Hydrogenated Polydextrose
DEFINITION
Hydrogenated Polydextrose is obtained by transition metal catalytic hydrogenation of Polydextrose in aqueous solution. It contains NLT 90.0% of dextrose polymer units, calculated on the anhydrous and ash-free basis. The polymer chain end groups are mainly sorbitol-terminated.
IDENTIFICATION
• A.
To 1 drop of a solution (1 in 10), add 4 drops of 5% phenol solution, then rapidly add 15 drops of sulfuric acid TS: a deep yellow to orange color is produced.
• B.
With vigorous swirling, add 1 mL of acetone to 1 mL of a solution (1 in 10): the solution remains clear.
• C.
With vigorous swirling, add 2 mL of acetone to the solution obtained in Identification test B: a heavy, milky turbidity develops immediately.
• D.
To 1 mL of a solution (1 in 50), add 4 mL of alkaline cupric citrate TS. Boil vigorously for 2–4 min. Remove from heat, and allow the precipitate (if any) to settle: the supernatant is blue or blue-green.
• E.
Meets the requirements for dextrose in Procedure 2, Limit of Monomers
ASSAY
• Procedure
Mobile phase:
0.001 N sulfuric acid. Pass through a filter of 0.5-µm or finer pore size, and degas.
Standard solution:
4.0 mg/mL of USP Polydextrose RS, calculated on the anhydrous and ash-free basis, in Mobile phase
Sample solution:
4.0 mg/mL of Hydrogenated Polydextrose, calculated on the anhydrous and ash-free basis, in Mobile phase
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
Refractive index
Detector temperature:
35 ± 0.1
Guard column:
4.6-mm × 3.0-cm; packing L17
Analytical column:
7.8-mm × 30-cm; packing L17
Flow rate:
0.6 mL/min
Injection size:
20 µL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 2.0%
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of dextrose polymer units in the Hydrogenated Polydextrose taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response for dextrose polymer units from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response for dextrose polymer units from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Polydextrose RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Hydrogenated Polydextrose in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
NLT 90.0% on the anhydrous and ash-free basis
IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
• Residue on Ignition  281
281 :
NMT 0.3%
:
NMT 0.3%
• Limit of Lead
[Note—Use reagent-grade chemicals with a lead content of as low as possible, as well as high-purity water and gases. Before use in this analysis, rinse all glassware and plasticware twice with 10% nitric acid and twice with 10% hydrochloric acid, and then rinse them thoroughly with Purified Water. ]
Matrix modifier solution:
10.0 mg/mL of dibasic ammonium phosphate
Lead nitrate stock solution:
Dissolve 159.8 mg of lead nitrate in 100 mL of water to which has been added 1 mL of nitric acid, then dilute with water to 1000 mL. Prepare and store this solution in glass containers free from soluble lead salts.
Standard lead solution:
On the day of use, dilute 10.0 mL of Lead nitrate stock solution with water to 100.0 mL. Each mL of Standard lead solution contains the equivalent of 10 µg of lead.
Standard solution A:
0.02 µg/mL of lead, from Standard lead solution in water
Standard solution B:
0.05 µg/mL of lead, from Standard lead solution in water
Standard solution C:
0.1 µg/mL of lead, from Standard lead solution in water
Standard solution D:
0.2 µg/mL of lead, from Standard lead solution in water
Standard solution E:
0.5 µg/mL of lead, from Standard lead solution in water
Sample solution:
Transfer 1.0 g of Hydrogenated Polydextrose, weighed and calculated on the anhydrous and ash-free basis, into a 10-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume.
Spiked sample solution:
Transfer 1.0 g of Hydrogenated Polydextrose, weighed and calculated on the anhydrous and ash-free basis, into a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dissolve in water. Add 100 µL of Standard lead solution, and dilute with water to volume. This solution contains 0.1 µg/mL of added lead.
Spectrometric conditions
Mode:
Graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometer, equipped with a pyrolytic tube with a platform
Lamp:
A lead hollow-cathode lamp, using a slit width of 0.7 mm (set low) and a deuterium arc lamp for background correction
Analytical wavelength:
Lead emission line of 283.3 nm
Autosampler
Sample volume:
10 µL
Alternative volume:
10 µL of Matrix modifier solution
Furnace program:
See the temperature program table below.
| Step | Dry | Char | Atomize | Clean | Recharge |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Temperature ( |
130 | 800 | 2400 | 2600 | 20 |
| Ramp time (s) |
20 | 20 | 0 | 1 | 2 |
| Hold time (s) |
40 | 40 | 6 | 5 | 20 |
| Argon flow rate (mL/min) |
300 | 300 | 50 | 300 | 300 |
Analysis
Samples:
10 µL of the Matrix modifier solution was added into each of the 10-µL aliquots of the five Standard solutions, a mixture of 10 µL of the Matrix modifier solution and 10 µL of the Sample solution, and a mixture of 10 µL of the Matrix modifier solution and 10 µL of the Spiked sample solution
Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the Samples using the Spectrometric conditions described above. Plot the absorbance of each Standard solution, compensated for background correction, versus its content of lead, in µg/mL, and draw the best straight line fitting the five points. From this plot, determine the concentrations, CT and CST, in µg/mL, of lead in the Sample solution and the Spiked sample solution, respectively.
