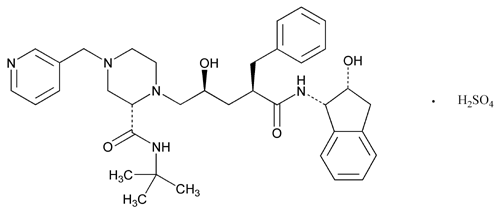
Indinavir Sulfate
C36H47N5O4·H2SO4




 711.87
711.87
d-erythro-Pentonamide, 2,3,5-trideoxy-N-(2,3-dihydro-2-hydroxy-1H-inden-1-yl)-5-[2-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-4-(3-pyridinylmethyl)-1-piperazinyl]-2-(phenylmethyl)-, [1(1S,2R),5(S)]-, sulfate (1:1) (salt).
(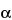 R,
R,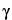 S,2S)-
S,2S)-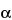 -Benzyl-2-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)-
-Benzyl-2-(tert-butylcarbamoyl)-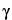 -hydroxy-N-[(1S,2R)-2-hydroxy-1-indanyl]-4-(3-pyridylmethyl)-1-piperazinevaleramide sulfate (1:1) (salt)
-hydroxy-N-[(1S,2R)-2-hydroxy-1-indanyl]-4-(3-pyridylmethyl)-1-piperazinevaleramide sulfate (1:1) (salt)


 [157810-81-6].
[157810-81-6].
d-erythro-Pentonamide, 2,3,5-trideoxy-N-(2,3-dihydro-2-hydroxy-1H-inden-1-yl)-5-[2-[[(1,1-dimethylethyl)amino]carbonyl]-4-(3-pyridinylmethyl)-1-piperazinyl]-2-(phenylmethyl)-, [1(1S,2R),5(S)]-, sulfate (1:1) (salt).
(
» Indinavir Sulfate contains not less than 98.5 percent and not more than 101.5 percent of C36H47N5O4·H2SO4, calculated on an anhydrous, solvent-free basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers, protected from moisture. Store at 25 , excursions permitted between 15
, excursions permitted between 15 and 30
and 30 .
.
Identification—
A:
Infrared Absorption  197M
197M —The IR absorption spectrum exhibits maxima at about 3.0–3.1, 5.9, 6.2, and 13.6 µm.
—The IR absorption spectrum exhibits maxima at about 3.0–3.1, 5.9, 6.2, and 13.6 µm.
B:
The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation corresponds to that in the chromatogram of the Standard preparation, as obtained in the Assay.
Specific rotation  781S
781S :
between +122
:
between +122 and +129
and +129 , at 365 nm, determined on the anhydrous, solvent-free basis.
, at 365 nm, determined on the anhydrous, solvent-free basis.
Test solution:
10 mg per mL, in water.
Water, Method I  921
921 :
not more than 1.5%, using 0.25 g.
:
not more than 1.5%, using 0.25 g.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.1%.
:
not more than 0.1%.
Heavy metals  231
231 —
—
Standard solution—
Into a 50-mL color-comparison tube, pipet 2 mL of Standard Lead Solution (10 µg per mL), and dilute with water to 25 mL. Using a pH meter or short-range pH indicator paper as an external indicator, adjust with 1 N acetic acid or 6 N ammonium hydroxide to a pH between 3.0 and 4.0, dilute with water to 40 mL, and mix.
Test solution—
In a 50-mL color-comparison tube, dissolve 2.0 g of Indinavir Sulfate in 25 mL of water. Using a pH meter or a suitable short-range pH indicator paper as an external indicator, adjust with 1 N acetic acid or 6 N ammonium hydroxide to a pH between 3.0 and 4.0, dilute with water to 40 mL, and mix.
Blank solution—
To a 50-mL color-comparison tube, add 25 mL of water. Using a pH meter or a suitable short-range pH indicator paper as an external indicator, adjust with 1 N acetic acid or 6 N ammonium hydroxide to a pH between 3.0 and 4.0, dilute with water to 40 mL, and mix.
Procedure—
To each tube, add 10 mL of hydrogen sulfide TS, mix, allow to stand for 5 minutes, and view downward over a white surface: the color of the Test solution is not darker than that of the Standard solution. The intensity of the color of the Blank solution is less than or equal to the intensity of that of the Test solution.
Chromatographic purity—
Solution A—
Dissolve 0.54 g of monobasic potassium phosphate and 2.79 g of dibasic potassium phosphate in 2 L of water.
Solution B—
Use acetonitrile.
Diluent—
Prepare a mixture of Solution A and Solution B (1:1).
Mobile phase—
Use variable mixtures of Solution A and Solution B as directed for Chromatographic system. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
System suitability solution—
Transfer about 40 mg of USP Indinavir System Suitability RS to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with Diluent to volume, and mix.
Test solution—
Transfer about 50 mg of Indinavir Sulfate, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with Diluent to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 220-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.0 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 220-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.0 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows.
