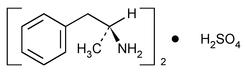Dextroamphetamine Sulfate
(dex'' troe am fet' a meen sul' fate).
Benzeneethanamine,
(+)-
» Dextroamphetamine Sulfate, the dextrorotatory isomer of amphetamine sulfate, contains not less than 98.0 percent and not more than 102.0 percent of (C9H13N)2·H2SO4, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed containers.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
USP Dextroamphetamine Related Compound A RS
1-Phenyl-2-propanol.
C9H12O 136.20 [CAS-14898-87-4].
1-Phenyl-2-propanol.
C9H12O 136.20 [CAS-14898-87-4].
USP Dextroamphetamine Related Compound B RS
Phenyl acetone.
C9H10O 134.18 [CAS-103-79-7].
Phenyl acetone.
C9H10O 134.18 [CAS-103-79-7].
Identification—
B:
The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation corresponds to that in the chromatogram of the Standard preparation, as obtained in the Assay.
pH  791
791 :
between 5.0 and 6.0, in a solution (1 in 20).
:
between 5.0 and 6.0, in a solution (1 in 20).
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 105
—
Dry it at 105 for 2 hours: it loses not more than 1.0% of its weight.
for 2 hours: it loses not more than 1.0% of its weight.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.1%.
:
not more than 0.1%.
Related compounds—
Solution A, Solution B, Mobile phase, Resolution solution, and Chromatographic system—
Prepare as directed in the Assay.
Standard solution—
Use the Standard preparation.
Test solution—
Use the Assay preparation.
Procedure—
Inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, and record the chromatograms. Identify the impurities based on the relative retention times given in Table 1, and measure the peak responses. Calculate the percentage of each dextroamphetamine related compound in the portion of Dextroamphetamine Sulfate taken by the formula:
100(CS / CU)(rU /rS)(1/F)
in which CS and CU are the concentrations, in mg per mL, of dextroamphetamine sulfate in the Standard solution and the Test solution, respectively; rU is the peak area of each impurity obtained from the Test solution; rS is the peak area of dextroamphetamine obtained from the Standard solution; and F is the relative response factor for each of the impurities relative to dextroamphetamine.
Table 1
| Related Compound |
Relative Retention Time (RRT) |
Relative Response Factor (F) |
Limit (w/w %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cathinone | 0.81 | 55.6 | NMT 0.25 |
| Dextroamphetamine | 1.0 | 1.0 | — |
| Benzaldehyde | 1.73 | 105.3 | NMT 0.25 |
| Dextroamphetamine related compound A | 1.88 | 1.5 | NMT 0.25 |
| Dextroamphetamine related compound B | 2.05 | 1.8 | NMT 0.25 |
| Individual unspecified impurity | — | 1.0 | NMT 0.1 |
| Total | — | — | NMT 1.0 |
Assay—
Solution A—
Add 5.0 mL of trifluoroacetic acid to 900 mL of water; adjust with ammonium hydroxide to a pH of 2.2±0.1; then add 100 mL of acetonitrile. Mix well, and degas.
Solution B—
Use degassed acetonitrile.
Mobile phase—
Use variable mixtures of Solution A and Solution B as directed for Chromatographic system. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Standard preparation—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Dextroamphetamine Sulfate RS in a suitable volumetric flask, and dilute quantitatively with Solution A to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 2.0 mg per mL.
Resolution solution—
Transfer about 40 mL of the Standard preparation to a 50-mL volumetric flask. Using a microliter syringe, add 1 µL each of USP Dextroamphetamine Related Compound A RS and USP Dextroamphetamine Related Compound B RS. Dilute with Standard preparation to volume.
Assay preparation—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of Dextroamphetamine Sulfate in a suitable volumetric flask, and dilute quantitatively with Solution A to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 2.0 mg per mL.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 257-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. The column is maintained at 40
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 257-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. The column is maintained at 40 . The chromatograph is programmed as follows, and data is collected for 30 minutes.
. The chromatograph is programmed as follows, and data is collected for 30 minutes.
Chromatograph the Resolution solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure. Identify the peaks using the relative retention times given in Table 1: the resolution, R, between dextroamphetamine related compound A and dextroamphetamine related compound B is not less than 3.0; the tailing factor for dextroamphetamine sulfate is not more than 3.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections of the Standard preparation is not more than 2.0%. [note—For identification purposes, the approximate relative retention times are given in Table 1. ]
| Time (minutes) |
Solution A
(%) |
Solution B
(%) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–15 | 100®65 | 0®35 | linear gradient |
| 15–20 | 65®0 | 35®100 | linear gradient |
| 20–22 | 0 | 100 | isocratic |
| 22–23 | 0®100 | 100®0 | linear gradient |
| 23–30 | 100 | 0 | re-equilibration |
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the dextroamphetamine peak. Calculate the quantity, in percent of (C9H13N)2·H2SO4, in the portion of Dextroamphetamine Sulfate taken by the formula:
100(CS / CU)(rU / rS)
in which CS and CU are the concentrations of dextroamphetamine sulfate, in mg per mL, of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation, respectively; and rU and rS are the peak responses for dextroamphetamine sulfate in the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Ravi Ravichandran, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8330 |
(SM42010) Monographs - Small Molecules 4 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 2858
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 34(4) Page 921