Alpha-Lactalbumin
C626H958N162O196S9 14178

 [9051-29-0].
[9051-29-0].
C626H958N162O196S9 14178
DEFINITION
Alpha-Lactalbumin is a lyophilized or spray-dried powder of compact globular metalloprotein that may contain a single bound calcium ion and is capable of binding zinc and other metals. Alpha-Lactalbumin is isolated either from bovine milk or from whey, both of which should be from edible sources suitable for human use. All materials derived from bovine sources must originate from countries free of bovine spongiform encephalopathy. It contains alpha-lactalbumin at NLT 90.0% of the labeled total protein content. The remainder consists mostly of beta-lactoglobulin. It may contain suitable stabilizers.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. SDS-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
Gel fixing solution:
In a 1-L Pyrex bottle, thoroughly mix 500 mL of water, 400 mL of alcoholic TS, and 100 mL of glacial acetic acid.
Gel staining solution:
Prepare a solution of Coomassie blue G-250 having a concentration of 0.25 g/L in a 10.0% (v/v) acetic acid solution.1 Store at room temperature.
Destaining solution:
10.0% (v/v) acetic acid in water[Note—This solution may be stored at room temperature for up to 6 months from the date prepared. ]
Sample buffer:
Prepare a solution containing 200 mM tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane hydrochloride (Tris-HCl), 2% (w/v) sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), 40% (v/v) glycerol, and 0.04% (w/v) Coomassie blue G-250. If necessary, adjust with hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide to a pH of 6.8.2
Running buffer:
Prepare a solution containing 100 mM tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, 100 mM N-tris(hydroxymethyl)methylglycine (tricine), and 0.1% (w/v) SDS in water. If necessary, adjust with hydrochloric acid or sodium hydroxide to a pH of 8.3.3 In a 400-mL beaker, thoroughly mix 35 mL of the solution so obtained (or 10× Tris/Tricine/SDS buffer)4 with 315 mL of water.
Molecular weight marker:
Use a suitable molecular weight marker containing protein bands between 3.5 and 27 kDa.
Molecular weight standard solution:
Transfer 16 µL of the Sample buffer into a 0.5-mL microcentrifuge tube. Pipet 4 µL of the Molecular weight marker into the microcentrifuge tube, and mix. Incubate the mixture in the closed microcentrifuge tube for 5 min at 95 . After incubation, allow the tube to stand for 5 min at room temperature. Centrifuge at 5000 rpm for 1 min.
. After incubation, allow the tube to stand for 5 min at room temperature. Centrifuge at 5000 rpm for 1 min.
Alpha-Lactalbumin standard stock solution:
1.0% (w/v) of USP Alpha-Lactalbumin RS in water in a 2-mL centrifuge tube.
Alpha-Lactalbumin standard working solution:
Pipet 21 µL of the Sample buffer and 3 µL of the Alpha-Lactalbumin standard stock solution into a 0.5-mL microcentrifuge tube, and mix. Proceed as directed for Molecular weight standard solution beginning with “Incubate the mixture”.
Sample stock solution:
1.0% (w/v) of Alpha-Lactalbumin in water in a 2-mL centrifuge tube.
Sample solution:
Pipet 21 µL of the Sample buffer and 3 µL of the Sample stock solution into a 0.5-mL microcentrifuge tube, and mix. Proceed as directed for Molecular weight standard solution beginning with “Incubate the mixture”.
SDS-PAGE gel and apparatus set-up:
Following the manufacturer’s instructions, assemble and fill a 16.5% Tris-Tricine Ready Gel5 in the Mini-Protean III Electrophoresis Module,6 or in an equivalent module. Add Running buffer appropriately to this apparatus.
Analysis
Gel loading:
Load 10 µL of the Molecular weight standard solution, 2.5 µL of the Alpha-Lactalbumin standard working solution, and 2.5 µL of the Sample solution, respectively, into the 16.5% Tris-Tricine SDS-PAGE gel. [Note—The loaded samples contain approximately 3 µg of protein based on the sample weight. ]
Running the gel:
Set the voltage to 100 V, and run at a constant voltage. Run the gel until the tracking dye front is approximately 10 mm from the bottom of the gel (approximately 80–90 min).
