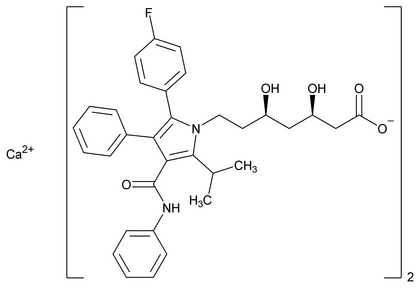
Atorvastatin Calcium
C66H68CaF2N4O10·3H2O 1209.42
C66H68CaF2N4O10 1155.34
1H-Pyrrole-1-heptanoic acid, 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-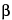 ,
,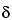 -dihydroxy-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-[(phenylamino)carbonyl]-, calcium salt (2:1), trihydrate [R-(R*,R*)]-;
-dihydroxy-5-(1-methylethyl)-3-phenyl-4-[(phenylamino)carbonyl]-, calcium salt (2:1), trihydrate [R-(R*,R*)]-;
Calcium (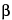 R,
R,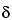 R)-2-(p-fluorophenyl)-
R)-2-(p-fluorophenyl)-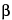 ,
,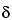 -dihydroxy-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)pyrrole-1-heptanoate (1:2), trihydrate
-dihydroxy-5-isopropyl-3-phenyl-4-(phenylcarbamoyl)pyrrole-1-heptanoate (1:2), trihydrate


 [344423-98-9].
[344423-98-9].
Anhydrous

 [134523-03-8].
[134523-03-8].
(a tor'' va stat' in kal' see um).
C66H68CaF2N4O10·3H2O 1209.42
C66H68CaF2N4O10 1155.34
1H-Pyrrole-1-heptanoic acid, 2-(4-fluorophenyl)-
Calcium (
Anhydrous
DEFINITION
Atorvastatin Calcium contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of C66H68 CaF2N4O10, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Infrared Absorption  197K
197K
• B. Calcium
Diluent:
Methanol, water, and hydrochloric acid (75:25:2)
Blank:
Diluent
Sample solution:
0.05 mg/mL of Atorvastatin Calcium in Diluent
Analysis
Samples:
Sample solution and Blank
Spectrometric conditions
Mode:
Atomic absorption spectrophotometry
Analytical wavelength:
Calcium emission line at 422.7 nm
Flame:
Air–acetylene
Acceptance criteria:
The Sample solution exhibits a significant absorption at the calcium emission line at 422.7 nm.
ASSAY
• Procedure
Buffer:
3.9 g/L of ammonium acetate in water. Adjust with glacial acetic acid to a pH of 5.0 ± 0.1.
Solution A:
Acetonitrile, stabilizer-free tetrahydrofuran, and Buffer (21:12:67)
Solution B:
Acetonitrile, stabilizer-free tetrahydrofuran, and Buffer (61:12:27)
Diluent:
N,N-dimethylformamide
Mobile phase:
See the gradient table below.
[Note—If necessary, adjust the Mobile phase by increasing or decreasing the percentage of acetonitrile or the pH of the ammonium acetate solution to achieve a retention time of 26–34 min for the atorvastatin peak. ]
| Time (min) |
Solution A (%) |
Solution B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 40 | 100 | 0 |
| 70 | 20 | 80 |
| 85 | 0 | 100 |
| 100 | 0 | 100 |
| 105 | 100 | 0 |
| 115 | 100 | 0 |
System suitability solution:
0.05 mg/mL of USP Atorvastatin Calcium RS and 0.06 mg/mL of USP Atorvastatin Related Compound B RS in Diluent
Standard solution:
0.4 mg/mL of USP Atorvastatin Calcium RS in Diluent. [Note—Use sonication if necessary ]
Sample solution:
0.4 mg/mL of Atorvastatin Calcium in Diluent. [Note—Use sonication if necessary. ]
Chromatographic system
[Note—If significant fronting of the peaks for atorvastatin related compound B and atorvastatin is observed, use the following Diluent to prepare the Sample solution, Standard solution, and System suitability solution: acetonitrile, stabilizer-free tetrahydrofuran, and water (1:1:2). ]
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 244 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 25-cm; 5-µm packing L7
Column temperature:
35
Flow rate:
1.5 mL/min
Injection size:
20 µL
System suitability
Samples:
System suitability solution and Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 1.5 between the peaks for atorvastatin related compound B and atorvastatin, System suitability solution
Tailing factor:
NMT 1.6, Standard solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 0.6%, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of C66H68CaF2N4O10 in the portion of Atorvastatin Calcium taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Atorvastatin Calcium RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Atorvastatin Calcium in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
98.0%–102.0% on the anhydrous basis
IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
• Heavy Metals
Diluent:
Methanol and water (9:1)
Sample solution:
Dissolve 250 mg of the sample in 30 mL of Diluent.
