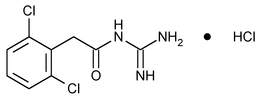
Guanfacine Hydrochloride
(gwahn' fa seen hye'' droe klor' ide).
Benzeneacetamide, N-(aminoiminomethyl)-2,6-dichloro-, monohydrochloride.
N-Amidino-2-(2,6-dichlorophenyl)acetamide monohydrochloride
» Guanfacine Hydrochloride contains not less than 98.0 percent and not more than 102.0 percent of C9H9Cl2N3O·HCl, calculated on the dried basis.[Caution—Guanfacine Hydrochloride is a potent antihypertensive drug. Minimize flying dust, and avoid all bodily and respiratory contact with this substance.
]
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers.
Identification—
B:
The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation corresponds to that in the chromatogram of the Standard preparation, as obtained in the Assay.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 105
—
Dry it at 105 for 4 hours: it loses not more than 0.5% of its weight.
for 4 hours: it loses not more than 0.5% of its weight.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.1%.
:
not more than 0.1%.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
0.002%.
:
0.002%.
[note—Prepare all solutions in the tests for Related compounds and Chromatographic purity immediately prior to use, and apply to plates as quickly as possible. ]
Related compounds—
Spray reagent—
[Caution—Avoid contact with o-tolidine. Prepare and use this Spray reagent in a well-ventilated hood.] Dissolve 50 mg of o-tolidine in 100 mL of alcohol, and mix.
Chlorine chamber—
Transfer 1.5 g of potassium permanganate to a 100-mL beaker, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix. Transfer 25 mL of this solution to a beaker, and place the beaker inside a chromatographic chamber. Pipet 10 mL of hydrochloric acid into the beaker, and cover the chamber.
Developing solvent system—
Prepare a fresh mixture of ethyl acetate, glacial acetic acid, and acetonitrile (70:25:3).
Standard solutions—
Dissolve accurately weighed quantities of USP Guanfacine Hydrochloride RS and guanidine hydrochloride in methanol to obtain a solution having a known concentration of 0.4 mg each of USP Guanfacine Hydrochloride RS and guanidine hydrochloride per mL. Quantitatively dilute this solution with methanol to obtain Standard solutions having the following compositions:
| Standard Solution | Dilution | Concentration (µg RS and Guanidine Hydrochloride per mL) | Percentage (% for Comparison with Test Specimen) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | (undiluted) | 400 | 2.0 |
| 2 | (1 in 2) | 200 | 1.0 |
| 3 | (1 in 4) | 100 | 0.5 |
| 4 | (1 in 8) | 50 | 0.25 |
Test solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of Guanfacine Hydrochloride in methanol to obtain a solution having a concentration of about 20 mg per mL.
Procedure—
Use a thin-layer chromatographic plate (see Chromatography  621
621 coated with a 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel. Prewash the plates by placing in a chromatographic chamber saturated with Developing solvent system. Remove the plates from the chamber, and allow to dry. Separately apply 10 µL each of the Standard solutions and the Test solution to the chromatographic plate. Allow the spots to dry, and develop the chromatogram in Developing solvent until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the chamber, mark the solvent front, and allow the plate to air-dry for about 1 hour. Examine the plate under short-wavelength UV light. Place the dried plate in the Chlorine chamber for 15 minutes, remove, and allow the excess chlorine to evaporate by air drying for 5 minutes. Spray the plate with Spray reagent, and examine: any spot due to guanidine hydrochloride observed in the chromatogram of the Test solution is not greater in size or intensity than the guanidine hydrochloride spot obtained from Standard solution 3 (0.5%); no other individual impurity spot observed in the chromatogram of the Test solution is greater in size or intensity than the guanfacine hydrochloride spot obtained from Standard solution 4 (0.25%); and the sum of all impurities found, including guanidine hydrochloride, is not more than 1.0%.
coated with a 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel. Prewash the plates by placing in a chromatographic chamber saturated with Developing solvent system. Remove the plates from the chamber, and allow to dry. Separately apply 10 µL each of the Standard solutions and the Test solution to the chromatographic plate. Allow the spots to dry, and develop the chromatogram in Developing solvent until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the chamber, mark the solvent front, and allow the plate to air-dry for about 1 hour. Examine the plate under short-wavelength UV light. Place the dried plate in the Chlorine chamber for 15 minutes, remove, and allow the excess chlorine to evaporate by air drying for 5 minutes. Spray the plate with Spray reagent, and examine: any spot due to guanidine hydrochloride observed in the chromatogram of the Test solution is not greater in size or intensity than the guanidine hydrochloride spot obtained from Standard solution 3 (0.5%); no other individual impurity spot observed in the chromatogram of the Test solution is greater in size or intensity than the guanfacine hydrochloride spot obtained from Standard solution 4 (0.25%); and the sum of all impurities found, including guanidine hydrochloride, is not more than 1.0%.