Gel fixing:
Remove the gel, transfer to a plastic container, and soak in the Gel fixing solution for 30 min on a shaking rack. Decant the Gel fixing solution. Rinse with water, and decant.
Gel staining:
Pour approximately 100 mL of the Gel staining solution into the staining container. Place the gel into the staining container, and allow the stain to completely cover the gel. Place the staining container on an appropriate shaker, and stain the gel for 60–90 min with gentle shaking.
Destaining:
Drain the Gel staining solution into an appropriate waste container, and add 100 mL of Destaining solution to the container to cover the gel. Place the container on an appropriate shaker, and shake with gentle agitation for 30 min. Discard the used Destaining solution, and repeat destaining as necessary. Repeat rinsing with Destaining solution three to four times at 30-min intervals or until the gel is destained to the desired clarity.
Acceptance criteria:
The Alpha-Lactalbumin has one major band at 14 kDa, a minor band at 16 kDa, and a molecular weight that is similar to that of USP Alpha-Lactalbumin RS.
• B.
The retention time of the major peak for alpha-lactalbumin from the Sample solution corresponds to that of the Standard solution, as obtained in the test for Content of Alpha-Lactalbumin in the Assay.
ASSAY
• Content of Alpha-Lactalbumin
Mobile phase:
Prepare a solution of 0.02 M Tris-HCl, 0.5% SDS, and 0.1 N sodium chloride. Adjust the pH of the solution to 5.95 ± 0.05. Pass this solution through a filter having a 0.5-µm or finer porosity, and degas.
Standard solution:
1.0 mg/mL of USP Alpha-Lactalbumin RS in Mobile phase. [Note—Prepare it immediately before use. ]
System suitability solutuion:
0.5 mg/mL of USP Alpha-Lactalbumin RS and 0.5 mg/mL of beta-lactoglobulin in Mobile phase
Sample solution:
1.0 mg/mL of Alpha-Lactalbumin in Mobile phase
Chromatographic system
(See Chromatography  621
621 , System Suitability.)
, System Suitability.)
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 280 nm
Column:
7.8-mm × 30-cm analytical column, packing L33
[Note—Equilibrate the column for approximately 90 min at 0.6 mL/min of Mobile phase or until a stable baseline is achieved. ]
Flow rate:
0.6 mL/min
Injection size:
20 µL
System suitability
Sample:
System suitability solution
[Note—The relative retention times for beta-lactoglobulin and alpha-lactalbumin are 0.91 and 1.00, respectively. ]
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 1.65 between beta-lactoglobulin and alpha-lactalbumin
Tailing factor:
Not greater than 1.1 for the alpha-lactalbumin peak
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the purity of Alpha-Lactalbumin as a percentage of total protein:
Result = (rU/rS) × [CS/(CU × P)] × 100
| rU | = | = peak response for alpha-lactalbumin from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response for alpha-lactalbumin from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Alpha-Lactalbumin RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Alpha-Lactalbumin in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
| P | = | = percentage of total protein content |
Acceptance criteria:
Content of alpha-lactalbumin is NLT 90.0% of the labeled total protein content.
• Total Protein Content
Sample:
250 mg of Alpha-Lactalbumin
Analysis:
Combust the Sample in the presence of pure oxygen (99.9%) in an airtight oven at 950 with a suitable nitrogen analyzer. The components such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and moisture are absorbed by various in-line chemical filters. All nitrogenous matter is converted into nitrogen in the presence of catalytic converters. The weight percent of nitrogen is measured by a thermal conductivity detector. Blank the system by analyzing a suitable nitrogen blank material, such as powdered cellulose, and obtaining a zero reading. Calibrate and qualify the system by using EDTA. The relative standard deviation for replicate runs is NMT 0.5%. Calculate the weight percent of total protein content in Alpha-Lactalbumin by multiplying the percentage of nitrogen found by 6.23.
with a suitable nitrogen analyzer. The components such as carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide, and moisture are absorbed by various in-line chemical filters. All nitrogenous matter is converted into nitrogen in the presence of catalytic converters. The weight percent of nitrogen is measured by a thermal conductivity detector. Blank the system by analyzing a suitable nitrogen blank material, such as powdered cellulose, and obtaining a zero reading. Calibrate and qualify the system by using EDTA. The relative standard deviation for replicate runs is NMT 0.5%. Calculate the weight percent of total protein content in Alpha-Lactalbumin by multiplying the percentage of nitrogen found by 6.23.
