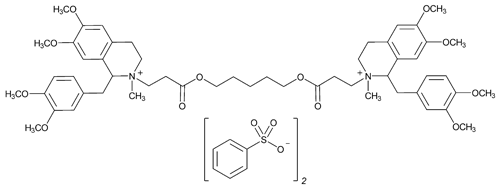
Atracurium Besylate
(a'' tra kure' ee um bes' i late).
C65H82N2O18S2




 1243.48
1243.48
Isoquinolinium, 2,2¢-[1,5-pentanediylbis[oxy(3-oxo-3,1-propanediyl)]]bis[1-[(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-dimethoxy-2-methyl-, dibenzenesulfonate.
2-(2-Carboxyethyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-dimethoxy-2-methyl-1-veratrylisoquinolinium benzenesulfonate, pentamethylene ester

 [64228-81-5].
[64228-81-5].
Isoquinolinium, 2,2¢-[1,5-pentanediylbis[oxy(3-oxo-3,1-propanediyl)]]bis[1-[(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)methyl]-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-dimethoxy-2-methyl-, dibenzenesulfonate.
2-(2-Carboxyethyl)-1,2,3,4-tetrahydro-6,7-dimethoxy-2-methyl-1-veratrylisoquinolinium benzenesulfonate, pentamethylene ester
» Atracurium Besylate contains not less than 96.0 percent and not more than 102.0 percent of C65H82N2O18S2, calculated on the anhydrous basis. It contains not less than 5.0 percent and not more than 6.5 percent of the trans-trans isomer, not less than 34.5 percent and not more than 38.5 percent of the cis-trans isomer, and not less than 55.0 percent and not more than 60.0 percent of the cis-cis isomer.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers, in a cold place. [note—Atracurium Besylate is unstable at room temperature. ]
Identification—
A:
Infrared Absorption  197K
197K .
.
B:
The retention times of the three main isomeric peaks in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation correspond to those in the chromatogram of the Standard preparation, as obtained in the Assay.
Water, Method I  921
921 :
not more than 5.0%.
:
not more than 5.0%.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.2%.
:
not more than 0.2%.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
20 µg per g.
:
20 µg per g.
Limit of methyl benzenesulfonate—
Buffer solution, Solution A, Solution B, and Mobile phase—
Prepare as directed in the Assay.
Standard solution—
Prepare a solution of methyl benzenesulfonate in acetonitrile having a known concentration of about 0.2 mg per mL. Quantitatively dilute a portion of this solution with Solution A to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 1 µg per mL.
Test solution—
Transfer about 100 mg of Atracurium Besylate, accurately weighed, to a 10-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with Solution A to volume, and mix.
Resolution solution—
Transfer 1 mL of the Test solution and 5 mL of a solution containing 0.2 mg of methyl benzenesulfonate per mL acetonitrile to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with Solution A to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 217-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains base-deactivated packing L1. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 217-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains base-deactivated packing L1. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
Chromatograph the Resolution solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between the trans-trans isomer and methyl benzenesulfonate is not less than 12.0. Chromatograph duplicate injections of the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the responses for duplicate injections do not differ from each other by more than 12%.
| Time (minutes) |
Solution A
(%) |
Solution B
(%) |
Elution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 80 | 20 | equilibration |
| 0–5 | 80 | 20 | isocratic |
| 5–15 | 80®75 | 20®25 | linear gradient |
| 15–25 | 75 | 25 | isocratic |
| 25–30 | 75®55 | 25®45 | linear gradient |
| 30–38 | 55®0 | 45®100 | linear gradient |
| 38–45 | 0 | 100 | isocratic |
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 100 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the methyl benzenesulfonate peaks: the peak response obtained from the Test solution is not greater than that obtained from the Standard solution. Not more than 0.01% of methyl benzenesulfonate is found.
Limit of toluene—
Standard solution—
Prepare a solution in organic-free water (see Residual Solvents  467
467 ) containing 100 µg of toluene per mL.
) containing 100 µg of toluene per mL.
Test solution—
Dissolve in organic-free water (see Residual Solvents  467
467 ) an accurately weighed portion of the material to be tested to obtain a final solution having a known concentration of about 20 mg of the test material per mL.