Standard lead solution:
Prepared as directed under Heavy Metals  231
231 .
.
Reference solution:
Dilute 0.5 mL of the Standard lead solution with Diluent to 30 mL.
Blank solution:
20 mL of Diluent
Monitor solution:
Dissolve 250 mg of Atorvastatin Calcium in 0.5 mL of the Standard lead solution, and dilute with Diluent to 30 mL.
Analysis
Samples:
Sample solution, Reference solution, Blank solution, and Monitor solution
To each solution, add 2 mL of pH 3.5 Acetate Buffer, prepared as directed under Heavy Metals  231
231 . Mix, add to 1.2 mL of thioacetamide–glycerin base TS, and mix immediately. Pass the solutions through a membrane filter of 0.45-µm pore size. Compare the spots on the filters obtained with the different solutions: the brown color of the spot from the Sample solution is not more intense than that of the spot from the Reference solution. The test is invalid if the Reference solution does not show a slight brown color compared to the Blank solution, or if the color of the Monitor solution is not at least as intense as the color of the Reference solution.
. Mix, add to 1.2 mL of thioacetamide–glycerin base TS, and mix immediately. Pass the solutions through a membrane filter of 0.45-µm pore size. Compare the spots on the filters obtained with the different solutions: the brown color of the spot from the Sample solution is not more intense than that of the spot from the Reference solution. The test is invalid if the Reference solution does not show a slight brown color compared to the Blank solution, or if the color of the Monitor solution is not at least as intense as the color of the Reference solution.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 20 ppm
Organic Impurities
• Procedure
Buffer, Solution A, Solution B, Diluent, Mobile phase, System suitability solution, and Chromatographic system:
Proceed as directed for the Assay.
Standard solution:
1.5 µg/mL each of USP Atorvastatin Related Compound A RS, USP Atorvastatin Related Compound B RS, USP Atorvastatin Related Compound C RS, and USP Atorvastatin Related Compound D RS in Diluent
Sample solution:
1 mg/mL of Atorvastatin Calcium in Diluent. [Note—Use sonication if necessary. ]
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Chromatograph the Standard solution, and identify the components on the basis of their relative retention times, given in Impurity Table 1.
Calculate the percentage of each of the atorvastatin related compounds A, B, C, and D in the portion of Atorvastatin Calcium taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of the relevant atorvastatin related compound from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of the relevant atorvastatin related compound from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of the relevant atorvastatin related compound in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Atorvastatin Calcium in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Calculate the percentage of any other individual impurity in the portion of Atorvastatin Calcium taken:
Result = (rU/rT) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of any other individual impurity from the Sample solution |
| rT | = | = sum of the responses of all the peaks from the Sample solution |
[Note—Disregard any peak observed in the blank; the reporting level for impurities is 0.05%. ]
Acceptance criteria
Individual impurities:
See Impurity Table 1.
Total impurities:
NMT 1.0%. [Note—This total does not include atorvastatin related compound E, as determined in the test for Enantiomeric Purity. ]
Impurity Table 1
| Name | Relative Retention Time | Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Atorvastatin related compound Aa | 0.8 | 0.3 |
| Atorvastatin related compound Bb | 0.9 | 0.3 |
| Atorvastatin | 1.0 | n/a |
| Atorvastatin related compound Cc | 1.2 | 0.3 |
| Atorvastatin related compound Dd, e | 2.1 | 0.1 |
| Any other individual impurity | — | 0.1 |
|
a
Desfluoro impurity.
b
3S,5R isomer.
c
Difluoro impurity.
d
Epoxide impurity.