Calculate the percentage recovery taken:
Result = [(CST  CT)/A] × 100
CT)/A] × 100
| A | = | = quantity of lead added to the Spiked sample solution, 0.1 µg/mL |
Calculate the content, in µg/g, of lead in Hydrogenated Polydextrose taken:
Result = (CT/W) × V
| W | = | = weight of Hydrogenated Polydextrose taken to prepare the Sample solution (g) |
| V | = | = volume of the Sample solution, 10 mL |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.5 µg/g; recovery is 80%–120%
• Limit of Nickel
[Note—All glassware used must be soaked in 1% Nitric acid for at least 2 h and then rinsed with water. ]
1% Nitric acid:
Cautiously add 10 mL of nitric acid to a 1000-mL volumetric flask containing about 500 mL of water. Mix, and dilute with water to volume.
Blank solution:
Use 1% Nitric acid.
Nickel stock standard solution:
Immediately before use, dilute an appropriate amount of nickel standard* with 1% Nitric acid to prepare a solution containing the equivalent of 10 µg/mL of nickel.
Standard solutions:
Into four identical 100-mL volumetric flasks, introduce respectively 1.0, 2.0, 5.0, and 10.0 mL of Nickel stock standard solution. Dilute with 1% Nitric acid to volume, and mix. These standards contain 0.1, 0.2, 0.5, and 1.0 µg/mL of nickel.
Sample solution:
Weigh 5 g of Hydrogenated Polydextrose into a 100-mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in and dilute with 1% Nitric acid to volume, and mix.
Spectrometric conditions
Mode:
Atomic absorption spectrophotometer equipped with an air–acetylene flame
Lamp:
Nickel hollow-cathode
Analytical wavelength:
352.0 nm
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution of 0.2 µg/mL of nickel
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 20%
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solutions and Sample solution
Use the Blank solution to zero the instrument. Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the Samples at least three times each. Record the average of the steady readings for each of the Samples. Clear the nebulizer using the Blank solution, and aspirate each of the Samples in turn. The standard chosen for reslope should be run every four to five samples. If there is a significant change in its response, reslope and repeat the previous samples.
Plot the absorbances of the Standard solutions versus concentration, in µg/mL, of nickel, and draw the straight line best fitting the four plotted points. From the graph so obtained, determine the concentration, C, in µg/mL, of nickel in the Sample solution. Calculate the quantity, in µg, of nickel in each g of Hydrogenated Polydextrose taken:
Result = (V × C)/W
| V | = | = volume of the Sample solution, 100 mL |
| W | = | = weight of Hydrogenated Polydextrose taken to prepare the Sample solution (g) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 2 µg/g
Organic Impurities
• Procedure 1: Limit of 5-Hydroxymethylfurfural and Related Compounds
Sample solution:
1.0 g of Hydrogenated Polydextrose, weighed and calculated on the anhydrous and ash-free basis, diluted with water to 100 mL
Analysis:
Determine the absorbance of the Sample solution in a 1-cm quartz cell at 283 nm, with a suitable spectrophotometer, using water as the blank.
Calculate the percentage of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural and related compounds in the Hydrogenated Polydextrose taken:
Result = (V × Mr × A)/(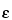 283 × L × W) × 100
283 × L × W) × 100
| V | = | = volume of the Sample solution, 0.1 L |
| Mr | = | = molecular weight of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural, 126 g/mol |
| A | = | = absorbance of the Sample solution |
| = | = molar extinction coefficient of 5-hydroxymethylfurfural at a wavelength of 283 nm, 16,830 L·mol |
|
| L | = | = path length of the spectrophotometer cell (cm) |
| W | = | = weight of Hydrogenated Polydextrose taken to prepare the Sample solution (g) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.1%
• Procedure 2: Limit of Monomers
Mobile phase, Sample solution, and Chromatographic system:
Prepare as directed in the Assay.
