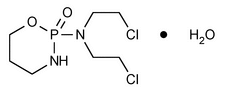Cyclophosphamide
C7H15Cl2N2O2P·H2O 279.10
C7H15Cl2N2O2P 261.09
2H-1,3,2-Oxazaphosphorin-2-amine, N,N-bis(2-chloroethyl)tetrahydro-, 2-oxide, monohydrate, (±);
(±)-2-[Bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]tetrahydro-2H-1,3,2-oxazaphosphorine 2-oxide monohydrate

 [6055-19-2].
[6055-19-2].
Anhydrous

 [50-18-0].
[50-18-0].
(sye'' kloe fos' fa mide).
C7H15Cl2N2O2P·H2O 279.10
C7H15Cl2N2O2P 261.09
2H-1,3,2-Oxazaphosphorin-2-amine, N,N-bis(2-chloroethyl)tetrahydro-, 2-oxide, monohydrate, (±);
(±)-2-[Bis(2-chloroethyl)amino]tetrahydro-2H-1,3,2-oxazaphosphorine 2-oxide monohydrate
Anhydrous
DEFINITION
Cyclophosphamide contains NLT 97.0% and NMT 103.0% of C7H15Cl2N2O2P, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
[Caution—Great care should be taken in handling Cyclophosphamide, as it is a potent cytotoxic agent.
]
IDENTIFICATION
• B.
The retention time of the major peak of the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution, as obtained in the Assay.
ASSAY
• Procedure
Mobile phase:
Acetonitrile and water (3:7)
Ethylparaben solution:
Dissolve 185 mg of ethylparaben in 250 mL of alcohol in a 1000-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
System suitability solution:
Transfer USP Cyclophosphamide RS, equivalent to 25 mg of anhydrous cyclophosphamide, to a 50-mL volumetric flask, add 25 mL of water, and shake to dissolve the USP Reference Standard. Add 5.0 mL of Ethylparaben solution, and dilute with water to volume.
Standard solution:
0.5 mg/mL of USP Cyclophosphamide RS in water
Sample solution:
0.5 mg/mL of Cyclophosphamide in water
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 195 nm
Column:
3.9-mm × 30-cm; packing L1
Flow rate:
1.5 mL/min
Injection size:
25 µL
System suitability
Sample:
System suitability solution
[Note—The relative retention times for cyclophosphamide and ethylparaben are about 0.7 and 1.0, respectively. ]
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 2 between cyclophosphamide and ethylparaben
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 2% from six replicate injections, cyclophosphamide peak
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of C7H15Cl2N2O2P in the Cyclophosphamide taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Cyclophosphamide RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL). [Note—Concentration is calculated on the anhydrous basis. ] |
| CU | = | = concentration of Cyclophosphamide in the Sample solution (mg/mL). [Note—Nominal concentration is calculated on the anhydrous basis. ] |
Acceptance criteria:
97.0%–103.0% on the anhydrous basis
IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
Organic Impurities
• Procedure 1: Limit of Propanolamine
Diluent:
Methylene chloride and dehydrated alcohol (17:3)
Standard solution:
12.5 µg/mL of USP Propanolamine RS in Diluent. [Note—Propanolamine in the Standard solution is 0.025% of Cyclophosphamide in the Sample solution. ]
Sample solution:
50 mg/mL of Cyclophosphamide in Diluent
Chromatographic system
Mode:
TLC
Adsorbent:
0.1-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel
Application volume:
2 µL
Developing solvent system A:
Toluene, methylene chloride, and methanol (5:5:1). Prepare at time of use.
Developing solvent system B:
Methanol and glacial acetic acid (9:1)
Solution A:
Hydrochloric acid and water (7:18)
Solution B:
5 g/L of potassium permanganate in water
Reagent A:
Solution A and Solution B (1:1). [Note—Mix in a small beaker at the time of use under a fume hood to generate chlorine gas, and immediately place the beaker with solution into closed TLC chamber (placed in a fume hood). ]
Reagent B:
100 mg of tetramethylbenzidine in 2.5 mL of methylene chloride, and diluted with cyclohexane to 100 mL
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Develop with Developing solvent system A over a path of 7 cm followed by air drying for 15 min. Develop again in Developing solvent system B over a path of 2 cm followed by air drying for NLT 10 min. [Note—Transfer Developing solvent system B to the chamber 15 min before development. ] Dry the plate at 45 under a vacuum for 50 min. Place the plate in a closed chromatography tank (placed in a fume hood) containing Reagent A, and leave the plate in the tank for 10 min. Remove the plate and place it in a fume hood for 10 min to remove the excess chlorine. Stain the plate by dipping it into Reagent B. Remove it from Reagent B and wait for 15 min, evaluate it with a suitable densitometer, equipped with a filter having its maximum transmittance at 375 nm, and locate and scan the spot produced by propanolamine from the Standard solution and any spot from the Sample solution having the same RF as that produced by propanolamine from the Standard solution.