Acceptance criteria:
Total protein content is NLT 90.0%.
OTHER COMPONENTS
• Limit of Beta-Lactoglobulin
Mobile phase, System suitability solution, Sample solution, Chromatographic system, and System suitability:
Prepare as directed in the test for Content of Alpha-Lactalbumin.
Standard solution:
1.0 mg/mL of beta lactoglobulin in Mobile phase. [Note—Prepare it immediately before use. ]
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of beta-lactoglobulin as a percentage of total protein:
Result = (rU/rS) × [CS/(CU × P)] × 100
| rU | = | = peak response for beta-lactoglobulin from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response for beta-lactoglobulin from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of beta-lactoglobulin in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Alpha-Lactalbumin in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
| P | = | = percentage of total protein content |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 6.5%, calculated on the total protein basis
• Content of Calcium
Standard stock solution:
Dissolve 1.249 g of calcium carbonate in 270 mL of 3 N hydrochloric acid (dilute 250 mL of hydrochloric acid with water to 1000 mL) in a 1000-mL volumetric flask. Dilute with water to volume, and mix. Dilute 50 mL of the solution so obtained to 1000 mL. The Standard stock solution contains 25 µg/mL of calcium.7
Lanthanum chloride solution:
Weigh 11.7 g (± 100 mg) of lanthanum oxide, and transfer to a 1000-mL volumetric flask. Add enough water to wet the powder, and then slowly add 50 mL of hydrochloric acid. [Caution—Exothermic reaction.
] Let the test specimen dissolve, dilute with water to volume, and mix. This solution contains 1% (w/v) of lanthanum and is stable for up to 6 months when stored at room temperature.
Blank solution:
10-fold dilution of Lanthanum chloride solution
Working standard solutions:
To five identical 25-mL volumetric flasks add 0, 5, 10, 15, and 20 mL, respectively, of Standard stock solution. Add 2.5 mL of Lanthanum chloride solution, and dilute with water to volume. The Working standard solutions contain 0, 5, 10, 15, and 20 µg/mL of calcium, each containing 0.1% (w/v) of lanthanum.
Sample solution:
Transfer 1.0 g of Alpha-Lactalbumin to a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 10 mL of Lanthanum chloride solution, and dilute with water to volume.
Spectrometric conditions
Mode:
Atomic absorption spectrophotometry
Analytical wavelength:
422.7 nm
Lamp:
Calcium hollow-cathode lamp
Flame:
Reduced air–acetylene
Analysis
Samples:
Working standard solutions and Sample solution
Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the Samples using the Blank solution. [Note—Optimize flame parameters in accordance with the instrument manufacturer’s instructions. ]
Plot the absorbances of the Working standard solutions versus the concentration, in µg/mL, of calcium, and draw the straight line best fitting the five plotted points. From the graph so obtained, determine the concentration, C, in µg/mL, of calcium in the Sample solution.
Calculate the quantity of calcium (Ca), in mg, in each g of Alpha-Lactalbumin taken:
Result = (V × C)/W × F × 100
| V | = | = volume of the Sample solution, 100 mL |
| C | = | = as determined above |
| W | = | = weight of Alpha-Lactalbumin taken to prepare the Sample solution (g) |
| F | = | = conversion factor for µg to mg (10-3 mg/µg) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 1 mg/g of calcium
IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
• Ash:
Ignite 1 g of Alpha-Lactalbumin at NMT 550 until free from carbon. Cool in a desiccator, and weigh: NMT 3.5% is found.
until free from carbon. Cool in a desiccator, and weigh: NMT 3.5% is found.