) an accurately weighed portion of the material to be tested to obtain a final solution having a known concentration of about 20 mg of the test material per mL.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector, a 0.53-mm × 30-m fused silica analytical column coated with a 5-µm chemically cross-linked G27 stationary phase and a 0.53-mm × 5-m silica guard column deactivated with phenylmethyl siloxane. The carrier gas is helium with a linear velocity of about 35 cm per second. [note—When a makeup gas is used, nitrogen is recommended. ] The injection port temperature and the detector temperature are maintained at 70
)—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector, a 0.53-mm × 30-m fused silica analytical column coated with a 5-µm chemically cross-linked G27 stationary phase and a 0.53-mm × 5-m silica guard column deactivated with phenylmethyl siloxane. The carrier gas is helium with a linear velocity of about 35 cm per second. [note—When a makeup gas is used, nitrogen is recommended. ] The injection port temperature and the detector temperature are maintained at 70 and 260
and 260 , respectively. The column temperature is programmed as follows. Initially, the column temperature is maintained at 35
, respectively. The column temperature is programmed as follows. Initially, the column temperature is maintained at 35 for 5 minutes, then increased at a rate of 8
for 5 minutes, then increased at a rate of 8 per minute to 175
per minute to 175 , followed by an increase at a rate of 35
, followed by an increase at a rate of 35 per minute to 260
per minute to 260 , and maintained at 260
, and maintained at 260 for at least 16 minutes. Inject the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation of the toluene peak from replicate injections is not more than 15%.
for at least 16 minutes. Inject the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation of the toluene peak from replicate injections is not more than 15%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 1 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks: the toluene peak from the Test solution is not greater than the toluene peak obtained from the Standard solution. Not more than 0.5% of toluene is found.
Chromatographic purity—
Buffer solution, Solution A, Solution B, and Mobile phase—
Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Standard solution—
Transfer 1.0 mL of the Standard preparation, prepared as directed in the Assay, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with Solution A to volume, and mix.
Test solution—
Use the Assay preparation.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
Prepare as directed in the Assay. Chromatograph the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the responses of the cis-cis isomers from not fewer than two injections do not differ by more than 10%.
)—
Prepare as directed in the Assay. Chromatograph the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the responses of the cis-cis isomers from not fewer than two injections do not differ by more than 10%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure all of the peak responses, except the three main isomeric peaks. Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Atracurium Besylate taken by the formula:
10,000(1/F)(C/W)(ri / rS)
in which F is the relative response factor of the impurity peak, which is 1.9 for laudanosine and 1.0 for all other unidentified impurities; C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of the cis-cis isomer in the Standard solution; W is the weight, in mg, of Atracurium Besylate taken to prepare the Test solution; ri is the peak response for each impurity obtained from the Test solution; and rS is the peak response for the cis-cis isomer obtained from the Standard solution: not more than 0.5% of laudanosine is found, not more than 1.0% of any other individual impurity is found, and not more than 3.5% of total impurities is found. [note—For identification purposes, the relative retention time for laudanosine is about 0.3. ]
Assay—
Buffer solution—
Transfer about 10.2 g of monobasic potassium phosphate to a 1000-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in about 950 mL of water. While stirring, adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 3.1, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Solution A—
Prepare a mixture of Buffer solution, acetonitrile, and methanol (75:20:5).
Solution B—
Prepare a mixture of Buffer solution, methanol, and acetonitrile (50:30:20).
Mobile phase—
Use variable mixtures of Solution A and Solution B as directed for Chromatographic system. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Standard preparation—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Atracurium Besylate RS in Solution A to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 1.0 mg per mL.
Assay preparation—
Transfer about 100 mg of Atracurium Besylate, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with Solution A to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 280-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains base-deactivated packing L1. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 280-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains base-deactivated packing L1. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between the trans-trans isomer and the cis-trans isomer and between the cis-trans isomer and the cis-cis isomer is not less than 1.1; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%. [note—For identification purposes, the relative retention times are about 0.8, 0.9, and 1.0 for the trans-trans isomer, the cis-trans isomer, and the cis-cis isomer, respectively. ]
| Time (minutes) |
Solution A
(%) |
Solution B
(%) |
Elution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | 80 | 20 | equilibration |
| 0–5 | 80 | 20 | isocratic |
| 5–15 | 80®40 | 20®60 | linear gradient |
| 15–25 | 40 | 60 | isocratic |
| 25–30 | 40®0 | 60®100 | linear gradient |
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the three isomeric peaks. Calculate the quantity, in mg, of C65H82N2O18S2 in the portion of Atracurium Besylate taken by the formula:
100C(rU / rS)
in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Atracurium Besylate RS in the Standard preparation; and rU and rS are the sums of the peak responses for the trans-trans isomer, the trans-cis isomer, and the cis-cis isomer obtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Ravi Ravichandran, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8330 |
(SM42010) Monographs - Small Molecules 4 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 2267
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 37(4)