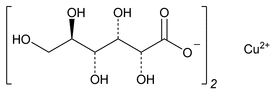
Copper Gluconate
(kop' er gloo' koe nate).
DEFINITION
Copper Gluconate contains NLT 98.0% and NMT 102.0% of copper gluconate (C12H22CuO14).
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Identification Tests—General, Copper  191
191 :
A 50-mg/mL solution meets the requirements.
:
A 50-mg/mL solution meets the requirements.
• B. Thin-Layer Chromatographic Identification Test
Standard solution:
10 mg/mL of USP Potassium Gluconate RS
Sample solution:
10 mg/mL of Copper Gluconate, heating in a water bath at 60 , if necessary, to dissolve
, if necessary, to dissolve
Chromatographic system
Mode:
TLC
Adsorbent:
0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel
Application volume:
5 µL
Developing solvent system:
Alcohol, ethyl acetate, ammonium hydroxide, and water (50:10:10:30)
Spray reagent:
Dissolve 2.5 g of ammonium molybdate in 50 mL of 2 N sulfuric acid in a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 1.0 g of ceric sulfate, swirl to dissolve, and dilute with 2 N sulfuric acid to volume.
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Develop the chromatogram until the solvent front has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the chamber, and dry at 110 for 20 min. Allow to cool, and spray with the Spray reagent. Heat the plate at 110
for 20 min. Allow to cool, and spray with the Spray reagent. Heat the plate at 110 for about 10 min.
for about 10 min.
Acceptance criteria:
The principal spot of the Sample solution corresponds in color, size, and RF value to that of the Standard solution.
ASSAY
• Procedure
Sample:
1.5 g of Copper Gluconate
Blank:
100 mL of water
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry  541
541 .)
.)
Mode:
Indirect titration
Titrant:
0.1 N sodium thiosulfate VS
Endpoint detection:
Visual
Analysis:
Dissolve the Sample in 100 mL of water. Add 2 mL of glacial acetic acid and 5 g potassium iodide, mix, and titrate with Titrant to a light yellow color. Add 2 g of ammonium thiocyanide, and mix. Add 3 mL of starch TS, and continue titrating to a milk-white endpoint. Perform the Blank determination.
Calculate the percentage of copper gluconate (C12H22CuO14) in the Sample taken:
Result = {[(VS  VB) × N × F]/W} × 100
VB) × N × F]/W} × 100
| VS | = | = Titrant volume consumed by the Sample (mL) |
| VB | = | = Titrant volume consumed by the Blank (mL) |
| N | = | = actual normality of the Titrant (mEq/mL) |
| F | = | = equivalency factor, 453.8 mg/mEq |
| W | = | = Sample weight (mg) |
Acceptance criteria:
98.0%–102.0%
IMPURITIES
• Chloride and Sulfate, Chloride  221
221
Standard solution:
1.0 mL of 0.020 N hydrochloric acid
Sample:
1.0 g
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.07%
• Chloride and Sulfate, Sulfate  221
221
Standard solution:
1.0 mL of 0.020 N sulfuric acid
Sample:
2.0 g
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.05%
• Limit of Lead
[Note—For the preparation of all aqueous solutions and for the rinsing of glassware before use, use water that has been passed through a strong-acid, strong-base, mixed-bed ion-exchange resin. Select all reagents to have as low a content of lead as practicable, and store all reagent solutions in containers of borosilicate glass. Cleanse glassware before use by soaking in warm 8 N nitric acid for 30 min and by rinsing with deionized water. ]
Standard stock solution:
Transfer 10.0 mL of Lead Nitrate Stock Solution, prepared as directed in Heavy Metals  231
231 , to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 40 mL of water and 5 mL of nitric acid, and dilute with water to volume.
, to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 40 mL of water and 5 mL of nitric acid, and dilute with water to volume.
Standard solution:
Transfer 0.40 mL of Standard stock solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 50 mL of water and 1 mL of nitric acid, and dilute with water to volume. This solution contains 0.04 µg/mL of lead.
Sample stock solution:
Transfer 4 g of Copper Gluconate to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 50 mL of water and 5 mL of nitric acid, and sonicate to dissolve the specimen. Dilute with water to volume. Transfer 4.0 mL of this solution to a second 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 50 mL of water and 1 mL of nitric acid, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Blank:
Transfer 1.2 mL of nitric acid to a 100-mL volumetric flask and dilute with water to volume.
