Add the following:
DEFINITION
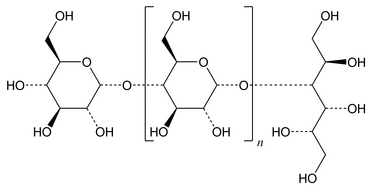
Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate is a mixture that contains NLT 50% of hydrogenated polysaccharides containing more than 3 d-glucopyranosyl units terminated with a d-glucityl unit, calculated on the anhydrous basis. Other ingredients can include sorbitol, maltitol, and other sugar polyols.
IDENTIFICATION
• A.
It meets the requirements of the test for Content of Maltitol and Sorbitol.
• B.
It meets the requirements of the test for Content of Hydrogenated Polysaccharides.
• C. Limit of Diethylene Glycol and Ethylene Glycol
[Note—Perform this test for liquid products of Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate. ]
Diluent:
Acetone and water (96:4)
Standard stock solution:
0.5 mg/mL of USP Diethylene Glycol RS and 0.5 mg/mL of USP Ethylene Glycol RS in Diluent
Internal standard stock solution:
0.5 mg/mL of 1,3-butanediol (internal standard) in Diluent
Standard solution:
0.04 mg/mL of USP Diethylene Glycol RS, 0.04 mg/mL of USP Ethylene Glycol RS, and 0.04 mg/mL of 1,3-butanediol (internal standard), in Diluent, prepared from the Standard stock solution and the Internal standard stock solution
Sample solution:
Transfer 1.0 g of Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate to a 25-mL volumetric flask. Add 1.0 mL of water to the flask, and mix on a vortex mixer for 3 min. Add 2.0 mL of the Internal standard stock solution, and add the remaining Diluent to the flask in three equal portions to volume. Mix the contents for about 3 min after each addition of Diluent. Pass a portion of the supernatant layer through a nylon filter of 0.45-µm pore size. Discard the first 2 mL of the filtrate, and collect the rest of the filtrate for analysis. [Note—Acetone is used to precipitate sugar alcohols. ]
Chromatographic system
Mode:
GC
Detector:
Flame ionization
Column:
0.32-mm × 15-m fused-silica capillary; 0.25-µm layer of phase G46
Temperature
Detector:
300
Injection port:
240
Column:
See Table 1.
Table 1
| Initial Temperature ( |
Temperature Ramp ( |
Final Temperature ( |
Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 70 | — | 70 | 2 |
| 70 | 50 | 300 | 5 |
Carrier gas:
Helium
Flow rate:
3.0 mL/min
Injection size:
1.0 µL
Injection type:
Split injection. The split ratio is about 10:1. [Note—A general-purpose split/splitless, tapered, glass wool, deactivated liner is used. ]
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
[Note—See Table 2. Relative retention times are provided for information only, and the standards should be used to ensure appropriate peak identification. ]
Table 2
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
|---|---|
| Ethylene glycol | 1.0 |
| 1,3-Butanediol (internal standard) |
2.0 |
| Diethylene glycol | 2.5 |
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 15 between ethylene glycol and 1,3-butanediol
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Based on the Standard solution, identify the peaks of ethylene glycol, 1,3-butanediol (internal standard), and diethylene glycol. Compare peak area ratios of ethylene glycol to the internal standard and of diethylene glycol to the internal standard in the Standard solution and Sample solution, respectively.
Acceptance criteria
Diethylene glycol:
The peak area ratio of diethylene glycol to the internal standard in the Sample solution is NMT the peak area ratio of diethylene glycol to the internal standard in the Standard solution, corresponding to NMT 0.10% of diethylene glycol in Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate.
Ethylene glycol:
The peak area ratio of ethylene glycol to the internal standard in the Sample solution is NMT the peak area ratio of ethylene glycol to the internal standard in the Standard solution, corresponding to NMT 0.10% of ethylene glycol in Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate.