• Heavy Metals, Method II  231
231 :
NMT 10 ppm
:
NMT 10 ppm
• Limit of Phosphorus
Hydrochloric acid solution:
Pipet 250 mL of hydrochloric acid into a 1000-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Molybdovanadate reagent:
Dissolve 20 g of ammonium molybdate in 200 mL of water with the aid of heat, and then allow the molybdate solution to cool. Dissolve 1.0 g of ammonium vanadate in 125 mL of water with the aid of heat, cool, and add 160 mL of hydrochloric acid. Gradually add, with stirring, the molybdate solution to the vanadate solution, and dilute with water to 1000 mL.
Phosphorus standard stock solution I:
Transfer 8.8 g of monobasic potassium phosphate (KH2PO4), previously dried for 2 h at 105 , to a 1000-mL volumetric flask, and add 750 mL of water to dissolve. Dilute with water to volume. This solution contains 2 mg/mL of phosphorus. [Note—Store the solution in a refrigerator. ]
, to a 1000-mL volumetric flask, and add 750 mL of water to dissolve. Dilute with water to volume. This solution contains 2 mg/mL of phosphorus. [Note—Store the solution in a refrigerator. ]
Phosphorus standard stock solution II:
Immediately before use, dilute 50 mL of Phosphorus standard stock solution I with water to 1000 mL. [Note—Store in a refrigerator. ]
Standard solutions:
Transfer 0.0 mL, 5.0 mL, 8.0 mL, 10.0 mL, and 15.0 mL of Phosphorus standard stock solution II, respectively, to five identical 100-mL volumetric flasks. Proceed as directed in the Analysis: after treatment with the Molybdovanadate reagent, the resulting final phosphorus concentrations for the Standard solutions are 0.0, 5.0, 8.0, 10.0, and 15.0 µg/mL, respectively.
Sample solution:
Transfer 4.0 g of Alpha-Lactalbumin to an ashing dish. Dry the test specimen on a hot plate or steam bath. Ignite in a muffle furnace at a maximum temperature of 600 until free of carbon. Cool, add 40 mL of Hydrochloric acid solution and several drops of nitric acid, and bring to boil on a hot plate. Cool, transfer to a 100-mL volumetric flask by rinsing the ashing dish with water, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Pipet 20.0 mL of the Sample solution into a 100-mL volumetric flask.
until free of carbon. Cool, add 40 mL of Hydrochloric acid solution and several drops of nitric acid, and bring to boil on a hot plate. Cool, transfer to a 100-mL volumetric flask by rinsing the ashing dish with water, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Pipet 20.0 mL of the Sample solution into a 100-mL volumetric flask.
Spectrometric conditions
Mode:
UV-Vis
Analytical Wavelength:
400 nm
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solutions and the Sample solution
To each of the flasks containing the Samples, add 20.0 mL of Molybdovanadate reagent, dilute with water to volume, mix, and allow to stand for exactly 10 min for maximum color development. The Standard solutions and the Sample solution are treated identically. Concomitantly determine the absorbances of each of the Samples in 1-cm cells using the Spectrometric conditions described above. Use one of the Standard solutions with phosphorus concentration at 0.0 µg/mL to zero the spectrophotometer. Plot the absorbances of the Standard solutions versus concentration, in µg/mL, of phosphorus, and draw the straight line best fitting the four plotted points. From the graph so obtained, determine the concentration, C, in µg/mL, of phosphorus in the Sample solution.
Calculate the quantity, in µg, of phosphorus in each g of Alpha-Lactalbumin taken:
Result = (V × C)/W × D
| V | = | = volume of the Sample solution, 100 mL |
| C | = | = as determined above |
| W | = | = weight of Alpha-Lactalbumin taken to prepare the Sample solution (g) |
| D | = | = dilution factor, 5 |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 700 µg/g of phosphorus
Organic Impurities
• Procedure 1: Limit of Lipid (Fat)
Weighing dish preparation:
Pre-dry the clean dishes under the same conditions that will be used for final drying after fat extraction. Ensure that all surfaces where weighing dishes will be placed (i.e., hot plate, desiccator, etc.) are clean and free of particulates. At the end of oven drying, place the weighing dishes in a desiccator, and cool to room temperature. Immediately before use, weigh the dishes to the nearest 0.1 mg, and record the weights. Check the balance zero after weighing each dish. Protect the weighed dishes from contamination with extraneous matter.
