- British Pharmacopoeia Volume IV
- Herbal Drugs, Herbal Drug Preparations and Herbal Medicinal Products
Refined and Quantified Ginkgo Dry Extract |
 |
(Ph. Eur. monograph 1827)
Ph Eur
Refined and quantified dry extract produced from Ginkgo leaf (1828).
- — flavonoids, expressed as flavone glycosides (Mr 756.7): 22.0 per cent to 27.0 per cent (dried extract);
- — bilobalide: 2.6 per cent to 3.2 per cent (dried extract);
- — ginkgolides A, B and C: 2.8 per cent to 3.4 per cent (dried extract);
- — ginkgolic acids: maximum 5 ppm (dried extract).
The extract is produced from the herbal drug by an appropriate procedure using organic solvents and their mixtures with water, physical separation steps as well as other suitable processes.
Bright yellow-brown, powder or friable mass.
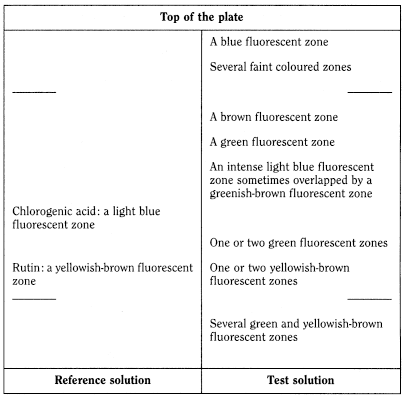
Thin-layer chromatography (2.2.27).
Test solution Dissolve 20.0 mg of the extract to be examined in 10 mL of a mixture of 2 volumes of water R and 8 volumes of methanol R.
Reference solution Dissolve 1.0 mg of chlorogenic acid R and 3.0 mg of rutin R in 20 mL of methanol R.
Plate TLC silica gel plate R (5-40 µm) or [TLC silica gel plate R (2-10 µm)].
Mobile phase anhydrous formic acid R, glacial acetic acid R, water R, ethyl acetate R (7.5:7.5:17.5:67.5 V/V/V/V).
Application 20 µL [or 5 µL], as bands.
Development Over a path of 17 cm [or 6 cm].
Drying At 100-105 °C.
Detection Spray the plate whilst still hot with a 10 g/L solution of diphenylboric acid aminoethyl ester R in methanol R, then spray with a 50 g/L solution of macrogol 400 R in methanol R; allow to dry in air for about 30 min and examine in ultraviolet light at 365 nm.
Results See below the sequence of zones present in the chromatograms obtained with the reference solution and the test solution. Furthermore, other, weaker fluorescent zones may be present in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution.
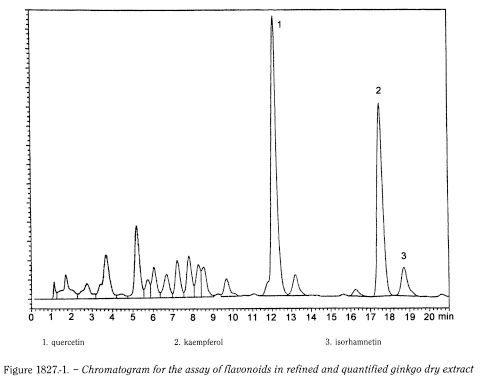
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Dissolve 0.200 g of the extract to be examined in 20 mL of methanol R. Add 15.0 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R and 5 mL of water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with methanol R. Transfer 10.0 mL of this solution into a 10 mL brown-glass vial. Close the vial with a tight rubber membrane stopper and secure with an aluminium crimped cap. Heat on a water-bath for 25 min. Allow to cool to 20 °C.
Reference solution Dissolve 10.0 mg of quercetin dihydrate CRS in 20 mL of methanol R. Add 15.0 mL of dilute hydrochloric acid R and 5 mL of water R and dilute to 50.0 mL with methanol R.
- — size: l = 0.125 m, Ø = 4 mm;
- — stationary phase: octadecylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm);
- — temperature: 25 °C.
- — mobile phase A: 0.3 g/L solution of phosphoric acid R adjusted to pH 2.0;
- — mobile phase B: methanol R;
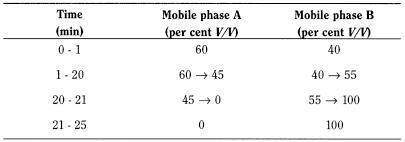
Flow rate 1.0 mL/min.
Detector Spectrophotometer at 370 nm.
Injection 10 µL.
Relative retention With reference to quercetin (retention time = about 12.5 min): kaempferol = about 1.4; isorhamnetin = about 1.5.
System suitability Test solution:
- — resolution: minimum 1.5 between the peaks due to kaempferol and isorhamnetin.
Determine the sum of the areas including all the peaks from the peak due to quercetin to the peak due to isorhamnetin in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution (see Figure 1827.-1).
