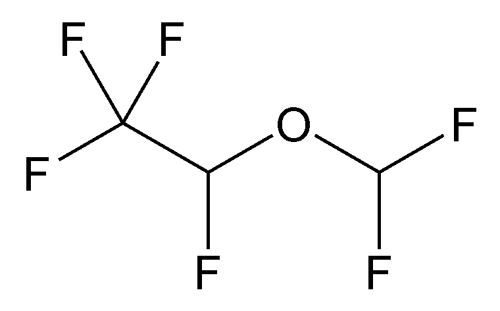
Desflurane
C3H2F6O 168.04
Ethane, 2-(difluoromethoxy)-1,1,1,2-tetrafluoro-, (±)-;
(±)-2-Difluoromethyl 1,2,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl ether

 [57041-67-5].
[57041-67-5].
(des floo' rane).
C3H2F6O 168.04
Ethane, 2-(difluoromethoxy)-1,1,1,2-tetrafluoro-, (±)-;
(±)-2-Difluoromethyl 1,2,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl ether
DEFINITION
Desflurane contains NLT 99.7% and NMT 100.0% of C3H2F6O.
IDENTIFICATION
• The IR absorption spectrum of Desflurane obtained using a gas cell exhibits maxima only at the same wavelengths as that of a similar preparation of USP Desflurane RS.
ASSAY
• Procedure
Using the results from the Organic Impurities procedure, calculate the percentage of C3H2F6O in the sample of Desflurane taken by subtracting the sum of all impurities found from 100.0%.
Acceptance criteria:
99.7%–100.0%
IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
• Limit of Nonvolatile Residue:
Transfer 20.0 mL of Desflurane to an evaporating dish, and evaporate with a stream of nitrogen to dryness: the weight of the residue does not exceed 2.0 mg (0.01%).
• Limit of Antimony
Diluent A:
Nitric acid and water (1:1)
Diluent B:
Nitric acid and hydrochloric acid (9:1)
Standard solutions:
Transfer 0.1 mL (234 mg) of antimony pentachloride to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dilute with Diluent B to volume, and mix. This stock solution contains about 1906 µg of antimony/mL. Dilute a portion of this solution quantitatively and stepwise with Diluent B to obtain Standard solutions containing 2.5, 5.0, and 10.0 µg of antimony/mL.
Sample solution:
Weigh a stoppered stock bottle containing a quantity of Desflurane at ambient temperature, and then cool it in powdered dry ice. Using a cold syringe, transfer 5–7 mL of Desflurane from the cold bottle to a separator containing 20 mL of Diluent A. Allow the stock bottle containing the remaining Desflurane to come to ambient temperature, weigh it, and calculate the quantity, in g, of Desflurane taken for the test. Allow the Desflurane in the separator to evaporate, and with the aid of a few mL of Diluent A, transfer the acid solution to a clean, dry beaker. Add 1 mL of hydrochloric acid to the solution in the beaker, and reduce the volume to 8 mL by evaporating on a hot plate. Transfer this solution to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with Diluent B to volume.
Spectrometric conditions
Mode:
Atomic absorption spectrophotometer
Analytical wavelength:
Antimony emission line at 217.6 nm
Lamp:
Antimony hollow-cathode
Flame:
Air–acetylene
Blank:
Diluent B
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solutions and Sample solution
Calculation:
Plot the absorbances of the Standard solutions versus the concentration (µg/mL) of antimony, and draw the straight line best fitting the three plotted points. From the graph so obtained, determine the concentration of antimony in the Sample solution.
Calculate the quantity, in µg/g, of antimony in the portion of Desflurane taken:
Result = (C/W) × V
| C | = | = concentration of antimony in the Sample solution (µg/mL) |
| W | = | = weight of Desflurane taken to prepare the Sample solution (g) |
| V | = | = volume of Sample solution |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 3 µg/g
• Limit of Fluoride
[Note—Store all solutions except Solution A in plastic containers. ]
Solution A:
57 mL of glacial acetic acid, 58 g of sodium chloride, and 4 g of (1,2-cyclohexylenedinitrilo)tetraacetic acid in 500 mL of water. Adjust with 5 N sodium hydroxide to a pH of 5.25 ± 0.25, and dilute with water to 1000 mL. An equivalent commercial preparation may be used.
Standard stock solution:
2210 µg/mL of USP Sodium Fluoride RS in water. Each mL of this solution contains 1000 µg of fluoride/mL.
Standard solutions:
Dilute volumes of Standard stock solution with Solution A to obtain solutions with concentrations of 0.1, 0.3, 0.5, 1.0, 3.0, and 5.0 µg of fluoride/mL.
Sample solution:
Transfer 20.0 mL of Desflurane to a 60-mL separator, add 20.0 mL of water, shake for 1 min, and allow the layers to separate. Drain the lower organic layer and a small portion of the aqueous layer into a beaker, and discard. Transfer 10.0 mL of the aqueous phase remaining in the separator to a plastic cup, and add 10.0 mL of Solution A.
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solutions and Sample solution
Concomitantly measure the potentials (see pH  791
791 ), in mV, of the Samples with a pH meter capable of a minimum reproducibility of ±0.2 mV and equipped with a fluoride-specific ion-indicating electrode and a calomel reference electrode.
), in mV, of the Samples with a pH meter capable of a minimum reproducibility of ±0.2 mV and equipped with a fluoride-specific ion-indicating electrode and a calomel reference electrode.
