Omega-3-Acid Ethyl Esters
DEFINITION
Omega-3-Acid Ethyl Esters are obtained by transesterification of the body oil obtained from fish of families such as Engraulidae, Carangidae, Clupeidae, Osmeridae, Salmonidae, and Scombridae and subsequent purification processes including urea fractionation followed by molecular distillation. The content of eicosapentaenoic acid ethyl ester (EPAee) plus the content of docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester (DHAee) is NLT 800 mg/g and NMT 880 mg/g, with NLT 430 mg/g and NMT 495 mg/g of EPAee and NLT 347 mg/g and NMT 403 mg/g of DHAee. It contains NLT 90% (w/w) of the sum of alpha-linolenic acid ethyl ester (C18:3 n-3, EE), moroctic acid ethyl ester (C18:4 n-3, EE), eicosatetraenoic acid ethyl ester (C20:4 n-3, EE), eicosapentaenoic acid ethyl ester (EPAee) (C20:5 n-3, EE), heneicosapentaenoic acid ethyl ester (C21:5 n-3, EE), docosapentaenoic acid ethyl ester (C22:5 n-3, EE), and docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester (DHAee) (C22:6 n-3, EE). Tocopherol may be added as an antioxidant.
IDENTIFICATION
• The retention times of the peaks for eicosapentaenoic acid ethyl ester and docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester in the Test Solution correspond to those respective compounds in the Standard Solution, as obtained in the Assay.
ASSAY
• Content of EPAee, DHAee, and Total Omega-3-Acids Ethyl Esters
Analysis
Samples:
Standard Solution and Test Solution
Calculate the content of EPAee and DHAee in the portion of Omega-3-Acid Ethyl Esters taken:
Result = (RU/RS) × (CS/CU)
| RU | = | = peak area ratio of the EPAee or DHAee peak to the internal standard peak in Test Solution 3 |
| RS | = | = peak area ratio of the EPAee or DHAee peak to the internal standard peak in Standard Solution 1 |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Eicosapentaenoic Acid Ethyl Ester RS or USP Docosahexaenoic Acid Ethyl Ester RS in Standard Solution 1 (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Omega-3 Ethyl Esters in Test Solution 3 (g/mL) |
Calculate the content of total omega-3-acids ethyl esters in the portion of Omega-3-Acid Ethyl Esters taken:
Result = rFAn–3ee [(EPAee + DHAee)/(rEPAee + rDHAee)] + EPAee + DHAee
| rFAn–3ee | = | = sum of the peak areas of alpha-linolenic acid ethyl ester (C18:3 n-3, EE), moroctic acid ethyl ester (C18:4 n-3, EE), eicosatetraenoic acid ethyl ester (C20:4 n-3, EE), heneicosapentaenoic acid ethyl ester (C21:5 n-3, EE), and docosapentaenoic acid ethyl ester (C22:5 n-3, EE) in Test Solution 4 |
| EPAee | = | = content of EPAee (mg/g) |
| DHAee | = | = content of DHAee (mg/g) |
| rEPAee | = | = peak area of EPAee in Test Solution 4 |
| rDHAee | = | = peak area of DHAee in Test Solution 4 |
Acceptance criteria:
It conforms to the acceptance criteria in Table 1.
Table 1
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
Acceptance Criteria, NLT |
Acceptance Criteria, NMT |
|---|---|---|---|
| C18:3 n-3, EEa | 0.585 | — | — |
| C18:4 n-3, EEb | 0.608 | — | — |
| C20:4 n-3, EEc | 0.777 | — | — |
| C20:5 n-3, EE (EPAee)d | 0.796 | 430 mg/g | 495 mg/g |
| C21:5 n-3, EEe | 0.889 | — | — |
| C22:5 n-3, EEf | 0.977 | — | — |
| C22:6 n-3, EE (DHAee)g | 1.000 | 347 mg/g | 403 mg/g |
| EPAee + DHAee | — | 800 mg/g | 880 mg/g |
| Total omega-3-acid ethyl esters | — | 90% (w/w) | — |
|
a
Alpha-linolenic acid ethyl ester.
b
Moroctic acid ethyl ester.
c
Eicosatetraenoic acid ethyl ester.
d
Eicosapentaenoic acid ethyl ester.
e
Heneicosapentaenoic acid ethyl ester.