e
Atorvastatin related compound D may undergo a transformation equilibrium with its cyclic hemiketal form. The cyclic hemiketal of atorvastatin related compound D elutes about 1–2 min before atorvastatin related compound D. Use the sum of the areas of the two peaks as a peak response for atorvastatin related compound D in the Standard solution and the Sample solution.
|
||
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Enantiomeric Purity
Mobile phase:
Hexane, dehydrated alcohol, and trifluoroacetic acid (940:60:1)
System suitability stock solution:
5 mg/mL of USP Atorvastatin Calcium RS and 37.5 µg/mL of USP Atorvastatin Related Compound E RS in methanol. [Note—Atorvastatin related compound E is the 3S,5S enantiomer of atorvastatin. ]
System suitability solution:
Transfer 2.0 mL of the System suitability stock solution to a 10-mL volumetric flask, add 2.0 mL of dehydrated alcohol, and dilute with hexane to volume.
Sample solution:
Transfer 10 mg of Atorvastatin Calcium to a 10-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in 2.0 mL of methanol, add 2.0 mL of dehydrated alcohol, and dilute with hexane to volume.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 244 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 25-cm; packing L51
Flow rate:
1.0 mL/min
Injection size:
20 µL
System suitability
Samples:
System suitability solution
[Note—The elution order of the peaks is atorvastatin related compound E followed by atorvastatin. ]
Resolution:
NLT 2.0 between the peaks for atorvastatin related compound E and atorvastatin
Analysis
Samples:
Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of atorvastatin related compound E in the portion of Atorvastatin Calcium taken:
Result = (rU/rT) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response for atorvastatin related compound E |
| rT | = | = sum of the responses of the peaks for atorvastatin related compound E and atorvastatin |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.3% of atorvastatin related compound E
• Water Determination, Method Ia  921
921 :
3.5%–5.5%
:
3.5%–5.5%
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers, and store at room temperature.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Atorvastatin Related Compound A RS
Desfluoro impurity, or (3R,5R)-7-[3-(phenylcarbamoyl)-2-isopropyl-4,5-diphenyl-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid, calcium salt.
C66H70CaN4O10 1119.38
Desfluoro impurity, or (3R,5R)-7-[3-(phenylcarbamoyl)-2-isopropyl-4,5-diphenyl-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid, calcium salt.
C66H70CaN4O10 1119.38
USP Atorvastatin Related Compound B RS
3S,5R Isomer, or (3S,5R)-7-[3-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-isopropyl-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid, calcium salt.
C66H68CaF2N4O10 1155.34
3S,5R Isomer, or (3S,5R)-7-[3-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-isopropyl-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid, calcium salt.
C66H68CaF2N4O10 1155.34
USP Atorvastatin Related Compound C RS
Difluoro impurity, or (3R,5R)-7-[3-(phenylcarbamoyl)-4,5-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-2-isopropyl-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid, calcium salt.
C66H66F4N4O10 1191.34
Difluoro impurity, or (3R,5R)-7-[3-(phenylcarbamoyl)-4,5-bis(4-fluorophenyl)-2-isopropyl-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid, calcium salt.
C66H66F4N4O10 1191.34
USP Atorvastatin Related Compound D RS
Epoxide impurity, or 3-(4-fluorobenzoyl)-2-isobutyryl-3-phenyl-oxirane-2-carboxylic acid phenylamide.
C26H22FNO4 431.46
Epoxide impurity, or 3-(4-fluorobenzoyl)-2-isobutyryl-3-phenyl-oxirane-2-carboxylic acid phenylamide.
C26H22FNO4 431.46
USP Atorvastatin Related Compound E RS
3S,5S Enantiomer, or (3S,5S)-7-[3-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-isopropyl-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid, calcium salt.
C66H68CaF2N4O10 1155.34
3S,5S Enantiomer, or (3S,5S)-7-[3-(phenylcarbamoyl)-5-(4-fluorophenyl)-2-isopropyl-4-phenyl-1H-pyrrol-1-yl]-3,5-dihydroxyheptanoic acid, calcium salt.
C66H68CaF2N4O10 1155.34
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Elena Gonikberg, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8251 |
(SM32010) Monographs - Small Molecules 3 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 2263
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 35(1) Page 66