[Note—When taking measurements, immerse the electrodes in the solution, stir with a polytef-coated stirring bar and a magnetic stirrer having an insulated top until equilibrium is attained (about 1–2 min), and record the potential. Rinse the electrodes with Solution A, and dry, taking care to avoid damaging the crystal of the specific-ion electrode. ]
Plot the logarithms of the fluoride concentrations (µg/mL) of the Standard solutions versus the potential, in mV. From the measured potential of the Sample solution and the standard response line, determine the concentration, C (µg/mL), of fluoride in the Sample solution. Multiply C by 0.0002 to obtain the percentage of fluoride in the portion of Desflurane taken.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.001%
Organic Impurities
• Procedure
Standard stock solution:
To a suitable tared vial, fitted with a septum, add 20 mL (29.4 g) of Desflurane. Seal and re-weigh the vial to determine the weight of Desflurane added. To this vial sequentially add 20 µL of USP Desflurane Related Compound A RS, 23 µL of dichloromethane, 20 µL of chloroform, 38 µL of acetone, and 21 µL of USP Isoflurane RS. Record the weight after the addition of each impurity and determine the total weight.
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the Standard stock solution:
Result = WI/WT × PI
| WI | = | = weight of each impurity added (g) |
| WT | = | = total weight of the Standard stock solution (g) |
| PI | = | = purity of each impurity added (%) |
Standard solution:
To a suitable tared vial, fitted with a septum, add 10.2 mL (15 g) of Desflurane. Seal and re-weigh the vial to determine the weight of Desflurane added. To this vial add 250 µL of the Standard stock solution, and record the weight to determine the weight of the Standard stock solution added and the final weight of the Standard solution.
Calculate the spiked concentration (CS) of each impurity in the Standard solution:
Result = WI/WT × CI
| WI | = | = weight of Standard stock solution added (g) |
| WT | = | = total weight of the Standard solution (g) |
| CI | = | = concentration of each impurity in the Standard stock solution (%) |
System suitability solution:
To a suitable vial, fitted with a septum, add 10.2 mL (15 g) of Desflurane. Seal the vial. To this vial add 100 µL of the Standard stock solution.
Sample:
Desflurane
Chromatographic system
Mode:
GC
Detector:
Flame ionization
Column:
0.32-mm × 105-m capillary column coated with 1.5-µm film of G6
Carrier gas:
Helium
Autosampler/Syringe temperature:
2 –5
–5
Flow rate:
3 mL/min
Split flow:
25 mL/min
Temperature
Injection port:
150
Detector:
200
Column:
See the temperature program table below.
| Initial Temperature ( |
Temperature Ramp ( |
Final Temperature ( |
Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 30 | — | 30 | 11 |
| 30 | 20 | 50 | 13 |
Injection size:
3 µL
System suitability
Samples:
Standard solution and System suitability solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 3.0 between isoflurane and dichloromethane, Standard solution
Tailing factor:
NMT 1.5 for isoflurane, Standard solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 5% for each impurity, Standard solution
Signal-to-noise ratio:
NLT 40 for isoflurane, System suitability solution
Analysis
[Note—Injections of Desflurane used to prepare the Standard solution must be made to estimate the amount of known impurities that may be present in the solvent. The final concentration of each impurity is equal to the concentration of the impurity added plus the concentration inherent in the matrix. ]
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the final concentration of each impurity in the Standard solution:
Result = rU/(rS  rU) × CS + CS
rU) × CS + CS
| rU | = | = peak response of each impurity from the Desflurane used as the solvent |
| rS | = | = peak response of each impurity from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = spiked concentration of each impurity in the Standard solution (%) |
Calculate the percentage of each impurity observed in the Sample solution that is also present in the Standard solution:
Result = (rU/rS) × CF
| rU | = | = peak response of each impurity from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of each impurity from the Standard solution |
| CF | = | = final concentration of each impurity in the Standard solution (%) |
Calculate the percentage of all other impurities:
Result = (rU/rS) × CS × 1/F
| rU | = | = peak response of each impurity from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of Isoflurane from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Isoflurane RS in the Standard solution (%) |
| F | = | = relative response factor relative to isoflurane (see Impurity Table 1) |
Acceptance criteria:
See Impurity Table 1.
Total impurities:
NMT 0.3%
Impurity Table 1
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
Relative Response Factor |
Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Desfluranea | 1.0 | — | — |
| Dichlorofluoromethane | 1.04 | 0.43 | 0.01 |
| Trichlorofluoromethane | 1.07 | 0.15 | 0.001 |
| Desflurane related compound Ab,a | 1.12 | — | 0.10 |
| Trichlorotrifluoroethane | 1.35 | 1.3 | 0.001 |
| Dichloromethanea | 1.44 | — | 0.001 |
| Isofluranea | 1.55 | 1.0 | 0.20 |
| Chloroforma | 1.88 | — | 0.006 |
| Acetonea | 2.12 | — | 0.010 |
|
a
These impurities are present in the Standard solution and are quantified by external standards.
b
Bis-(1,2,2,2-tetrafluoroethyl)ether.
|
|||
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Acidity or Alkalinity
Bromocresol purple solution:
0.5 mg/mL of bromocresol purple. Prepared by dissolving 50 mg of bromocresol purple in 0.92 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide and 20 mL of ethanol, and then diluting with water to 100 mL.
Sample solution:
Transfer 20 mL of Desflurane to a separatory funnel, and add 20 mL of carbon dioxide-free water. Shake for 3 min, allow the layers to separate, and discard the lower organic layer. Collect the upper layer, and add 0.2 mL of Bromocresol purple solution.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.1 mL of 0.01 M sodium hydroxide or 0.6 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid is required to change the color of the indicator.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers. Store at controlled room temperature. Replace the cap securely after each use.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Sodium Fluoride RS
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Domenick Vicchio, Ph.D.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-998-6828 |
(SM42010) Monographs - Small Molecules 4 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 2823
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 36(1) Page 93