Calculate the percentage content of flavonoids, expressed as flavone glycosides, using the following expression:
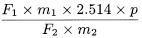
F 1 |
= |
sum of the areas of all the peaks from the peak due to quercetin to the peak due to isorhamnetin in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution |
F 2 |
= |
area of the peak due to quercetin in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution |
m 1 |
= |
mass of quercetin dihydrate CRS in the reference solution, in grams |
m 2 |
= |
mass of the extract to be examined used to prepare the test solution, in grams |
p |
= |
percentage content of anhydrous quercetin in quercetin dihydrate CRS. |
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Place 0.120 g of the extract to be examined in a 25 mL beaker and dissolve it in 10 mL of phosphate buffer solution pH 5.8 R by stirring. Transfer the solution into a chromatography column, about 0.15 m long and about 30 mm in internal diameter, containing 15 g of kieselguhr for chromatography R. Wash the beaker with 2 quantities, each of 5 mL, of phosphate buffer solution pH 5.8 R and transfer the washings to the chromatography column. Allow to stand for 15 min. Elute with 100 mL of ethyl acetate R. Evaporate the eluate to dryness at a pressure not exceeding 4 kPa in a water-bath at 50 °C. The residue of solvent is eliminated by an air-current. Take up the residue in 2.5 mL of the mobile phase.
Reference solution (a) Dissolve 30.0 mg of benzyl alcohol CRS in the mobile phase and dilute to 100.0 mL with the mobile phase.
Reference solution (b) Place 0.120 g of the ginkgo dry extract for peak identification CRS in a 25 mL beaker and dissolve it in 10 mL of phosphate buffer solution pH 5.8 R by stirring, then proceed as described for the test solution.
- — size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4 mm;
- — stationary phase: octylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm);
- — temperature: 25 °C.
Mobile phase tetrahydrofuran R, methanol R, water R (10:20:75 V/V/V).
Flow rate 1.0 mL/min.
Detection Refractometer maintained at 35 °C.
Injection 100 µL.
Identification of peaks Use the chromatogram supplied with ginkgo dry extract for peak identification CRS and the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution (b) to identify the peaks due to bilobalide and ginkgolides A, B and C.
- — the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (b) is similar to the chromatogram supplied with ginkgo dry extract for peak identification CRS.
Calculate the percentage content of bilobalide, using the following expression:
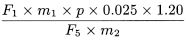
Calculate the percentage content of ginkgolide A, using the following expression:
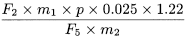
Calculate the percentage content of ginkgolide B, using the following expression:
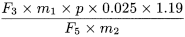
Calculate the percentage content of ginkgolide C, using the following expression:
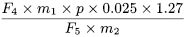
F 1 |
= |
area of the peak due to bilobalide in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution |
F 2 |
= |
area of the peak due to ginkgolide A in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution |
F 3 |
= |
area of the peak due to ginkgolide B in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution |
F 4 |
= |
area of the peak due to ginkgolide C in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution |
F 5 |
= |
area of the peak due to benzyl alcohol in the chromatogram obtained with reference solution (a) |
m 1 |
= |
mass of benzyl alcohol CRS in reference solution (a), in grams |
m 2 |
= |
mass of the extract to be examined used to prepare the test solution, in grams |
p |
= |
percentage content of benzyl alcohol in benzyl alcohol CRS. |
Calculate the percentage content of the sum of ginkgolides A, B and C, using the following expression:
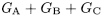
G A |
= |
percentage content of ginkgolide A |
G B |
= |
percentage content of ginkgolide B |
G C |
= |
percentage content of ginkgolide C. |
Liquid chromatography (2.2.29).
Test solution Dissolve 0.500 g of the powdered extract to be examined in 8 mL of methanol R, sonicating if necessary, and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent. Centrifuge if necessary.
Reference solution Dissolve 10.0 mg of ginkgolic acids CRS in 8 mL of methanol R, sonicating if necessary, and dilute to 10.0 mL with the same solvent. Dilute 2.0 mL of this solution to 10.0 mL with methanol R.
- — size: l = 0.25 m, Ø = 4.6 mm;
- — stationary phase: octylsilyl silica gel for chromatography R (5 µm);
- — temperature: 35 °C.
- — mobile phase A: dilute 0.1 mL of trifluoroacetic acid R to 1000 mL with water R;
- — mobile phase B: dilute 0.1 mL of trifluoroacetic acid R to 1000 mL with acetonitrile R;
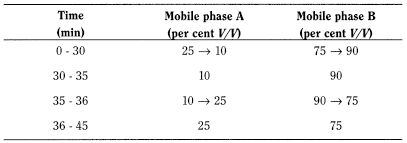
Flow rate 1.0 mL/min.
Detection Spectrophotometer at 210 nm.
Injection 50 µL.
Identification of components Use the chromatogram supplied with ginkgolic acids CRS and the chromatogram obtained with the test solution to identify the peaks due to ginkgolic acids C13, C15 and C17.
System suitability Reference solution:
- — resolution: minimum 2.0 between the peaks due to ginkgolic acids C13 and C15;
- — symmetry factor: 0.8 to 2.0 for the peaks due to ginkgolic acids C13, C15 and C17.
Calculate the content in parts per million of ginkgolic acids expressed as ginkgolic acid C17, using the following expression:
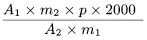
A 1 |
= |
sum of the areas of the peaks due to the ginkgolic acids C13, C15 and C17 in the chromatogram obtained with the test solution |
A 2 |
= |
area of the peak due to ginkgolic acid C17 in the chromatogram obtained with the reference solution |
m 1 |
= |
mass of the extract to be examined used to prepare the test solution, in grams |
m 2 |
= |
mass of ginkgolic acids CRS used to prepare the reference solution, in grams |
p |
= |
percentage content of ginkgolic acid C17 in ginkgolic acids CRS. |
Ph Eur