f
Docosapentaenoic acid ethyl ester (clupanodonic acid ethyl ester).
g
Docosahexaenoic acid ethyl ester.
|
|||
IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
• Fats and Fixed Oils  401
401 :
NMT 0.1 ppm each of Pb, Cd, As, and Hg
:
NMT 0.1 ppm each of Pb, Cd, As, and Hg
Organic Impurities
• Cholesterol
Internal standard stock solution:
3 mg/mL of 5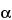 -cholestane in n-heptane
-cholestane in n-heptane
Internal standard solution:
0.3 mg/mL of 5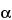 -cholestane in n-heptane. [Note—Prepare fresh prior to use. ]
-cholestane in n-heptane. [Note—Prepare fresh prior to use. ]
Standard stock solution:
3.0 mg/mL of cholesterol in n-heptane. [Note—This solution is stable for 6 months stored in a freezer. ] Transfer 1.0 mL of this solution to a 10.0-mL volumetric flask. Dilute with n-heptane to volume. [Note—Prepare this solution fresh daily. ]
Standard solution:
Transfer 1.0 mL of Standard stock solution and 1.0 mL of Internal standard solution to a 15-mL centrifuge tube. Proceed as directed in the Sample solution beginning with “Evaporate to dryness”.
Alpha tocopherol stock solution:
1.5–2.0 mg/mL of USP Alpha Tocopherol RS in n-heptane. [Note—This solution is stable for 12 months stored in a freezer. ]
System suitability solution:
Mix 1.0 mL of the Standard stock solution, 1.0 mL of the Internal standard stock solution, and 2.0 mL of Alpha tocopherol stock solution in a 50-mL volumetric flask. Evaporate to dryness with the aid of heat, and dilute with ethyl acetate to volume. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution with ethyl acetate to 10.0 mL. [Note—This solution is stable for 6 months stored in a freezer. ]
Sample solution:
Transfer 100 mg of Omega-3-Acid Ethyl Esters to a 15-mL centrifuge tube. Add 1.0 mL of Internal standard solution. Evaporate to dryness at about 50 with a gentle stream of nitrogen. Add 0.5 mL of 50% potassium hydroxide and 3 mL of alcohol, fill the tube with nitrogen, and cap. Heat the sample at 100
with a gentle stream of nitrogen. Add 0.5 mL of 50% potassium hydroxide and 3 mL of alcohol, fill the tube with nitrogen, and cap. Heat the sample at 100 for 60 min, using a heating block. Cool for about 10 min. Add 6 mL of water to the tube, and shake for 1 min. Extract the solution four times with 2.5-mL portions of ethyl ether, using a vortex mixer or suitable shaker for 1 min for each extraction. Transfer and combine the extracts into a large centrifuge tube, and wash with 5 mL of water, mixing completely with gentle inversion. Remove the water phase, and add 5 mL of 0.5 M potassium hydroxide to the ether phase, mixing carefully to avoid an emulsion. Remove the potassium hydroxide, and add another 5 mL of water mixing carefully. Transfer the ether phase into a small centrifuge tube. [Note—If an emulsion has occurred, a small amount of sodium chloride may be added to obtain a separation of the phases. ] Evaporate the ether phase to dryness under a stream of nitrogen with careful heating. Dissolve the sample in 600 µL of ethyl acetate, and mix well. Transfer 200 µL of this solution to a sample vial, and dilute with ethyl acetate to about 2 mL.
for 60 min, using a heating block. Cool for about 10 min. Add 6 mL of water to the tube, and shake for 1 min. Extract the solution four times with 2.5-mL portions of ethyl ether, using a vortex mixer or suitable shaker for 1 min for each extraction. Transfer and combine the extracts into a large centrifuge tube, and wash with 5 mL of water, mixing completely with gentle inversion. Remove the water phase, and add 5 mL of 0.5 M potassium hydroxide to the ether phase, mixing carefully to avoid an emulsion. Remove the potassium hydroxide, and add another 5 mL of water mixing carefully. Transfer the ether phase into a small centrifuge tube. [Note—If an emulsion has occurred, a small amount of sodium chloride may be added to obtain a separation of the phases. ] Evaporate the ether phase to dryness under a stream of nitrogen with careful heating. Dissolve the sample in 600 µL of ethyl acetate, and mix well. Transfer 200 µL of this solution to a sample vial, and dilute with ethyl acetate to about 2 mL.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
GC
Detector:
Flame ionization
Column:
0.25-mm × 30-m capillary column coated with a G27 phase of 0.25-µm thickness
Temperature
Injector:
320
Detector:
300
Column:
See the temperature program table below.
