DISSOLUTION AND IN VITRO PRODUCT PERFORMANCE
As noted for an official preparation, USP monographs provide a public specification that includes a list of tests, references to analytical procedures, and acceptance criteria. Most solid oral dosage forms, including oral suspensions, require a dissolution or a drug release test. Drug dissolution and drug release testing are described in USP general chapters Dissolution  711
711 and Drug Release
and Drug Release  724
724 . These public specifications are used for quality control tests and for market approval. The USP dissolution test in the monograph is related to BA and BE only when closely allied with a sound regulatory determination. Without this link it should be regarded solely as a quality control test for batch release. FDA Guidances are (1) Guidance for Industry—Dissolution Testing of Immediate Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms (1977) (http://www.fda.gov/; search by document title) and (2) Guidance for Industry—Extended Release Oral Dosage Forms: Development, Evaluation, and Application of In Vitro/In Vivo Correlation (1977) (http://www.fda.gov/; search by document title).
. These public specifications are used for quality control tests and for market approval. The USP dissolution test in the monograph is related to BA and BE only when closely allied with a sound regulatory determination. Without this link it should be regarded solely as a quality control test for batch release. FDA Guidances are (1) Guidance for Industry—Dissolution Testing of Immediate Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms (1977) (http://www.fda.gov/; search by document title) and (2) Guidance for Industry—Extended Release Oral Dosage Forms: Development, Evaluation, and Application of In Vitro/In Vivo Correlation (1977) (http://www.fda.gov/; search by document title).
Dissolution and In Vitro Bioavailability
Drug dissolution and release tests are very useful during drug product development in identifying critical manufacturing attributes such as the impact of ingredient properties and the impact of the manufacturing process on drug product performance. During product development, optimum dissolution conditions need to be developed to discriminate drug product formulations and changes in manufacturing processes. After the finished dosage form is approved for marketing, drug dissolution and release tests are useful in predicting possible changes in performance due to scale-up and postapproval changes (SUPAC). See the following FDA guidances:
Guidance for Industry—Immediate Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms, Scale-Up and Postapproval Changes: Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls, In Vitro Dissolution Testing, and In Vivo Bioequivalence Documentation (1995) (http://www.fda.gov/; search by document title) and
Guidance for Industry—SUPAC-MR: Modified-Release Solid Oral Dosage Forms: Scale-Up and Postapproval Changes: Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls; In Vitro Dissolution Testing and In Vivo Bioequivalence Documentation (1977) (http://www.fda.gov/; search by document title).
For some oral drug products, in vitro drug dissolution can be related to in vivo performance, such as bioavailability and/or systemic drug exposure. USP general information chapter In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Dosage Forms  1088
1088 describes various approaches to in vitro–in vivo correlation (IVIVC).
describes various approaches to in vitro–in vivo correlation (IVIVC).
Dissolution and In Vitro Equivalence
The dissolution test is a powerful in vitro physiochemical test that measures drug product quality and performance for a variety of dosage forms, such as solid oral dosage forms, transdermal dosage forms, suspensions, and certain semisolid dosage forms. The USP tests for finished dosage forms can be divided into two types: (1) drug product quality tests and (2) drug product performance tests. Product quality tests are intended to assess attributes such as assay and content uniformity; product performance tests are designed to assess product performance and in many cases relate to dissolution. For details regarding the performance of a dissolution test, see USP general chapters  711
711 ,
,  724
724 ,
,  1088
1088 , and
, and  1092
1092 .
.
The in vitro dissolution test was initially developed as a quality control tool to ensure drug product quality and batch-to-batch consistency. The test procedures for conducting dissolution tests are described in USP general chapters  711
711 and
and  724
724 . The development of the BCS brings new understanding and power to the dissolution test. The BCS classifies the drug substance according to the solubility and the permeability of the drug through a biomembrane such as the intestinal mucosal cells. The dissolution rate of the drug from the dosage form is important in substantiating biowaivers based on the BCS.
. The development of the BCS brings new understanding and power to the dissolution test. The BCS classifies the drug substance according to the solubility and the permeability of the drug through a biomembrane such as the intestinal mucosal cells. The dissolution rate of the drug from the dosage form is important in substantiating biowaivers based on the BCS.
Dissolution Profile Comparisons
In vitro drug dissolution and release testing can be related to in vivo drug performance, such as BA. The comparisons of dissolution profiles are gaining importance as a means of documenting comparative BA studies—that is, BE. A biowaiver is the replacement or waivers of in vivo BE studies by an in vitro test.
A model independent mathematical approach is used to compare the dissolution profile of two products: (1) to compare the dissolution profile between the T (generic, multisource) product and R (comparator) product in biowaiver considerations; (2) to compare the dissolution profile between the two strengths of products from a given manufacturer; and (3) for SUPAC after the product is approved. For comparing the dissolution profile, the similarity factor f2 should be computed using the equation
where Rt and Tt are the cumulative percentage of the drug dissolved at each of the selected n time points of the reference and test product, respectively. An f2 value of 50 or greater (50 to 100) ensures dissolution profile similarity and the sameness or equivalence of the two curves, and thus the performance of the two products. At a minimum, three points, no more than one point exceeding 85%, should be used for similarity profile comparison. For products that dissolve very rapidly (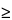 85% dissolution in 15 minutes) a profile comparison is not necessary.
85% dissolution in 15 minutes) a profile comparison is not necessary.