ASSAY
• Content of Maltitol and Sorbitol
Mobile phase:
Degassed water
Standard solution:
Dissolve accurately weighed quantities of USP Maltose Monohydrate RS, USP Maltitol RS, USP Dextrose RS, and USP Sorbitol RS in water to obtain a solution having known concentrations of about 1.0 mg/mL for each, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Sample solution:
Transfer a quantity of Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate, equivalent to 100 mg on the anhydrous basis, to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Dilute with water to volume, and mix. Transfer approximately 10 mL of the solution into a separate container, shake the solution for 30 s, pass through a filter of 0.45-µm or finer pore size into a suitable autosampler vial, and seal.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
Refractive index
Column:
7.7-mm × 30-cm; packing L58
Temperature
Detector:
40
Column:
80 , controlled within ±2
, controlled within ±2
Flow rate:
0.3 mL/min
Injection size:
50 µL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
[Note—See Table 3 for relative retention times. ]
Table 3
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
|---|---|
| Maltose | 0.81 |
| Maltitol | 0.84 |
| Dextrose | 0.94 |
| Sorbitol | 1.00 |
[Note—Sorbitol is the last peak to elute. ]
System suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 2.0% for the maltitol peak
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of each component, maltose (PM1), maltitol (PM2), dextrose (PD), and sorbitol (PS), in the solid portion of Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate taken:
Result = V × (rU/rS) × (C/W) × 100
| V | = | = volume of the Sample solution, 100 mL |
| rU | = | = peak response for the respective component (maltose, maltitol, dextrose, sorbitol) from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response for the respective component (maltose, maltitol, dextrose, sorbitol) from the Standard solution |
| C | = | = concentration of the respective component (maltose, maltitol, dextrose, sorbitol) in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| W | = | = weight of Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate that was taken to prepare the Sample solution (mg), calculated on the anhydrous basis |
Acceptance criteria:
Less than 50% of total maltitol and sorbitol and less than 1% of total maltose and dextrose, on the anhydrous basis
• Content of Hydrogenated Polysaccharides
Mobile phase, Standard solution, Sample solution, and Chromatographic system:
Prepare as directed in the test for Content of Maltitol and Sorbitol.
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Inject a volume (about 50 µL) of the Sample solution, and measure all the peak areas. The elution pattern includes the higher-molecular-weight hydrogenated polysaccharides containing more than 11 d-glucopyranosyl units, followed by some individual peaks representing hydrogenated polysaccharides containing NMT 10 d-glucopyranosyl units, if this hydrogenated species is present. The higher-molecular-weight hydrogenated polysaccharides containing more than 11 d-glucopyranosyl units can be integrated into one peak; the relative retention time is about 0.29 relative to the peak of sorbitol. The relative retention times for hydrogenated polysaccharides containing NMT 10 d-glucopyranosyl units are given in Table 4.
Table 4
| Hydrogenated Species for Degree of Polymerization (DP) |
Relative Retention Time |
|---|---|
| Sorbitol (HDP 1) | 1.00 |
| Maltitol (HDP 2) | 0.84 |
| Maltotriitol (HDP 3) | 0.72 |
| Maltotetraitol (HDP 4) | 0.64 |
| Maltopentaitol (HDP 5) | 0.58 |
| Maltohexaitol (HDP 6) | 0.53 |
| Maltoheptaitol (HDP 7) | 0.48 |
| Maltooctaitol (HDP 8) | 0.45 |
| Maltononaitol (HDP 9) | 0.42 |
| Maltodecaitol (HDP 10) | 0.40 |
Calculate the percentage of hydrogenated polysaccharides containing more than 3 d-glucopyranosyl units in the solid portion of Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate taken:
Result = (rU/rT) × 100
| rU | = | = sum of peak areas of hydrogenated polysaccharides containing more than 3 d-glucopyranosyl units from the Sample solution |
| rT | = | = sum of all the peak areas from the Sample solution |
Acceptance criteria:
NLT 50% of hydrogenated polysaccharides containing more than 3 d-glucopyranosyl units, on the anhydrous basis
IMPURITIES
• Residue on Ignition  281
281 :
NMT 0.15%, ignition of a quantity of Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate equivalent to 1.0 g of solid, on the anhydrous basis
:
NMT 0.15%, ignition of a quantity of Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate equivalent to 1.0 g of solid, on the anhydrous basis
• Limit of Chloride
Sample solution:
Transfer a quantity of Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate, equivalent to 25 g on the anhydrous basis, to a beaker, add 100 mL of water, and stir until the Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate is completely dissolved.