| Initial Temperature ( |
Temperature Ramp ( |
Final Temperature ( |
Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 170 | 0 | 170 | 1 |
| 170 | 4 | 320 | 1.5 |
Carrier gas:
Helium
Flow rate:
1.3 mL/min
Injection size:
1 µL
Injection type:
Splitless injection system
System suitability
Sample:
System suitability solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 1.2 between alpha tocopherol and cholesterol
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the content of total cholesterol in the portion of Omega-3-Acid Ethyl Esters taken:
Result = (RU/RS) × (MS/MU)
| RU | = | = ratio of the cholesterol peak to the internal standard from the Sample solution |
| RS | = | = ratio of the cholesterol peak to the internal standard from the Standard solution |
| MS | = | = weight of cholesterol in the Standard solution (mg) |
| MU | = | = weight of Omega-3-Acid Ethyl Esters in the Sample solution (g) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 3.0 mg/g
• Oligomers
Mobile phase:
Tetrahydrofuran
Sample solution 1:
5.0 mg/mL of Omega-3-Acid Ethyl Esters in tetrahydrofuran
Sample solution 2:
[Note—Use Sample solution 2 where the results of this test using Sample solution 1 exceed the Acceptance criteria due to the presence of monoglycerides. ] Weigh 50 mg of Omega-3-Acid Ethyl Esters into a quartz tube, add 1.5 mL of a 20-g/L solution of sodium hydroxide in methanol, cover with nitrogen, cap tightly with a polytef-lined cap, mix, and heat on a water bath for 7 min. Allow to cool. Add 2.0 mL of boron trichloride–methanol solution, cover with nitrogen, cap tightly, mix and heat on a water bath for 30 min. Cool to 40 –50
–50 , add 1 mL of isooctane, cap, and shake vigorously for NLT 30 s. Immediately add 5 mL of saturated sodium chloride solution, cover with nitrogen, cap, and shake thoroughly for NLT 15 s. Transfer the upper layer to a separate tube. Shake the methanol layer with 1 mL of isooctane. Wash the combined isooctane extracts with 2 quantities, each of 1 mL of water. Carefully evaporate the solvent under a stream of nitrogen, then add 10.0 mL of tetrahydrofuran to the residue. Add a small amount of anhydrous sodium sulfate, and filter.
, add 1 mL of isooctane, cap, and shake vigorously for NLT 30 s. Immediately add 5 mL of saturated sodium chloride solution, cover with nitrogen, cap, and shake thoroughly for NLT 15 s. Transfer the upper layer to a separate tube. Shake the methanol layer with 1 mL of isooctane. Wash the combined isooctane extracts with 2 quantities, each of 1 mL of water. Carefully evaporate the solvent under a stream of nitrogen, then add 10.0 mL of tetrahydrofuran to the residue. Add a small amount of anhydrous sodium sulfate, and filter.
System suitability solution:
Monodocosahexaenoin, didocosahexaenoin, and tridocosahexaenoin in Mobile phase, with concentrations of about 0.5, 0.3, and 0.2 mg/mL, respectively. [Note—Suitable grades of monodocosahexaenoin, didocosahexaenoin, and tridocosahexaenoin may be obtained from Nu-Chek Prep. ]
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
Differential refractometer
Columns:
Three concatenated 7.8-mm × 30-cm columns; 7-µm packing L21, with pore sizes in the range 5–50 nm, arranged with decreasing pore size from the injector to the detector to fulfill the system suitability requirements.