Analysis
Transfer 0.5 g of Alpha-Lactalbumin to a Mojonnier-style ether extraction flask that has the capacity to hold a volume of 21–23 mL in the lower bulb plus neck at the bottom of the flask. The flask has a smooth, round opening at the top that can be sealed when closed with cork. Add 10 mL of water at a temperature of 40 , and mix. Add 1.5 mL of ammonium hydroxide to the Alpha-Lactalbumin, and mix thoroughly. Add 3 drops of phenolphthalein TS to help sharpen the visual appearance of the interface between the ether and the aqueous layers during extraction. Add 10 mL of alcohol, close with the cork stopper that has been water soaked, and shake the flask for 15 s.
, and mix. Add 1.5 mL of ammonium hydroxide to the Alpha-Lactalbumin, and mix thoroughly. Add 3 drops of phenolphthalein TS to help sharpen the visual appearance of the interface between the ether and the aqueous layers during extraction. Add 10 mL of alcohol, close with the cork stopper that has been water soaked, and shake the flask for 15 s.
For the first extraction, add 25 mL of ether, replace the cork stopper, and shake the flask very vigorously for approximately 1 min, releasing built-up pressure by loosening the stopper as necessary. Add 25 mL of petroleum ether, replace the cork stopper, and repeat vigorous shaking for about 1 min. Centrifuge the flask at about 600 rpm for NLT 30 s to obtain a clean separation of the aqueous (bright pink) and the ether phases. Decant the ether solution into a suitable weighing dish prepared as directed for Weighing dish preparation. When the ether solution is decanted into the dish, be careful not to pour any suspended solids or aqueous phase into the weighing dish. Ether can be evaporated at NMT 100 from the dish while conducting the second extraction.
from the dish while conducting the second extraction.
For the second extraction, add 5 mL of alcohol to the original flask, close with the cork stopper, and shake vigorously for 15 s. Add 15 mL of ether, replace the cork, and shake the flask vigorously for about 1 min. Add 15 mL of petroleum ether, replace the cork stopper, and repeat vigorous shaking for about 1 min. Centrifuge the flask at about 600 rpm for NLT 30 s to obtain a clean separation of the aqueous (bright pink) and the ether phases. If the interface is below the neck of the flask, add water to bring the level about halfway up to the neck. Add water slowly down the inside surface of the flask so that there is minimum disturbance of the interface. Decant the ether solution for the second extraction into the same weighing dish used for the first extraction.
For the third extraction, omit addition of the alcohol and repeat the procedure used for the second extraction. Completely evaporate the solvents in a hood on a hot plate at NMT 100 , and avoid spattering. Dry the extracted fat and the weighing dish to constant weight in a forced air oven at 100
, and avoid spattering. Dry the extracted fat and the weighing dish to constant weight in a forced air oven at 100 ± 1
± 1 for NLT 30 min or in a vacuum oven at 70
for NLT 30 min or in a vacuum oven at 70 to 75
to 75 at more than 50.8 cm (20 inches) of vacuum for NLT 7 min. Remove the weighing dish from the oven, and place in a desiccator to cool to room temperature. Record the weight of the weighing dish containing the fat.
at more than 50.8 cm (20 inches) of vacuum for NLT 7 min. Remove the weighing dish from the oven, and place in a desiccator to cool to room temperature. Record the weight of the weighing dish containing the fat.
Run a blank determination using water, and record the weight of any dry residue collected. The reagent blank should be less than 2.0 mg of residue. [Note—A negative number is not acceptable. ]
Calculate the weight percent of lipid (fat) in the portion of Alpha-Lactalbumin taken:
Result = [(W2  W1)
W1)  W3]/W × 100
W3]/W × 100
| W1 | = | = weight of empty weighing dish (g) |
| W2 | = | = weight of the weighing dish containing fat (g) |
| W3 | = | = weight of the reagent blank residue (g) |
| W | = | = weight of the Alpha-Lactalbumin taken for the fat extraction (g) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 1.0% is found. The difference between duplicate runs is NMT 0.03% fat.