Chromatographic purity—
Spray reagent 1—
Prepare a mixture of tertiary butyl alcohol and water (9:1).
Spray reagent 2—
Dissolve 5 g of 4,4¢-tetramethyldiaminodiphenylmethane in 20 mL of glacial acetic acid, add 10 mL of water, and mix (Solution 1). Dissolve 6 g of potassium iodide in 120 mL of water, and mix (Solution 2). Dissolve 0.3 g of ninhydrin in 10 mL of glacial acetic acid, dilute with water to 100 mL, and mix (Solution 3). Mix Solution 1 and Solution 2, and add 9 mL of Solution 3.
Developing solvent system—
Prepare a fresh mixture of hexanes, diisopropyl ether, toluene, and glacial acetic acid (60:30:5:3).
Reference solutions—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of 2,6-dichlorophenylacetic acid in a mixture of methanol and water (9:1) to obtain a solution having a concentration of 1 mg per mL (Reference solution 1). Quantitatively dilute this solution with a mixture of methanol and water (9:1) to obtain Reference solution 2 and Reference solution 3 having known concentrations of 0.5 and 0.25 mg per mL of 2,6-dichlorophenylacetic acid, respectively.
Test solution—
Prepare a solution of Guanfacine Hydrochloride in a mixture of methanol and water (9:1), containing 100 mg per mL.
Procedure—
Use a thin-layer chromatographic plate (see Chromatography  621
621 ) coated with a 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel. Prewash the plates by placing in a chromatographic chamber saturated with Developing solvent system. Remove the plates from the chamber, and allow to dry. Separately apply 25 µL of each of the Reference solutions and the Test solution to the chromatographic plate. Allow the spots to dry, and develop the chromatograms in the Developing solvent system until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the chamber, mark the solvent front, and allow the plate to air-dry for 30 minutes. Examine the plate under short-wavelength UV light. Spray the plate with Spray reagent 1, wait for 1 minute, and then spray with Spray reagent 2. Place the wet plate under short-wavelength UV light for 10 minutes, remove, and observe under white light: no spot observed in the chromatogram of the Test solution, other than that due to guanfacine hydrochloride, is greater in size or intensity than the principal spot obtained from Reference solution 2 (0.5%); and the sum of all impurities found is not more than 1.0%.
) coated with a 0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel. Prewash the plates by placing in a chromatographic chamber saturated with Developing solvent system. Remove the plates from the chamber, and allow to dry. Separately apply 25 µL of each of the Reference solutions and the Test solution to the chromatographic plate. Allow the spots to dry, and develop the chromatograms in the Developing solvent system until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the chamber, mark the solvent front, and allow the plate to air-dry for 30 minutes. Examine the plate under short-wavelength UV light. Spray the plate with Spray reagent 1, wait for 1 minute, and then spray with Spray reagent 2. Place the wet plate under short-wavelength UV light for 10 minutes, remove, and observe under white light: no spot observed in the chromatogram of the Test solution, other than that due to guanfacine hydrochloride, is greater in size or intensity than the principal spot obtained from Reference solution 2 (0.5%); and the sum of all impurities found is not more than 1.0%.
Assay—
Dilute phosphoric acid—
Prepare a mixture of water and phosphoric acid (4:1).
Buffer solution—
Dissolve 68 g of monobasic potassium phosphate in water, dilute with water to 1000 mL, and mix. Dilute 100 mL of this solution with water to 1000 mL, add 5 mL of triethylamine, mix, and adjust with Dilute phosphoric acid to a pH of 3.0.
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of Buffer solution and acetonitrile (79:21). Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Standard preparation—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Guanfacine Hydrochloride RS in a mixture of acetonitrile and water (3:1) to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 1 mg of USP Guanfacine Hydrochloride RS per mL. Transfer 2.0 mL of this solution to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dilute with Mobile phase to volume, and mix.
Assay preparation—
Transfer an accurately weighed quantity of about 50 mg of Guanfacine Hydrochloride to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with a mixture of acetonitrile and water (3:1) to volume, and mix. Transfer 2.0 mL of this solution to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dilute with Mobile phase to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 220-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains packing L1. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the responses as directed for Procedure: the capacity factor, k¢, is between 2 and 5; the column efficiency is not less than 1500 theoretical plates; the tailing factor is not more than 2; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 220-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains packing L1. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the responses as directed for Procedure: the capacity factor, k¢, is between 2 and 5; the column efficiency is not less than 1500 theoretical plates; the tailing factor is not more than 2; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the areas for the major peaks. Calculate the quantity, in mg, of C9H9Cl2N3O·HCl in the portion taken by the formula:
1.25C(rU/rS)
in which C is the concentration, in µg per mL, of USP Guanfacine Hydrochloride RS in the Standard preparation; and rU and rS are the guanfacine hydrochloride peaks obtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Sujatha Ramakrishna, Ph.D.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8349 |
(SM22010) Monographs - Small Molecules 2 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 3391
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 27(1) Page 1789