Flow rate:
0.8 mL/min
Injection size:
40 µL
System suitability
Sample:
System suitability solution
Suitability requirements
Elution order:
Tridocosahexaenoin, didocosahexaenoin, and monodocosahexaenoin
Resolution:
NLT 2.0 between monodocosahexaenoin and didocosahexaenoin, and NLT 1.0 between didocosahexaenoin and tridocosahexaenoin
Analysis
Sample:
Sample solution
Measure the areas of the major peaks. Calculate the percentage of oligomers in the portion of Omega-3-Acid Ethyl Esters taken to prepare Sample solution 1:
Result = (rI/rT) × 100
| rI | = | = sum of the areas of the peaks with a retention time less than that of the ethyl esters peaks |
| rT | = | = sum of the areas of all peaks |
Calculate the percentage of oligomers in the portion of Omega-3-Acid Ethyl Esters taken to prepare Sample solution 2:
Result = (rI/rT) × 100
| rI | = | = sum of the areas of all peaks with retention times shorter than that of the methyl esters |
| rT | = | = sum of the areas of all peaks |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 1.0% of oligomers
• Limit of Dioxins, Furans, and Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs):
Determine the content of polychlorinated dibenzo-para-dioxins (PCDDs) and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs) by method No. 1613 revision B of the Environmental Protection Agency. Determine the content of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) by method No. 1668 revision A of the Environmental Protection Agency.
Acceptance criteria:
The sum of PCDDs and PCDFs is NMT 1 pg/g of WHO toxic equivalents. The sum of PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls, IUPAC congeners PCB-28, PCB-52, PCB-101, and PCB-118, PCB-138, PCB-153, PCB-180) is NMT 0.5 ppm.
• Limit of Total Unidentified Fatty Acids Ethyl Esters:
From the chromatogram obtained with Test Solution 4 in the Assay for Content of EPAee, DHAee, and Total Omega-3-Acids Ethyl Esters, determine the peak area of the largest single unidentified peak with a relative retention time different from those in the following table.
| Identified Ethyl Ester |
Relative Retention Time |
|---|---|
| Phytanic acid | 0.416 |
| C16:3 n-4 | 0.431 |
| C16:4 n-1 | 0.468 |
| C18:3 n-6 | 0.557 |
| C18:3 n-4 | 0.574 |
| C18:3 n-3 | 0.585 |
| C18:4 n-3 | 0.608 |
| C18:4 n-1 | 0.618 |
| Furan acid 5 | 0.691 |
| C19:5 | 0.710 |
| C20:3 n-6 | 0.720 |
| C20:4 n-6 | 0.736 |
| Furan acid 7 | 0.744 |
| C20:4 n-3 | 0.777 |
| Furan acid 8 | 0.783 |
| EPA | 0.796 |
| Furan acid 9 | 0.867 |
| C21:5 n-3 | 0.889 |
| C22:4 | 0.917 |
| Furan acid 10 | 0.922 |
| C22:5 n-6 | 0.939 |
| Furan acid 11 | 0.963 |
| C22:5 n-3 | 0.977 |
| DHA | 1.000 |
Calculate the content of unidentified fatty acids ethyl esters in area percentage:
Result = 100  (100 × S Aiee/rT)
(100 × S Aiee/rT)
| Aiee | = | = peak area for each identified ethyl ester in the table above |
| rT | = | = sum of the areas of all peaks except solvents, BHT, and internal standard |
Acceptance criteria:
The area of the largest single unidentified peak is NMT 0.5% of the total area. The total area of unidentified peaks as calculated above is NMT 2%.
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Fats and Fixed Oils  401
401 , Acid Value:
NMT 2.0 mg of KOH/g
, Acid Value:
NMT 2.0 mg of KOH/g
• Fats and Fixed Oils  401
401 , Anisidine Value:
NMT 15
, Anisidine Value:
NMT 15
• Fats and Fixed Oils  401
401 , Peroxide Value:
NMT 10.0
, Peroxide Value:
NMT 10.0
• Absorbance
Sample solution:
Transfer 300 mg, accurately weighed, into a 50-mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in, and dilute immediately with isooctane to volume. Pipet 2.0 mL into a 50-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with isooctane to volume.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.55, determined at 233 nm, with isooctane being used as the blank
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers under a nitrogen atmosphere. Store at controlled room temperature.
• Labeling:
The label states the content of DHA ethyl ester and EPA ethyl ester in mg/g, the sum of the EPA and DHA ethyl esters contents in mg/g, and the content of the total omega-3-acid ethyl esters in percentage (w/w). It also states the name of any added antioxidant.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Docosahexaenoic Acid Ethyl Ester RS 
All cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic ethyl ester.
C24H36O2 356.55

All cis-4,7,10,13,16,19-docosahexaenoic ethyl ester.
C24H36O2 356.55
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Huy T. Dinh, M.S.
Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8594 |
(DS2010) Monographs - Dietary Supplements |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 4110
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 35(5) Page 1190