Sample solution A:
Mix 10.0 mL of the Sample stock solution with 10.0 mL of Blank. This solution contains 0.00 µg/mL of added lead from the Standard solution.
Sample solution B:
Mix 10.0 mL of the Sample stock solution with 4.0 mL of the Standard solution and 6.0 mL of Blank. This solution contains 0.008 µg/mL of added lead from the Standard solution.
Sample solution C:
Mix 10.0 mL of the Sample stock solution with 7.0 mL of the Standard solution and 3.0 mL of Blank. This solution contains 0.014 µg/mL of added lead from the Standard solution.
Sample solution D:
Mix 10.0 mL of the Sample stock solution with 10.0 mL of the Standard solution. This solution contains 0.020 µg/mL of added lead from the Standard solution.
Instrumental conditions
Mode:
Graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometry
Analytical wavelength:
283.3 nm
Lamp:
Lead hollow-cathode
Argon flow rate:
3 L/min, or as noted
Graphite tube temperature:
See Table 1.
Table 1
| Temperature ( |
Time (s) |
|---|---|
| 70 | 10 |
| 90 | 60 |
| 120 | 15 |
| 250 (no gas flow) | 5 |
| 250 | 10 |
| 250 (no gas flow) | 2 |
| 2000 | 3.2 |
Injection volume:
20 µL
Analysis
Samples:
Blank and Sample solutions A, B, C, and D
The graphite tube is temperature-programmed to reach 2000 in about 2 min, as shown in Table 1. When the temperature reaches 2000
in about 2 min, as shown in Table 1. When the temperature reaches 2000 , determine the absorbance at 283.3 nm, corrected for background absorption. Inject the Sample solutions and Blank, and determine the absorbances. Correct the absorbance values from the Sample solutions by subtracting from each the absorbance value from the Blank. Plot the corrected absorbances of the Sample solutions versus their added lead concentrations, in µg/mL. Draw the straight line best fitting the four points, and extrapolate the line until it intercepts the concentration axis. From the intercept, determine the concentration, C, in µg/mL, of lead in Sample solution A.
, determine the absorbance at 283.3 nm, corrected for background absorption. Inject the Sample solutions and Blank, and determine the absorbances. Correct the absorbance values from the Sample solutions by subtracting from each the absorbance value from the Blank. Plot the corrected absorbances of the Sample solutions versus their added lead concentrations, in µg/mL. Draw the straight line best fitting the four points, and extrapolate the line until it intercepts the concentration axis. From the intercept, determine the concentration, C, in µg/mL, of lead in Sample solution A.
Calculate the content of lead in the portion of Copper Gluconate taken:
Result = (C × V)/W
| C | = | = concentration of lead in the Sample solution A (µg/mL), determined from the intercept of the linear regression line |
| V | = | = volume of solvent taken to prepare the Sample solution A (mL) |
| W | = | = weight of Calcium Gluconate taken to prepare the Sample solution A (g) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 25 µg/g
• Reducing Substances
Sample:
1.0 g of Copper Gluconate
Blank:
10 mL of water
Titrimetric system
(See Titrimetry  541
541 .)
.)
Mode:
Residual titration
Titrant:
0.1 N iodine VS
Back-titrant:
0.1 N sodium thiosulfate VS
Endpoint detection:
Visual
Analysis:
Transfer the Sample to a 250-mL conical flask, add 10 mL of water to dissolve the Sample, then add 25 mL of alkaline cupric citrate TS. Cover the flask, boil gently for 5 min, accurately timed, and cool rapidly to room temperature. Add 25 mL of 0.6 N acetic acid, 10.0 mL of Titrant, and 10 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid, and titrate with Back-titrant, adding 3 mL of starch TS as the endpoint is approached. Perform the Blank determination.
Calculate the percentage of reducing substances (as dextrose) in the Sample taken:
Result = {[(VB  VS) × N × F]/W} × 100
VS) × N × F]/W} × 100
| VB | = | = Back-titrant volume consumed by the Blank (mL) |
| VS | = | = Back-titrant volume consumed by the Sample (mL) |
| N | = | = actual normality of the Back-titrant (mEq/mL) |
| F | = | = equivalency factor, 27 mg/mEq |
| W | = | = Sample weight (mg) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 1.0%
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Huy T. Dinh, M.S.
Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8594 |
(DS2010) Monographs - Dietary Supplements |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 2770