Standard solution:
0.08 mg/mL of each for USP 1,6-Anhydro-d-glucose RS and USP Sorbitol RS, and 0.04 mg/mL of USP Dextrose RS, in Mobile phase
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
[Note—See the relative retention times table below. ]
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
|---|---|
| Dextrose (glucose) | 0.7 |
| Sorbitol | 0.8 |
| An isomer of 1,6-anhydro-d-glucose (d-anhydroglucose furanose form) |
0.9 |
| 1,6-Anhydro-d-glucose (levoglucosan) (d-anhydroglucose pyranose form) |
1.0 |
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 1.0
Relative standard derivation:
NMT 5.0%
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Use the peak response of USP 1,6-Anhydro-d-glucose RS in the Standard solution for calculation of the percentage of the isomer of 1,6-anhydro-d-glucose in the Sample solution. Calculate the percentage of each monomer in the portion of Hydrogenated Polydextrose taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response for the respective monomer from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response for the respective monomer from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of the respective standard monomer in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Hydrogenated Polydextrose in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 4.0% of 1,6-anhydro-d-glucose, NMT 5.75% for sorbitol and NMT 0.25% for dextrose
[Note—In the case of 1,6-anhydro-d-glucose, the peak areas for the pyranose and furanose forms are combined. ]
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Molecular Weight Limit
Mobile phase:
Dissolve 35.0 g of sodium nitrate and 1.0 g of sodium azide in 100 mL of water. Dilute with water to 4 L. Pass through a filter of 0.45-µm or finer pore size, and degas by applying an aspirator vacuum for 30 min. The resulting Mobile phase is 0.1 N sodium nitrate containing 0.025% sodium azide.
Standard solution:
Transfer 20 mg each of USP Dextrose RS, stachyose, and 5800-, 23,700-, and 100,000-molecular weight (MW) pullulan standards into a 10-mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in and dilute with Mobile phase to volume. Pass through a syringe filter of 0.45-µm or finer pore size into a suitable autosampler vial, and seal.
Sample solution:
Transfer 50 mg of Hydrogenated Polydextrose into a 10-mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in and dilute with Mobile phase to volume. Pass through a syringe filter of 0.45-µm or finer pore size into a suitable autosampler vial, and seal.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
Refractive index set at a sensitivity of 4 × 10 6 refractive index units full scale and maintained at a temperature of 35 ± 0.1
6 refractive index units full scale and maintained at a temperature of 35 ± 0.1
Column:
7.8-mm × 30-cm; packing L39
Column temperature:
45
Flow rate:
0.8 mL/min
[Note—After installation of a new column, pump Mobile phase through the column overnight at a rate of 0.3 mL/min. Before calibration or analysis, increase the flow slowly over a 1-min period to 0.8 mL/min. Continue to pump Mobile phase through the column at this flow rate for at least 1 h before the first injection. Check the flow gravimetrically, and adjust it if necessary. Reduce the flow rate to about 0.1 mL/min when the system is not in use. ]
Injection size:
50 µL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
Chromatograph five replicate injections of the Standard solution, allowing 15 min between injections, and record the retention times of the components of the Standard solution.
Insert the average retention time along with the molecular weight of each component in the Standard solution into the calibration table of the molecular weight distribution software. Check the regression results for a cubic fit of the calibration points, and obtain a correlation coefficient, R, for the line.
Suitability requirements
Retention time:
The retention times for each component determined on replicate injections agree within ±2 s.
Resolution:
Dextrose and stachyose are baseline resolved from one another and from the 5800-MW pullulan standard.
[Note—Prominent negative baseline valleys are usually observed between the peaks for the 5800-, 23,700-, and 100,000-MW pullulan standards. ]
Correlation coefficient R:
NLT 0.9999
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Use the molecular weight distribution software of the data reduction system to generate a molecular weight distribution plot of Hydrogenated Polydextrose.
Acceptance criteria:
No measurable peak above a molecular weight of 22,000 is found.
• pH  791
791 :
5.0–7.0, in a solution (1 in 10)
:
5.0–7.0, in a solution (1 in 10)
• Water Determination, Method I  921
921 :
NMT 4.0%. Use a mixture of Hydranal Solvent and Hydranal Formamide dry (2:1) as a solvent. Perform the titration at 50
:
NMT 4.0%. Use a mixture of Hydranal Solvent and Hydranal Formamide dry (2:1) as a solvent. Perform the titration at 50 in a jacketed beaker.
in a jacketed beaker.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers. Store in a cool and dry place.
*
Suitable nickel standards are available from e.g., Fisher Scientific, Fair Lawn, NJ (nickel, reference standard solution, 1000 ppm ±1%, certified, application for atomic absorption) or RICCA Chemical Company, Arlington, TX (nickel standard, 1000 ppm Ni, for atomic absorption).
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Robert H. Lafaver, M.S.
Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8335 |
(EXC2010) Monographs - Excipients |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 1898
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 35(5) Page 1210