• Procedure 2: Limit of Lactose
Carrez I solution:
Transfer 3.60 g of potassium ferrocyanide [K4Fe(CN)6·3H2O] to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Carrez II solution:
Transfer 7.20 g of zinc sulfate heptahydrate (ZnSO4·7H2O) to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix.
[Note—The following four test reagents are included in a test kit.8 ]
Test reagent 1:
About 600 mg of lyophilisate consisting of a mixture of citrate buffer (pH 6.6), nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) (35 mg), anhydrous magnesium sulfate, and stabilizers (added if necessary). Dissolve lyophilisate in 7.0 mL of water before use.
Test reagent 2:
About 1.7 mL of an enzyme suspension of 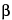 -galactosidase (approximately 100 Units).
-galactosidase (approximately 100 Units).
Test reagent 3:
34 mL of a solution consisting of 0.51 M potassium diphosphate buffer (pH 8.6), and stabilizers (added if necessary).
Test reagent 4:
About 1.7 mL of an enzyme suspension of galactose dehydrogenase (about 40 Units).
Sample solution:
Transfer 1.0 g of Alpha-Lactalbumin to a 100-mL volumetric flask, add about 60 mL of water, and mix. Add 5 mL of Carrez I solution, and mix. Add 5 mL of Carrez II solution, and mix. Add 10 mL of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide solution, and mix vigorously. Dilute with water to volume, and mix. Pass through a filter paper, and use the clear filtrate. [Note—This procedure breaks emulsions, absorbs some colors, and precipitates proteins. ]
Analysis
Label one glass or disposable plastic cuvet as “blank” and the second glass or disposable plastic cuvet as “test”. [Note—These two cuvets should be equivalent. ] To each cuvet, pipet 0.20 mL of Test reagent 1 and 0.05 mL of Test reagent 2. Pipet 0.10 mL of the Sample solution into the cuvet that is labeled “test”. Mix both cuvets with their stirrers, and incubate at 20 –25
–25 for 20 min. Pipet 1.00 mL of Test reagent 3 into each cuvet. Pipet 2.00 mL of water into the cuvet that is labeled “blank” and 1.90 mL of water into the cuvet containing the Sample solution. Mix, and incubate at 20
for 20 min. Pipet 1.00 mL of Test reagent 3 into each cuvet. Pipet 2.00 mL of water into the cuvet that is labeled “blank” and 1.90 mL of water into the cuvet containing the Sample solution. Mix, and incubate at 20 –25
–25 for about 2 min.
for about 2 min.
Determine the absorbances, AS1 and AB1, at 340 nm, for the Sample solution and the blank, respectively. Add 0.05 mL of Test reagent 4 to each cuvet. Mix and incubate at 20 –25
–25 until the reaction has stopped (about 10–15 min). Determine the absorbances AS2 and AB2, at 340 nm, again for the Sample solution and the blank, respectively. If the reaction has not stopped after 15 min, continue to read the absorbances at 2-min intervals until the absorbance for the Sample solution remains constant for two successive measurements.
until the reaction has stopped (about 10–15 min). Determine the absorbances AS2 and AB2, at 340 nm, again for the Sample solution and the blank, respectively. If the reaction has not stopped after 15 min, continue to read the absorbances at 2-min intervals until the absorbance for the Sample solution remains constant for two successive measurements.
Calculate the percentage of lactose in the portion of Alpha-Lactalbumin taken:
Result = V1 × V2 × Mr × [(AS2  AS1)
AS1)  (AB2
(AB2  AB1)]/(
AB1)]/(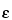 × L × V3 × W) × 100
× L × V3 × W) × 100
| V1 | = | = volume of the Sample solution, 0.1 L |
| V2 | = | = volume of the final sample solution in the cuvet, 3.30 mL |
| Mr | = | = molecular weight of lactose monohydrate, 360.32 g/mol |
| = | = absorption coefficient of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced form (NADH) at 340 nm, 6300 L·mol |
|
| L | = | = light path of the cuvet, 1.0 cm |
| V3 | = | = volume of the Sample solution taken into the cuvet, 0.1 mL |
| W | = | = weight of Alpha-Lactalbumin taken to prepare the Sample solution (g) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 1.0% of lactose
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Microbial Enumeration Tests  61
61 and Tests for Specified Microorganisms
and Tests for Specified Microorganisms  62
62 :
The total aerobic bacterial count does not exceed 1000 cfu/g. The total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 100 cfu/g. It meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli.
