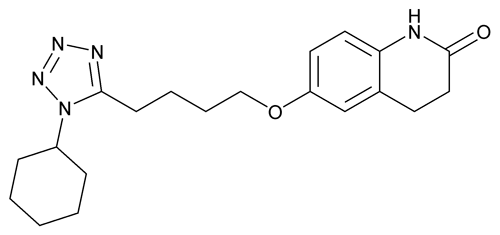
Cilostazol
(sye loe' sta zol).
2(1H)-Quinolinone, 6-[4-(1-cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy]-3,4-dihydro-.
6-[4-(1-Cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy]-3,4-dihydrocarbostyril
» Cilostazol contains not less than 98.0 percent and not more than 102.0 percent of C20H27N5O2, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers, and store at room temperature.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
Identification—
B:
The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation corresponds to that in the chromatogram of the Standard preparation, as obtained in the Assay.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 110
—
Dry it at 110 for 3 hours: it loses not more than 0.3% of its weight.
for 3 hours: it loses not more than 0.3% of its weight.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.1%.
:
not more than 0.1%.
Chloride  221
221 —
—
Test solution—
Dissolve 0.5 g of Cilostazol in 40 mL of dimethylformamide, add 6 mL of diluted nitric acid and dimethylformamide to make 50 mL.
Control solution—
To 0.25 mL of 0.01 M hydrochloric acid add 6 mL of diluted nitric acid and dimethylformamide to make 50 mL.
Procedure—
Add 1 mL of silver nitrate TS to the Test solution and to the Control solution, mix well, and allow to stand for 5 minutes, protecting from direct sunlight. Compare the opalescence developed in both solutions against a black background by viewing downward or transversely. The opalescence developed in the Test solution is not more than that of the Control solution (0.018%).
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
0.001%.
:
0.001%.
Related compounds—
Diluent, Solution A, Solution B, Mobile phase, System suitability solution, and Chromatographic system—
Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Standard solution—
Dissolve accurately weighed quantities of USP Cilostazol RS and USP Cilostazol Related Compound C RS in acetonitrile, with sonication if necessary, to obtain a solution having known concentrations of about 0.5 mg per mL of each component. Transfer 4 mL of this solution to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Further dilute this solution, stepwise if necessary, with Diluent to obtain a solution having known concentrations of about 0.4 µg per mL of each component.
Test solution—
Transfer about 20 mg of Cilostazol, accurately weighed, to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in 20 mL of acetonitrile, with sonication if necessary. Dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Calculate the percentage of cilostazol related compound C by the formula:
In addition to not exceeding the limits for impurities in Table 1, not more than 0.4% of total impurities is found.
0.1(CS / CT) (rU / rS)
in which CS is the concentration, in µg per mL, of cilostazol related compound C in the Standard solution; CT is the concentration, in mg per mL, of Cilostazol in the Test solution; rU is the peak response for cilostazol related compound C obtained from the Test solution; and rS is the peak response for cilostazol related compound C obtained from the Standard solution. Calculate the percentage of other impurities by the formula:
0.1(1/F) (CS / CT) (rU / rS)
in which F is the relative response factor from Table 1; CS is the concentration, in µg per mL, of cilostazol in the Standard solution; CT is the concentration, in mg per mL, of cilostazol in the Test solution; rU is the peak response for any other impurity obtained from the Test solution; and rS is the peak response for cilostazol obtained from the Standard solution.
Table 1
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
Relative Response Factor (F) |
Limit (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cilostazol related compound A1 | 0.2 | 1.7 | 0.1 |
| Cilostazol related compound B2 | 0.9 | 0.58 | 0.1 |
| Cilostazol | 1.0 | 1.0 | — |
| Cilostazol related compound C3 | 1.9 | — | 0.1 |
| Any other individual impurity | — | 1.0 | 0.1 |
|
1
6-Hydroxy-3,4-dihydro-1H-quinolin-2-one
|
|||
|
2
6-[4-(1-Cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)-butoxy]-1H-quinolin-2-one
|
|||
|
3
1-(4-(5-Cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-1-yl)butyl)-6-(4-(1-cyclohexyl-1H-tetrazol-5-yl)butoxy)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one
|
|||
Assay—
Diluent—
Use a mixture of water and acetonitrile (60:40).
Solution A—
Use a mixture of water and acetonitrile (70:30).
Solution B—
Use a mixture of water and acetonitrile (50:50).
Mobile phase—
Use variable mixtures of Solution A and Solution B as directed for Chromatographic system. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
System suitability solution—
Prepare a solution in Diluent having known concentrations of about 0.05 mg per mL each of USP Cilostazol RS, USP Cilostazol Related Compound A RS, and USP Cilostazol Related Compound B RS.
Standard preparation—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Cilostazol RS in acetonitrile, with sonication if necessary, to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 1.0 mg per mL. Transfer 4 mL of this solution to a 10-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Further dilute this solution with Diluent to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.04 mg per mL.
Assay preparation—
Transfer about 20 mg of Cilostazol, accurately weighed, to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in 20 mL of acetonitrile, sonicate if necessary, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Transfer 1 mL of this solution to a 10-mL volumetric flask, dilute with Diluent to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 254-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 10-cm column that contains 3.5-µm packing L7. The flow rate is about 1.0 mL per minute. The column temperature is maintained at 40
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 254-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 10-cm column that contains 3.5-µm packing L7. The flow rate is about 1.0 mL per minute. The column temperature is maintained at 40 . The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
Chromatograph the System suitability solution, identify the components using Table 1, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between cilostazol related compound B and cilostazol is not less than 3.0; the tailing factor for the cilostazol peak is not more than 2.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
| Time (minutes) |
Solution A
(%) |
Solution B
(%) |
Elution |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0–6.5 | 100®50 | 0®50 | linear gradient |
| 6.5–10 | 50®0 | 50®100 | linear gradient |
| 10–20 | 0 | 100 | isocratic |
| 20–20.1 | 0®100 | 100®0 | linear gradient |
| 20.1–28 | 100 | 0 | re-equilibration |
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Calculate the quantity, in mg, of C20H27N5O2 in the portion of Cilostazol taken by the formula:
500C(rU / rS)
in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of cilostazol in the Standard preparation; and rU and rS are the peak responses obtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Sujatha Ramakrishna, Ph.D.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8349 |
(SM22010) Monographs - Small Molecules 2 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 2663
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 34(3) Page 589