Analysis:
Add 1.0 mL of potassium chromate indicator solution (1 in 20) to the Sample solution. Slowly titrate with 0.1 N silver nitrate VS until a reddish-orange color persists.
Calculate the quantity, in µg, of chloride in each g of Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate taken:
Result = (F × Mr × N × V)/W
| F | = | = factor converting mg to µg, 103 µg/mg |
| Mr | = | = molar mass of chloride, 35.45 |
| N | = | = exact normality of the silver nitrate solution |
| V | = | = volume of the silver nitrate solution consumed in the titration (mL) |
| W | = | = weight of Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate taken to prepare the Sample solution (g) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 50 µg/g (ppm) of chloride
• Chloride and Sulfate, Sulfate  221
221 :
1.0 g of the solid portion of Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 0.10 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid: NMT 100 µg/g (ppm) of sulfate is found.
:
1.0 g of the solid portion of Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate shows no more sulfate than corresponds to 0.10 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid: NMT 100 µg/g (ppm) of sulfate is found.
• Limit of Nickel
[Note—When water is specified as the diluent, use deionized ultra-filtered water. ]
Digester solution (aqua regia):
Add 360 mL of hydrochloric acid and 240 mL of nitric acid to 1200 mL of water.
Blank solution:
Add 40 mL of nitric acid to a 2-L volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix well.
Internal standard solution:
Transfer 2.0 mL of commercially prepared yttrium reference standard solution (1000 ppm) to a 1-L volumetric flask, dilute with Blank solution to volume, and mix well. The Internal standard solution contains 2 µg/mL of yttrium.
Standard stock solution:
[Note—Prepare this solution fresh every two months. ] Quantitatively dilute an accurately measured volume of a commercially prepared nickel ICP standard (1000 ppm) with Blank solution to obtain a solution containing 10 µg/mL of nickel (Standard stock solution 10 ppm).
Standard solutions:
[Note—Prepare these solutions fresh weekly. ] Separately pipet 1.0, 2.0, and 4.0 mL of Standard stock solution, respectively, into three 200-mL volumetric flasks. Dilute the content in each flask with Blank solution to volume, and mix well. These are, respectively, the Standard nickel solution 50 ppb, Standard stock solution 100 ppb, and Standard nickel solution 200 ppb.
Sample solution:
Transfer a quantity of Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate, equivalent to 10.0 g on the anhydrous basis, into a 125-mL conical flask. Add 40 mL of Digester solution, and place on a hot plate. Heat the solution for about 20 min, being careful to prevent the solution from boiling over. Pull the sample off the hot plate just before it turns a dark caramel color. [Note—Do not overburn the sample. ] Transfer the flask's contents into a clean, dry, 50-mL volumetric flask with washings of Blank solution. Dilute with Blank solution to volume. Filter the sample into a 15-mL centrifuge tube, using a 10-mL BD syringe fitted with a syringe filter of 0.45-µm pore size.
Instrumental conditions
(See Plasma Spectrochemistry  730
730 .)
.)
Mode:
Inductively coupled plasma–optical emission spectroscopy (ICP–OES) configured in an axial optical alignment
Detector:
Set a UV detector to scan nickel at 232.005 nm and yttrium at 371.029 nm, and set the sample read time to 10 s minimum and 50 s maximum.