Chromatograph the System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between indinavir and indinavir related compound C is greater than 1.8; and the tailing factor, determined from the indinavir peak, is greater than 0.95 and less than 2.0.
| Time (minutes) |
Solution A
(%) |
Solution B
(%) |
Elution |
| 0–40 | 80®30 | 20®70 | linear gradient |
| 40–45 | 30 | 70 | isocratic |
| 45–47 | 30®80 | 70®20 | linear gradient |
| 47–52 | 80 | 20 | isocratic |
Procedure—
Inject about 20 µL of the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatogram, and measure the peak responses. Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the portion of Indinavir Sulfate taken by the formula:
100(ri / rs)
in which ri is the peak area response for each impurity; and rs is the sum of the responses of all the peaks: not more than 0.1% of any individual impurity specified in Table 1 is found; and not more than 0.5% of total impurities is found.
Table 1
| Indinavir Related Compound |
Approximate Relative Retention Time |
| A | 0.18 |
| B | 0.80 |
| C | 0.98 |
| D | 1.14 |
| E | 1.30 |
Content of alcohol—
Standard solution—
Transfer 1.0 mL of dehydrated alcohol, at 20 , to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Dilute an accurately measured volume of the resulting solution quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with water to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.001 mL of alcohol per mL of solution.
, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Dilute an accurately measured volume of the resulting solution quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with water to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.001 mL of alcohol per mL of solution.
Test solution—
Transfer about 400 mg of Indinavir Sulfate, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector and a 0.53-mm × 30-m capillary column coated with a 1.0-µm film of phase G14. The carrier gas is helium, flowing at a rate of 10 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows. The temperature of the column is maintained at 35
)—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector and a 0.53-mm × 30-m capillary column coated with a 1.0-µm film of phase G14. The carrier gas is helium, flowing at a rate of 10 mL per minute. The chromatograph is programmed as follows. The temperature of the column is maintained at 35 , the injection port temperature is maintained at 140
, the injection port temperature is maintained at 140 , and the detector temperature is maintained at 220
, and the detector temperature is maintained at 220 . At the end of each five-minute isothermal run, the oven temperature is increased to 200
. At the end of each five-minute isothermal run, the oven temperature is increased to 200 before adjusting the column temperature to 35
before adjusting the column temperature to 35 for the next injection. Chromatograph the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
for the next injection. Chromatograph the Standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 0.1 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Calculate the percentage of alcohol in the portion of Indinavir Sulfate taken by the formula:
 (790 mg/mL).]
(790 mg/mL).]
79,000(CS / CU)(rU / rS)
in which CS is the concentration, in mL per mL, of dehydrated alcohol in the Standard solution; CU is the concentration, in mg per mL, of Indinavir Sulfate in the Test solution; and rU and rS are the peak areas for alcohol obtained from the Test solution and the Standard solution, respectively: between 5.0% and 8.0% is found. [note—The value 79,000 = conversion to percent (100%) × density of alcohol at 20
Content of sulfate—
Methanolic formaldehyde solution—
Transfer 1000 mL of methanol to a suitable container, add 300 µL of formaldehyde, and mix.
Diluent—
Prepare a mixture of Methanolic formaldehyde solution and water (50:50).
Test solution—
Dissolve about 500 mg of Indinavir Sulfate, accurately weighed, in about 80 mL of Diluent.
Procedure—
Titrate with 0.1 M lead perchlorate VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically, using a lead-specific electrode in conjunction with a suitable reference electrode. Each mL of 0.1 M lead perchlorate VS is equivalent to 9.604 mg of sulfate: between 13.2% and 14.4% is found, calculated on the anhydrous and solvent-free basis.
Assay—
Dibutylammonium phosphate buffer—
Transfer 20 mL of dibutyl ammonium phosphate to 1000 mL of water. While stirring, adjust with sodium hydroxide TS to a pH of 6.5 ± 0.5.
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of Dibutylammonium phosphate buffer and acetonitrile (11:9). Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Standard preparation—
Dissolve a suitable quantity of USP Indinavir RS, accurately weighed, in Mobile phase to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.5 mg per mL.
Assay preparation—
Transfer about 60 mg of Indinavir Sulfate, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with Mobile phase to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 260-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L7. The flow rate is about 1.0 mL per minute. The column temperature is maintained at 40
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 260-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L7. The flow rate is about 1.0 mL per minute. The column temperature is maintained at 40 . Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the column efficiency is not less than 4000 theoretical plates; the tailing factor is less than 2.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 1.0%.
. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the column efficiency is not less than 4000 theoretical plates; the tailing factor is less than 2.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 1.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 10 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Calculate the quantity, in mg, of C36H47N5O4·H2SO4 in the portion of Indinavir Sulfate taken by the formula:
(1.1598)DC(rU / rS)
in which D is the dilution factor, in mL, for the Assay preparation; C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Indinavir RS in the Standard preparation; and rU and rS are the peak responses obtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively. [note—1.1598 = Indinavir Sulfate MW (711.87 g/mol)/Indinavir MW (613.80 g/mol).]
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
Chromatographic Column—
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Behnam Davani, Ph.D., M.B.A.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8394 |
(MDAA05) Monograph Development-Antivirals and Antimicrobials |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
USP32–NF27 Page 2625
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 32(2) Page 345
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 32 or NF 27.