under a vacuum for 50 min. Place the plate in a closed chromatography tank (placed in a fume hood) containing Reagent A, and leave the plate in the tank for 10 min. Remove the plate and place it in a fume hood for 10 min to remove the excess chlorine. Stain the plate by dipping it into Reagent B. Remove it from Reagent B and wait for 15 min, evaluate it with a suitable densitometer, equipped with a filter having its maximum transmittance at 375 nm, and locate and scan the spot produced by propanolamine from the Standard solution and any spot from the Sample solution having the same RF as that produced by propanolamine from the Standard solution.
Acceptance criteria
Propanolamine:
The spot of propanolamine from the Sample solution is not more intense than the spot of propanolamine from the Standard solution (0.025%).
• Procedure 2: Limit of Degradation Products
Diluent:
Methanol and water (1:1)
Standard solution A:
12 µg/mL of USP Cyclophosphamide Related Compound A RS in Diluent
Standard solution B:
12 µg/mL of USP Cyclophosphamide Related Compound B RS in Diluent
Standard solution C:
12 µg/mL of USP Cyclophosphamide Related Compound C RS in Diluent
Standard solution D:
15 µg/mL of USP Cyclophosphamide Related Compound D RS in Diluent.
[Note—Cyclophosphamide related compound D is free base (Mr = 260.66) and USP Cyclophosphamide Related Compound D RS is available as dihydrochloride salt (Mr = 333.58). ]
Standard solution E:
12 µg/mL of USP Cyclophosphamide RS in Diluent
Sample solution:
20 mg/mL of Cyclophosphamide in Diluent
Chromatographic system
Mode:
TLC
Adsorbent:
0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel mixture containing a fluorescent indicator
Application volume:
20 µL
Developing solvent system:
Methylene chloride, glacial acetic acid, methanol, and water (50:25:15:12)
Reagent A:
3.16 g/L solution of potassium permanganate in water and 10% hydrochloric acid (1:1). [Note—Mix in a small beaker at the time of use under a fume hood to generate chlorine gas, and immediately place the beaker with solution into closed TLC chamber (placed in a fume hood). ]
Reagent B:
Dissolve 250 mg of tetramethylbenzidine in 50 mL of dehydrated alcohol, and dilute with cyclohexane to 200 mL.
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution A, Standard solution B, Standard solution C, Standard solution D, Standard solution E, and Sample solution
[Note—Apply Standard solution E after the plate development in the Developing solvent system. Proceed as directed in the Analysis below. ]
Develop with Developing solvent system over a path of 10 cm followed by drying at room temperature for 15 min in a fume hood. Develop again in the fresh portion of the Developing solvent system over a path of 10 cm followed by drying at room temperature for 15 min in a fume hood. Apply Standard solution E at the starting point of the plate. Dry the plate in an oven at 50 under a vacuum for 20 min or using a TLC heating plate at 50
under a vacuum for 20 min or using a TLC heating plate at 50 for 20 min in a fume hood. Allow the plate to stand at room temperature for 5 min. Place the plate in a closed chromatography tank (placed in a fume hood) containing Reagent A, and leave the plate in the tank for 15 min. Remove the plate and place it in a fume hood for 15 min to remove the excess chlorine. Stain the plate by dipping it into Reagent B or spraying it with Reagent B. Examine the plate by visual evaluation.
for 20 min in a fume hood. Allow the plate to stand at room temperature for 5 min. Place the plate in a closed chromatography tank (placed in a fume hood) containing Reagent A, and leave the plate in the tank for 15 min. Remove the plate and place it in a fume hood for 15 min to remove the excess chlorine. Stain the plate by dipping it into Reagent B or spraying it with Reagent B. Examine the plate by visual evaluation.
Acceptance criteria
The spot of cyclophosphamide related compound A from the Sample solution is not more intense than the spot of cyclophosphamide related compound A from Standard solution A (0.06%).
The spot of cyclophosphamide related compound B from the Sample solution is not more intense than the spot of cyclophosphamide related compound B from Standard solution B (0.06%).
The spot of cyclophosphamide related compound C from the Sample solution is not more intense than the spot of cyclophosphamide related compound C from Standard solution C (0.06%).
The spot of cyclophosphamide related compound D from the Sample solution is not more intense than the spot of cyclophosphamide related compound D from Standard solution D (0.06%).
The spot of any individual unspecified impurity in the Sample solution is not more intense than the spot of cyclophosphamide from Standard solution E (0.06%).
Individual impurities:
See Impurity Table 1.
Impurity Table 1
| Name | Retardation Factor |
Acceptance Criteria, NMT (%) |
