- British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II
- Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances
Acetylcysteine |
 |
(Ph. Eur. monograph 0967)
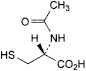
C 5 H 9 NO 3 S 163.2 616-91-1
Sulfydryl donor; antidote to paracetamol poisoning; mucolytic.
Ph Eur
(2R)-2-(Acetylamino)-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid.
98.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
White or almost white, crystalline powder or colourless crystals.
Freely soluble in water and in ethanol (96 per cent), practically insoluble in methylene chloride.
First identification A, C.
Second identification A, B, D, E.
A. Specific optical rotation (see Tests).
B. Melting point (2.2.14): 104 °C to 110 °C.
C. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Preparation Discs of potassium bromide R.
Comparison acetylcysteine CRS.
D. Examine the chromatograms obtained in the test for related substances.
Results The principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (b) is similar in retention time and size to the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b).
E. To 0.5 mL of solution S (see Tests) add 0.05 mL of a 50 g/L solution of sodium nitroprusside R and 0.05 mL of concentrated ammonia R. A dark violet colour develops.
Dissolve 1.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 20 mL with the same solvent.
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and colourless (2.2.2, Method II).
2.0 to 2.8.
To 2 mL of solution S add 8 mL of carbon dioxide-free water R and mix.
+ 21.0 to + 27.0 (dried substance).
In a 25 mL volumetric flask, mix 1.25 g with 1 mL of a 10 g/L solution of sodium edetate R. Add 7.5 mL of a 40 g/L solution of sodium hydroxide R, mix and dissolve. Dilute to 25.0 mL with phosphate buffer solution pH 7.0 R2.
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29). Except where otherwise prescribed, prepare the solutions immediately before use.
Test solution (a) Suspend 0.80 g of the substance to be examined in 1 mL of 1 M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 100.0 mL with water R.
Test solution (b) Dilute 5.0 mL of test solution (a) to 100.0 mL with water R. Dilute 5.0 mL of this solution to 50.0 mL with water R.
Test solution (c) Use test solution (a) after storage for at least 1 h.
Reference solution (a) Suspend 4.0 mg of acetylcysteine CRS, 4.0 mg of l-cystine R (impurity A), 4.0 mg of l-cysteine R (impurity B), 4.0 mg of acetylcysteine impurity C CRS and 4.0 mg of acetylcysteine impurity D CRS in 1 mL of 1 M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 100.0 mL with water R.
Reference solution (b) Suspend 4.0 mg of acetylcysteine CRS in 1 mL of 1 M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 100.0 mL with water R.
- — size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4 mm;
- — stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm).
Mobile phase Stir 3 volumes of acetonitrile R and 97 volumes of water R in a beaker; adjust to pH 3.0 with phosphoric acid R.
Flow rate 1.0 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 220 nm.
Injection 20 µL, 3 times; inject 0.01 M hydrochloric acid as a blank.
Run time 5 times the retention time of acetylcysteine (about 30 min).
Retention time Impurity A = about 2.2 min; impurity B = about 2.4 min; 2-methyl-2-thiazoline-4-carboxylic acid, originating in test solution (c) = about 3.3 min; acetylcysteine = about 6.4 min; impurity C = about 12 min; impurity D = about 14 min.
System suitability Reference solution (a):
- — resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to impurities A and B and minimum 2.0 between the peaks due to impurities C and D.
From the chromatogram obtained with test solution (a), calculate the percentage content of the known impurities (T1) and the unknown impurities (T2) using the following equations:
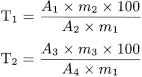
A 1 |
= |
peak area of individual impurity (impurity A, impurity B, impurity C and impurity D) in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (a); |
A 2 |
= |
peak area of the corresponding individual impurity (impurity A, impurity B, impurity C and impurity D) in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a); |
A 3 |
= |
peak area of unknown impurity in the chromatogram obtained with test solution (a); |
A 4 |
= |
peak area of acetylcysteine in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b); |
m 1 |
= |
mass of the substance to be examined in test solution (a); |
m 2 |
= |
mass of the individual impurity in reference solution (a); |
m 3 |
= |
mass of acetylcysteine in reference solution (b). |
- — impurities A, B, C, D: for each impurity, maximum 0.5 per cent;
- — any other impurity: for each impurity, maximum 0.5 per cent;
- — total: maximum 0.5 per cent;
- — disregard limit: 0.1 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent); disregard any peak with a retention time of about 3.3 min due to 2-methyl-2-thiazoline-4-carboxylic acid.
Maximum 10 ppm.
2.0 g complies with test C. Prepare the reference solution using 2 mL of lead standard (10 ppm Pb) R.
Maximum 10 ppm.
Atomic absorption spectrometry (2.2.23, Method II).
Test solution Dissolve 1.00 g in 0.001 M hydrochloric acid and dilute to 50.0 mL with the same acid.
Reference solutions Prepare the reference solutions using zinc standard solution (5 mg/mL Zn) R, diluting with 0.001 M hydrochloric acid.
Source Zinc hollow-cathode lamp.
Wavelength 213.8 nm.
Atomisation device Air-acetylene flame.
Use a correction procedure for non-specific absorption.
Maximum 1.0 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven in vacuo at 70 °C for 3 h.
Maximum 0.2 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
Dissolve 0.140 g in 60 mL of water R and add 10 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R. After cooling in iced water, add 10 mL of potassium iodide solution R and titrate with 0.05 M iodine, using 1 mL of starch solution R as indicator.
1 mL of 0.05 M iodine is equivalent to 16.32 mg of C5H9NO3S.
Protected from light.
Specified impurities A, B, C, D.
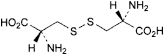
A. 3,3′-disulfanediylbis[(2R)-2-aminopropanoic acid] (l-cystine),
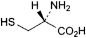
B. (2R)-2-amino-3-sulfanylpropanoic acid (l-cysteine),
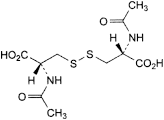
C. (2R,2′R)-3,3′-disulfanediylbis[2-(acetylamino)propanoic acid] (N,N′-diacetyl-l-cystine),
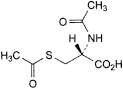
D. (2R)-2-(acetylamino)-3-(acetylsulfanyl)propanoic acid (N,S-diacetyl-l-cysteine).
Ph Eur