:
The total aerobic bacterial count does not exceed 1000 cfu/g. The total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 100 cfu/g. It meets the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli.
• Denaturation Temperature
Sample solution:
Prepare a protein dough by mixing 3 g of Alpha-Lactalbumin powder with 2 g of water. Place the dough into a well-sealed sample container.
Analysis:
Perform two measurements on the dough sample using a differential scanning calorimeter. Heat to 140 , and scan. Cool rapidly to below room temperature, and rescan. Apply a scan rate of 10
, and scan. Cool rapidly to below room temperature, and rescan. Apply a scan rate of 10 /min. Weigh pans before and after scanning to verify that no moisture loss occurs during the scanning process. Measure and record the denaturation temperatures as peak temperatures. The formation of two peaks indicates the presence of both the apo form and the holo form of Alpha-Lactalbumin.
/min. Weigh pans before and after scanning to verify that no moisture loss occurs during the scanning process. Measure and record the denaturation temperatures as peak temperatures. The formation of two peaks indicates the presence of both the apo form and the holo form of Alpha-Lactalbumin.
Acceptance criteria:
The denaturation temperature for Alpha-Lactalbumin in the apo form is between 50 and 52
and 52 ; the denaturation temperature for Alpha-Lactalbumin in the holo form is between 58
; the denaturation temperature for Alpha-Lactalbumin in the holo form is between 58 and 61
and 61 .
.
• pH  791
791 :
NMT 7.5, in a solution (1 in 10)
:
NMT 7.5, in a solution (1 in 10)
• Loss on Drying  731
731 :
Dry 1.0–1.5 g in a vacuum oven at 100
:
Dry 1.0–1.5 g in a vacuum oven at 100 , at a pressure of 660 mm of mercury, and with continuous dry air feed for 5 h: it loses NMT 6.5% of its weight.
, at a pressure of 660 mm of mercury, and with continuous dry air feed for 5 h: it loses NMT 6.5% of its weight.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight containers, and store at the temperature indicated on the label.
• Labeling:
Label it to state the protein content, expressed as a total protein percentage. Indicate the type of source material, expressed as bovine milk, whey, or both, used to manufacture the final product. Label it to indicate the storage conditions, the expiration date, and the name and concentration of any added stabilizers.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Alpha-Lactalbumin RS
1
A suitable gel staining solution is available from, e.g., Bio-Rad. Coomassie brilliant blue G-250 is available from Bio-Rad, Cat. # 161-0406.
2
A suitable sample buffer is available as Tricine sample buffer from Bio-Rad, Cat. # 161-0739.
3
An undiluted suitable running buffer is available as 10× Tris/Tricine/SDS buffer from Bio-Rad, Cat. # 161-0744.
4
Available as 10× Tris/Tricine/SDS buffer from Bio-Rad, Cat. # 161-0744.
5
Available from Bio-Rad, Cat. # 161-1107 or 161-1179.
6
Available from Bio-Rad, Cat. # 165-3302.
7
A commercially prepared, certificated AA standard is available as Calcium AA, ICP standards, 1000 ppm Ca in dilute hydrochloric acid, Cat. # ACA1KH, from RICCA. Make an appropriate dilution to obtain a final concentration of 25 µg/mL of calcium.
8
Available from Boehringer-Mannheim (R-Biopharm, Inc., 7950 Old US 27S, Marshall, MI 49068 USA; Tel: +1-877-789-3033 or +1-269-789-3033; Fax: +1-269-789-3070; www.r-biopharm.com).
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Robert H. Lafaver, M.S.
Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8335 |
(EXC2010) Monographs - Excipients |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 1832
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 34(3) Page 670