Azithromycin for Injection
» Azithromycin for Injection is a sterile, dry mixture of azithromycin and a suitable stabilizing agent. It contains not less than 90.0 percent and not more than 110.0 percent of the labeled amount of azithromycin (C38H72N2O12).
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in Containers for Sterile Solids as described under Injections  1
1 , and store at controlled room temperature.
, and store at controlled room temperature.
Labeling—
It meets the requirements for Labeling under Injections  1
1 .
.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
USP N-Demethylazithromycin RS
(2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-13-[(2,6-Dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-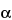 -l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-methylamino-
-l-ribo-hexopyranosyl)oxy]-2-ethyl-3,4,10-trihydroxy-3,5,6,8,10,12,14-heptamethyl-11-[[3,4,6-trideoxy-3-methylamino-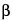 -d-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one.
-d-xylo-hexopyranosyl]oxy]-1-oxa-6-azacyclopentadecan-15-one.
C37H70N2O12 734.96
(2R,3S,4R,5R,8R,10R,11R,12S,13S,14R)-13-[(2,6-Dideoxy-3-C-methyl-3-O-methyl-
C37H70N2O12 734.96
USP Desosaminylazithromycin RS
USP Endotoxin RS
Identification—
The chromatogram of the Assay preparation obtained as directed in the Assay exhibits a major peak for azithromycin, the retention time of which corresponds to that exhibited in the chromatogram of the Standard preparation.
Bacterial endotoxins  85
85 —
It contains not more than 0.7 USP EU per mg of Azithromycin.
—
It contains not more than 0.7 USP EU per mg of Azithromycin.
Sterility  71
71 —
It meets the requirements when tested as directed for Membrane Filtration under Test for Sterility of the Product to be Examined.
—
It meets the requirements when tested as directed for Membrane Filtration under Test for Sterility of the Product to be Examined.
Uniformity of dosage units  905
905 :
meets the requirements.
:
meets the requirements.
pH  791
791 :
between 6.4 and 6.8, determined in a solution constituted as directed in the labeling.
:
between 6.4 and 6.8, determined in a solution constituted as directed in the labeling.
Water, Method I  921
921 :
not more than 2.0%.
:
not more than 2.0%.
Particulate matter  788
788 :
meets the requirements.
:
meets the requirements.
Limit of azithromycin N-oxide—
Potassium phosphate 0.02 M buffer—
Prepare as directed in the test for Related compounds.
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of Potassium phosphate 0.02 M buffer and acetonitrile (76.5:23.5). Adjust with 5 N potassium hydroxide to a pH of 11.0 ± 0.1. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Diluent—
A mixture of Potassium phosphate 0.02 M buffer and acetonitrile (76.5:23.5). Adjust with diluted phosphoric acid to a pH of 8.0 ± 0.1.
Stock standard solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed portion of USP Azithromycin RS in acetonitrile to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.6 mg per mL.
Standard solution—
Dilute the Stock standard solution quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with Diluent to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.006 mg of azithromycin per mL.
Resolution solution—
0.0015 mg/mL of azithromycin N-oxide and 0.45 mg/mL of azithromycin in Diluent.
Test solution—
Prepare as directed in the test for Related compounds.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with an amperometric electrochemical detector with a dual series glassy carbon electrode operated in the oxidative screen mode, with electrode 1 set at +0.70 ± 0.05 V and electrode 2 set at +0.82 ± 0.05 V and the background current optimized to 95 ± 25 nanoamperes; a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L29; and a 4.6-mm × 5-cm guard column that contains 5-µm packing L29. The flow rate is about 0.4 mL per minute. The autosampler temperature is maintained at 15
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with an amperometric electrochemical detector with a dual series glassy carbon electrode operated in the oxidative screen mode, with electrode 1 set at +0.70 ± 0.05 V and electrode 2 set at +0.82 ± 0.05 V and the background current optimized to 95 ± 25 nanoamperes; a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L29; and a 4.6-mm × 5-cm guard column that contains 5-µm packing L29. The flow rate is about 0.4 mL per minute. The autosampler temperature is maintained at 15 . Chromatograph the Resolution solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative retention times are about 0.38 and 1.0, respectively, for the azithromycin N-oxide and the azithromycin peaks. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the column efficiency is not less than 1000 theoretical plates; the tailing factor is not less than 0.9 and not more than 1.5; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 5%.