Analysis
Samples:
Blank solution, Standard solutions, and Sample solution
Take three replicate scans with the integration set to one point per peak. Set forward power from the RF generator to 1500 watts. The argon plasma feed gas flows at 15 L/min with the auxiliary gas (shear gas) set to flow at 0.5 L/min. Use a gem cone nebulizer with a nebulization gas flow rate of 0.55 L/min. Deliver the sample to the spray chamber with a multichannel peristaltic pump set to deliver sample at a rate of 1.00 mL/min. Add the Internal standard solution in-line via a mixing block between the sample probe and the spray chamber. Flush the samples through the system for 30 s at a rate of 4.0 mL/min before analysis. Program a 60-s read delay into the sampling routine to allow for fluid flow equilibration after the high-speed flush, before the first analytical read of the sample. Between samples, wash the pumping system by flushing the Blank solution for 30 s at a rate of 4.0 mL/min.
Instrument performance must be verified to conform to the manufacturer’s specifications for resolution and sensitivity. Before analyzing samples, the instrument must pass a suitable performance check.
Generate the calibration curve using the Blank solution, Standard nickel solution 50 ppb, Standard stock solution 100 ppb, and Standard nickel solution 200 ppb as follows. Scan the Internal standard solution while running the Blank solution to measure the intensity of the yttrium emission. Hold this value constant throughout the remainder of the test. Separately scan the Blank solution, Standard nickel solution 50 ppb, Standard stock solution 100 ppb, and Standard nickel solution 200 ppb for nickel and yttrium. [Note—Add the Internal standard solution via an in-line mixing chamber. ] Normalize the yttrium intensity to the value of the Internal standard solution. Apply this normalization factor to the nickel intensity, which is then referred to as the corrected nickel intensity. Construct a calibration curve by plotting the corrected nickel intensity versus the known concentrations, in ng/mL, of the nickel: the linear regression coefficient is NLT 0.999.
Similarly, analyze the Sample solution on the ICP. Plot the intensity of the emission of the Sample solution on the calibration curve. Obtain the concentration of nickel, C, in ng/mL, in the Sample solution through the calibration curve.
Calculate the content, in µg/g, of nickel in the solid portion of Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate taken:
Result = F × V × (C/W)
| F | = | = factor converting ng to µg, 10 |
| V | = | = volume of the Sample solution, 50 mL |
| C | = | = concentration of nickel in the Sample solution (ng/mL) |
| W | = | = weight of Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate calculated on the anhydrous basis (g) |
Acceptance criteria:
Nickel content is NMT 1 µg/g (ppm).
• Limit of Reducing Sugars
Analysis:
Dissolve a quantity of Hydrogenated Starch Hydrolysate, equivalent to 1.0 g on the anhydrous basis, in 6 mL of water with the aid of gentle heat, if necessary. Cool, and add 20.0 mL of cupric citrate TS and a few glass beads. Heat so that boiling begins after 4 min, and maintain boiling for 3 min. Cool rapidly, and add 40 mL of diluted acetic acid, 60 mL of water, and 20.0 mL of 0.05 N iodine VS. With continuous shaking, add 25 mL of a mixture of 6 mL of hydrochloric acid and 94 mL of water. When the precipitate has dissolved, titrate the excess of iodine with 0.05 N sodium thiosulfate VS, using 2 mL of starch TS as an indicator, added toward the end of the titration.
Acceptance criteria:
NLT 12.8 mL of 0.05 N sodium thiosulfate, corresponding to NMT 1% of reducing sugars
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Microbial Enumeration Tests  61
61 and Tests for Specified Microorganisms
and Tests for Specified Microorganisms  62
62 :
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 103 cfu/g, and the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 102 cfu/g. It meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli.
:
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 103 cfu/g, and the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 102 cfu/g. It meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli.
• pH  791
791 :
3.0–7.0, in a 20% (w/w) solution in freshly boiled and cooled water
:
3.0–7.0, in a 20% (w/w) solution in freshly boiled and cooled water
• Water Determination, Method I  921
921
For dried powder product:
NMT 6.0%
For liquid product:
Within ±1.5 units of the labeled value
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers. No storage requirements specified for liquid product; protect from moisture for dried powder product.
• Labeling:
Label it to indicate Water content, as the percentage of water, for liquid product.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Ethylene Glycol RS
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Hong Wang, Ph.D.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8351 |
(EXC2010) Monographs - Excipients |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 1976
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 37(1)