|
|---|---|---|---|
| Cyclophosphamide related compound Da | 0.15 | 0.06 | |
| Cyclophosphamide related compound Cb | 0.20 | 0.06 | |
| Cyclophosphamide related compound Bc | 0.43 | 0.06 | |
| Cyclophosphamide related compound Ad | 0.90 | 0.06 | |
| Any unspecified impurity | — | 0.06 | |
|
a
3-[2-(2-Chloroethylamino)ethylamino]propyl dihydrogen phosphate.
b
3-Aminopropyl dihydrogen phosphate.
c
3-(2-Chloroethyl)-2-oxo-2-hydroxy-1,3,6,2-oxadiazaphosphonane.
d
Bis(2-chloroethyl)amine hydrochloride.
|
|||
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Limit of Chloride
Sample solution:
Dissolve 2.0 g of Cyclophosphamide in 30 mL of water, and add 80 mL of isopropyl alcohol and 5 mL of 10% nitric acid.
Analysis:
Titrate potentiometrically with 0.01 N silver nitrate VS. Perform a blank determination, and make any necessary correction (see Titrimetry  541
541 ). Each 1.0 mL of 0.01 N silver nitrate equals 0.355 mg of chloride ion.
). Each 1.0 mL of 0.01 N silver nitrate equals 0.355 mg of chloride ion.
Calculate the percentage of chloride in the portion of Cyclophosphamide taken:
Result = [(V  B) × N × F × 100]/[TN × W × (100
B) × N × F × 100]/[TN × W × (100  A)/100]
A)/100]
| V | = | = sample titrant volume (mL) |
| B | = | = blank titrant volume (mL) |
| N | = | = titrant normality |
| F | = | = equivalence factor, 0.355 mg of chloride ion/mL of TN |
| TN | = | = theoretical normality, 0.01 N |
| W | = | = sample weight (mg) |
| A | = | = assay correction for water |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.033%
• Limit of Phosphate
Diluent:
0.2 g/mL of hydrochloric acid in water
Solution A:
Heat 20 g of tin with 85 mL of hydrochloric acid until no more hydrogen is released. Allow to cool. Transfer 1.0 mL of this solution into a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with Diluent to volume.
Standard stock solution:
0.72 g/L of monobasic potassium phosphate. Transfer 1.0 mL of this solution into a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Prepare immediately before use.
Standard solution:
Standard stock solution and water (1:49). Prepare immediately before use. [Note—This solution contains 100 µg/L of PO4. ]
Sample solution:
Dissolve 100 mg of Cyclophosphamide in water, and dilute to 100 mL.
Analysis:
To the Sample solution add 4 mL of sulfomolybdic acid TS. Shake and add 0.1 mL of Solution A. Prepare a standard in the same manner using the Standard solution. After 10 min, compare the colors using 20 mL of each solution in color comparison tubes in diffused daylight, viewing vertically against a white background.
Acceptance criteria:
Any color from the Sample solution is not more intense than that from the Standard solution (NMT 0.01%).
• Bacterial Endotoxins Test  85
85 :
Where the label states that Cyclophosphamide is sterile, it contains NMT 0.0625 USP Endotoxin Unit/mg of cyclophosphamide.
:
Where the label states that Cyclophosphamide is sterile, it contains NMT 0.0625 USP Endotoxin Unit/mg of cyclophosphamide.
• Sterility Tests  71
71 :
Where the label states that Cyclophosphamide is sterile, it meets the requirements.
:
Where the label states that Cyclophosphamide is sterile, it meets the requirements.
• pH  791
791 :
3.9–7.1, in a solution (1 in 100), determined 30 min after its preparation
:
3.9–7.1, in a solution (1 in 100), determined 30 min after its preparation
• Water Determination, Method I  921
921 :
5.7%–6.8%
:
5.7%–6.8%
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight containers at a temperature between 2 and 30
and 30 .
.
• Labeling:
Where the label states that Cyclophosphamide is sterile, the tests for Bacterial Endotoxins Test  85
85 and Sterility Tests
and Sterility Tests  71
71 should be performed.
should be performed.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Cyclophosphamide Related Compound A RS 
Bis(2-chloroethyl)amine hydrochloride.
C4H9Cl2N·HCl 178.49

Bis(2-chloroethyl)amine hydrochloride.
C4H9Cl2N·HCl 178.49
USP Cyclophosphamide Related Compound B RS 
3-(2-Chloroethyl)-2-oxo-2-hydroxy-1,3,6,2-oxadiazaphosphonane.
C7H16ClN2O3P 242.64

3-(2-Chloroethyl)-2-oxo-2-hydroxy-1,3,6,2-oxadiazaphosphonane.
C7H16ClN2O3P 242.64
USP Cyclophosphamide Related Compound D RS 
3-[2-(2-Chloroethylamino)ethylamino]propyl dihydrogen phosphate dihydrochloride.
C7H18ClN2O4P·2HCl 333.58

3-[2-(2-Chloroethylamino)ethylamino]propyl dihydrogen phosphate dihydrochloride.
C7H18ClN2O4P·2HCl 333.58
USP Endotoxin RS
USP Propanolamine RS
3-Aminopropan-1-ol.
C3H9NO 75.11
3-Aminopropan-1-ol.
C3H9NO 75.11
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Feiwen Mao, M.S.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8320 |
(SM32010) Monographs - Small Molecules 3 |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 2788
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 35(5) Page 1126