W is the weight, in mg, of Pilocarpine taken, and rU and rS are the peak responses due to isopilocarpine in the Test preparation and the Standard solution, respectively: not more than 2% of isopilocarpine is found. Calculate the percentage of all other impurities from the chromatogram of the Test preparation taken by the formula:
(208.26 / 271.27)50(C / W)(ri / rs)
in which ri is the peak response due to the impurity: no one impurity corresponding to one of the four peaks in the System suitability preparation exceeds 3%; no other individual impurity exceeds 0.5%. The sum total of all impurities, including isopilocarpine, is not more than 5.0%.
Assay—
Buffer solution—
Transfer 13.5 mL of phosphoric acid to a 1-liter beaker containing 700 mL of water. Add 3 mL of triethylamine, and dilute with water to 1000 mL. Adjust with 20% sodium hydroxide to a pH of 3.0.
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of Buffer solution and methanol (98:2). Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ). [note—Do not store this Mobile phase for more than 2 days. ]
). [note—Do not store this Mobile phase for more than 2 days. ]
Standard preparation—
Prepare a solution in water having an accurately known concentration of about 40 µg of USP Pilocarpine Nitrate RS per mL. [note—Use this solution within 24 hours of its preparation. ]
Assay preparation—
Transfer an accurately weighed quantity of about 15 mg of Pilocarpine to a 500-mL volumetric flask. Dilute with water to volume, and mix. [note—Use this solution within 24 hours of its preparation. ]
System suitability preparation—
Transfer accurately weighed quantities of about 30 mg each of pilocarpine hydrochloride and isopilocarpine nitrate to a 50-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Transfer 25 mL of this solution to a suitable flask, add 5 mL of 1 N sodium hydroxide, and reflux for 1 hour. Cool, and adjust the solution with 0.25 M phosphoric acid to a pH of 7.0. Quantitatively transfer this solution to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Dilute the remaining original solution with water to volume, and mix. Add 1 mL each of the refluxed and unrefluxed solutions to a 10-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system
(see Chromatography  621
621 )—The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 215-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 12.5-cm column that contains 3-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.0 mL per minute. Chromatograph replicate injections of the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation is not more than 2.0%. Chromatograph the System suitability preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: four peaks are observed; the resolution, R, between two adjacent peaks is not less than 1.2, the column efficiency determined for the pilocarpine peak is not less than 1500 theoretical plates, and the tailing factor, T, for the pilocarpine peak is not greater than 1.5. The relative retention times for the major peaks are about 0.67 for isopilocarpine, 0.76 for pilocarpine, 0.85 for pilocarpic acid, and 1.0 for isopilocarpic acid.
)—The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 215-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 12.5-cm column that contains 3-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.0 mL per minute. Chromatograph replicate injections of the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation is not more than 2.0%. Chromatograph the System suitability preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: four peaks are observed; the resolution, R, between two adjacent peaks is not less than 1.2, the column efficiency determined for the pilocarpine peak is not less than 1500 theoretical plates, and the tailing factor, T, for the pilocarpine peak is not greater than 1.5. The relative retention times for the major peaks are about 0.67 for isopilocarpine, 0.76 for pilocarpine, 0.85 for pilocarpic acid, and 1.0 for isopilocarpic acid.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 40 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for all the peaks. Calculate the quantity, in mg, of pilocarpine (C11H16N2O2) in the portion of Pilocarpine taken by the formula:
(208.26 / 271.27)500C(rU / rS)
in which 208.26 and 271.27 are the molecular weights of pilocarpine and pilocarpine nitrate, respectively, C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Pilocarpine Nitrate RS in the Standard preparation, and rU and rS are the peak responses for pilocarpine obtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Feiwen Mao, M.S.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8320 |
(SM32010) Monographs - Small Molecules 3 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 4320