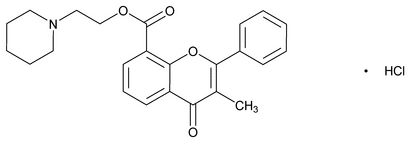
Flavoxate Hydrochloride
C24H25NO4·HCl 427.92
4H-1-Benzopyran-8-carboxylic acid, 3-methyl-4-oxo-2-phenyl-, 2-(1-piperidinyl)ethyl ester, hydrochloride;
2-Piperidinoethyl 3-methyl-4-oxo-2-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-8-carboxylate hydrochloride

 [3717-88-2].
[3717-88-2].
(flay vox' ate hye'' droe klor' ide).
C24H25NO4·HCl 427.92
4H-1-Benzopyran-8-carboxylic acid, 3-methyl-4-oxo-2-phenyl-, 2-(1-piperidinyl)ethyl ester, hydrochloride;
2-Piperidinoethyl 3-methyl-4-oxo-2-phenyl-4H-1-benzopyran-8-carboxylate hydrochloride
DEFINITION
Flavoxate Hydrochloride contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of C24H25NO4·HCl, calculated on the dried basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• B.
The retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution, as obtained in the Assay.
• C. Identification Tests—General, Chloride  191
191 :
A solution of 10 mg/mL meets the requirements of the silver nitrate precipitate.
:
A solution of 10 mg/mL meets the requirements of the silver nitrate precipitate.
ASSAY
• Procedure
Solution A:
Mixture of 1.0 g of sodium hexanesulfonate in 650 mL of water, 1 mL of triethylamine, and 1.0 mL of phosphoric acid
Mobile phase:
Add 350 mL of acetonitrile to Solution A.
Standard solution:
50 µg/mL of USP Flavoxate Hydrochloride RS in Mobile phase
Sample solution:
50 µg/mL of Flavoxate Hydrochloride in Mobile phase
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 293 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 15-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Flow rate:
1 mL/min
Injection size:
20 µL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
[Note—The retention time of flavoxate is about 4.3 min. ]
Suitability requirements
Column efficiency:
NLT 3000 theoretical plates
Tailing factor:
NMT 2.0
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 2.0%
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of C24H25NO4·HCl in the portion of Flavoxate Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Flavoxate Hydrochloride RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of Flavoxate Hydrochloride in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
98.0%–102.0% on the dried basis
IMPURITIES
Organic Impurities
• Procedure
Solution A:
0.05% (v/v) trifluoroacetic acid in water
Solution B:
Acetonitrile
Mobile phase:
See the gradient table below.
| Time (min) |
Solution A (%) |
Solution B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 68 | 32 |
| 15 | 68 | 32 |
| 25 | 20 | 80 |
| 35 | 20 | 80 |
| 36 | 68 | 32 |
| 41 | 68 | 32 |
Diluent:
Methanol and 0.02% trifluoroacetic acid (1:1)
Standard stock solution 1:
2 mg/mL of USP Flavoxate Hydrochloride RS in Diluent
Standard stock solution 2:
0.05 mg/mL of USP Flavoxate Related Compound A RS in Diluent
Standard stock solution 3:
0.05 mg/mL of USP Flavoxate Related Compound B RS in methanol
Standard stock solution 4:
0.05 mg/mL of USP Flavoxate Related Compound C RS prepared as follows: Dissolve USP Flavoxate Related Compound C RS first in methanol using 10% of final volume, then fill 10% of final volume with 0.02% trifluoroacetic acid. Dilute with Diluent to volume.
Standard solution:
1 mg/mL of USP Flavoxate Hydrochloride RS and 5 µg/mL each of USP Flavoxate Related Compound A RS, USP Flavoxate Related Compound B RS, and USP Flavoxate Related Compound C RS in Diluent from Standard stock solutions 1, 2, 3, and 4, respectively
Sample solution:
1 mg/mL of Flavoxate Hydrochloride in Diluent
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 240 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 15-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Column temperature:
30
Flow rate:
0.8 mL/min
Injection size:
10 µL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 2.0 between the flavoxate related compound B and flavoxate related compound C peaks
Tailing factor:
NMT 1.5 for the flavoxate related compounds A, B, and C peaks
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 2.0% for the flavoxate peak
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of flavoxate related compounds A, B, and C in the portion of Flavoxate Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (1/F) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of each individual impurity from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of flavoxate from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Flavoxate Hydrochloride RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Flavoxate Hydrochloride in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
| F | = | = relative response factor (see Impurity Table 1) |
Calculate the percentage of any other unspecified degradation product in the portion of Flavoxate Hydrochloride taken:
Result = (rU/rT) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of each unspecified impurity from the Sample solution |
| rT | = | = sum of responses of all peaks from the Sample solution |
Acceptance criteria
Individual impurities:
See Impurity Table 1.
Total impurities:
1.0%
Impurity Table 1
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
Relative Response Factor |
Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flavoxate | 1.0 | — | — |
| Flavoxate related compound Aa,* | 2.8 | 1.6 | 0.3 |
| Flavoxate related compound Bb,* | 3.5 | 1.5 | 0.1 |
| Flavoxate related compound Cc,* | 3.7 | 1.4 | 0.1 |
| Any single unspecified degradation product | — | 1.0 | 0.1 |
|
a
3-Methylflavone-8-carboxylic acid.
b
3-Methylflavone-8-carboxylic acid methyl ester.
c
3-Methylflavone-8-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
*
For identification and system suitability purposes only.
|
|||
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Loss on Drying  731
731 :
Dry a sample at 105
:
Dry a sample at 105 to constant weight: it loses NMT 0.5% of its weight.
to constant weight: it loses NMT 0.5% of its weight.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers, protected from light; and store at room temperature.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Flavoxate Hydrochloride RS
USP Flavoxate Related Compound A RS
3-Methylflavone-8-carboxylic acid.
C17H12O4 280.27
3-Methylflavone-8-carboxylic acid.
C17H12O4 280.27
USP Flavoxate Related Compound B RS
3-Methylflavone-8-carboxylic acid methyl ester.
C18H14O4 294.30
3-Methylflavone-8-carboxylic acid methyl ester.
C18H14O4 294.30
USP Flavoxate Related Compound C RS
3-Methylflavone-8-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
C19H16O4 308.33
3-Methylflavone-8-carboxylic acid ethyl ester.
C19H16O4 308.33
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Ravi Ravichandran, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8330 |
(SM42010) Monographs - Small Molecules 4 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 3198
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 35(6) Page 1454