- British Pharmacopoeia Volume I & II
- Monographs: Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Substances
Cetirizine Hydrochloride |
 |
(Cetirizine Dihydrochloride, Ph Eur monograph 1084)
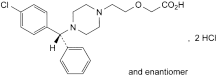
C21H25ClN2O3,2HCl 461.8 83881-52-1
Histamine H1 receptor antagonist; antihistamine.
Ph Eur
(RS)-2-[2-[4-[(4-Chlorophenyl)phenylmethyl]piperazin-1-yl]ethoxy]acetic acid dihydrochloride.
99.0 per cent to 101.0 per cent (dried substance).
White or almost white powder.
Freely soluble in water, practically insoluble in acetone and in methylene chloride.
First identification B, D.
Second identification A, C, D.
A. Ultraviolet and visible absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.25).
Test solution Dissolve 20.0 mg in 50 mL of a 10.3 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R and dilute to 100.0 mL with the same acid. Dilute 10.0 mL of this solution to 100.0 mL with a 10.3 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid R.
Spectral range 210-350 nm.
Absorption maximum At 231 nm.
Specific absorbance at the absorption maximum 359 to 381.
B. Infrared absorption spectrophotometry (2.2.24).
Comparison cetirizine dihydrochloride CRS.
C. Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution Dissolve 10 mg of the substance to be examined in water R and dilute to 5 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 10 mg of cetirizine dihydrochloride CRS in water R and dilute to 5 mL with the same solvent.
Reference solution (b) Dissolve 10 mg of chlorphenamine maleate CRS in water R and dilute to 5 mL with the same solvent. Mix 1 mL of the solution and 1 mL of reference solution (a).
Plate TLC silica gel GF254 plate R.
Mobile phase ammonia R, methanol R, methylene chloride R (1:10:90 V/V/V).
Application 5 µL.
Development Over 2/3 of the plate.
Drying In a current of cold air.
Detection Examine in ultraviolet light at 254 nm.
System suitability Reference solution (b):
- — the chromatogram shows 2 clearly separated spots.
Results The principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution is similar in position and size to the principal spot in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a).
D. It gives reaction (a) of chlorides (2.3.1).
Dissolve 1.0 g in carbon dioxide-free water R and dilute to 20 mL with the same solvent.
Solution S is clear (2.2.1) and not more intensely coloured than reference solution BY7 (2.2.2, Method II).
1.2 to 1.8 for solution S.
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Dissolve 20 mg of the substance to be examined in the mobile phase and dilute to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 2 mg of cetirizine dihydrochloride CRS and 2 mg of cetirizine impurity A CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 50.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of the solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b) Dilute 1.0 mL of the test solution to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase. Dilute 1.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (c) Dissolve the contents of a vial of cetirizine for peak identification CRS (containing impurities B, C, D, E and F) in 5.0 mL of the mobile phase.
- — size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
- — stationary phase: silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm).
Mobile phase dilute sulfuric acid R, water R, acetonitrile R (0.4:6.6:93 V/V/V).
Flow rate 1 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 230 nm.
Injection 20 µL.
Run time 3 times the retention time of cetirizine.
Identification of impurities Use the chromatogram supplied with cetirizine for peak identification CRS and the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (c) to identify the peaks due to impurities B, C, D, E and F; use the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) to identify the peak due to impurity A.
Relative retention With reference to cetirizine (retention time = about 9 min): impurity D = about 0.6; impurity B = about 0.8; impurity C = about 0.9; impurity E = about 1.2; impurity F = about 1.37; impurity A = about 1.42.
System suitability Reference solution (c):
- — peak-to-valley ratio: minimum 5, where Hp = height above the baseline of the peak due to impurity C and Hv = height above the baseline of the lowest point of the curve separating this peak from the peak due to cetirizine.
- — correction factors: for the calculation of content, multiply the peak areas of the following impurities by the corresponding correction factor: impurity A = 0.7; impurity C = 1.9; impurity D = 0.6; impurity E = 1.3; impurity F = 1.9;
- — impurities A, B, C, D, E, F: for each impurity, not more than 1.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.15 per cent);
- — unspecified impurities: for each impurity, not more than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.10 per cent);
- — total: not more than 3 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.3 per cent);
- — disregard limit: 0.5 times the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) (0.05 per cent).
Maximum 0.5 per cent, determined on 1.000 g by drying in an oven at 105 °C.
Maximum 0.2 per cent, determined on 1.0 g.
Dissolve 0.100 g in 70 mL of a mixture of 30 volumes of water R and 70 volumes of acetone R. Titrate with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide to the 2nd point of inflexion. Determine the end-point potentiometrically (2.2.20). Carry out a blank titration.
1 mL of 0.1 M sodium hydroxide is equivalent to 15.39 mg of C21H27Cl3N2O3.
Protected from light.
Specified impurities A, B, C, D, E, F.
Other detectable impurities (the following substances would, if present at a sufficient level, be detected by one or other of the tests in the monograph. They are limited by the general acceptance criterion for other/unspecified impurities and/or by the general monograph Substances for pharmaceutical use (2034). It is therefore not necessary to identify these impurities for demonstration of compliance. See also 5.10. Control of impurities in substances for pharmaceutical use): G.
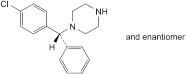
A. (RS)-1-[(4-chlorophenyl)phenylmethyl]piperazine,
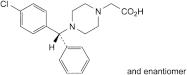
B. (RS)-2-[4-[(4-chlorophenyl)phenylmethyl]piperazin-1-yl]acetic acid,
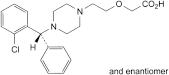
C. (RS)-2-[2-[4-[(2-chlorophenyl)phenylmethyl]piperazin-1-yl]ethoxy]acetic acid,
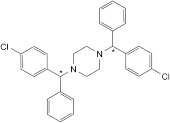
D. 1,4-bis[(4-chlorophenyl)phenylmethyl]piperazine,
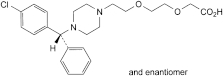
E. (RS)-2-[2-[2-[4-[(4-chlorophenyl)phenylmethyl]piperazin-1-yl]ethoxy]ethoxy]acetic acid (ethoxycetirizine),
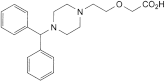
F. 2-[2-[4-(diphenylmethyl)piperazin-1-yl]ethoxy]acetic acid,
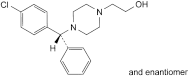
G. (RS)-2-[4-[(4-chlorophenyl)phenylmethyl]piperazin-1-yl]ethan-1-ol.
Ph Eur