. Chromatograph the Resolution solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative retention times are about 0.38 and 1.0, respectively, for the azithromycin N-oxide and the azithromycin peaks. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the column efficiency is not less than 1000 theoretical plates; the tailing factor is not less than 0.9 and not more than 1.5; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 5%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 25 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, and measure the area responses for all the peaks. Calculate the percentage of azithromycin N-oxide in the portion of Azithromycin for Injection taken by the formula:
(P/1000)(CS / CU)(ri / rS)(100)
in which (P/1000) is the potency, converted from µg per mg to mg per mg, of USP Azithromycin RS; CS is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Azithromycin RS in the Standard solution; CU is the concentration, in mg per mL, of azithromycin in the Test solution; ri is the response of the azithromycin N-oxide peak obtained from the Test solution; and rS is the response for the azithromycin peak in the Standard solution: not more than 1.0% of azithromycin N-oxide is found.
Related compounds—
Potassium phosphate 0.02 M buffer—
Dilute about 3.48 g of dibasic potassium phosphate with water to 1000 mL, and mix. Prior to use, pass through a filter having a porosity of 0.45 µm.
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of Potassium phosphate 0.02 M buffer and acetonitrile (54:46). Adjust with 10 N potassium hydroxide to a pH of 11.0 ± 0.1. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Diluent—
Use a mixture of water and acetonitrile (54 : 46).
Blank—
Use Diluent.
Stock standard solution—
Dissolve accurately weighed portions of USP Desosaminylazithromycin RS, USP N-Demethylazithromycin RS, and USP Azithromycin RS in acetonitrile; and dilute quantitatively with the same solvent to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.09 mg of desosaminylazithromycin, 0.21 mg of N-demethylazithromycin, and 0.30 mg of azithromycin per mL.
Standard solution—
Dilute the Stock standard solution quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with Diluent to obtain a solution having known concentrations of about 0.0018 mg of desosaminylazithromycin, 0.0042 mg of N-demethylazithromycin, and 0.006 mg of azithromycin per mL.
Test solution—
Reconstitute 3 vials individually, as directed in the labeling. Mix the contents of all the reconstituted vials. Dilute a portion of the mixture quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with Diluent to obtain a solution having a nominal concentration of about 0.6 mg of azithromycin per mL, based on the label claim. The Test solution must be injected immediately.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with an amperometric electrochemical detector with dual glassy carbon electrodes, operated in the oxidative screen mode, with electrode 1 set at +0.70 ± 0.05 V and electrode 2 set at +0.82 ± 0.05 V and with the background current optimized to 95 ± 25 nanoamperes; a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L67; and a 4.6-mm × 1-cm guard column that contains 5-µm packing L67. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. The column is maintained at about 40
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with an amperometric electrochemical detector with dual glassy carbon electrodes, operated in the oxidative screen mode, with electrode 1 set at +0.70 ± 0.05 V and electrode 2 set at +0.82 ± 0.05 V and with the background current optimized to 95 ± 25 nanoamperes; a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L67; and a 4.6-mm × 1-cm guard column that contains 5-µm packing L67. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. The column is maintained at about 40 . The autosampler temperature is maintained at 15
. The autosampler temperature is maintained at 15 . Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative retention times are as shown in Table 1; the resolution, R, between desosaminylazithromycin and N-demethylazithromycin is not less than 1.5; the tailing factor of the peaks for desosaminylazithromycin, N-demethylazithromycin, and azithromycin is not more than 1.5; the column efficiency is not less than 1500 theoretical plates for the azithromycin peak; and the relative standard deviation of the desosaminylazithromycin, N-demethylazithromycin, and azithromycin peaks for replicate injections is not more than 5%.
. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative retention times are as shown in Table 1; the resolution, R, between desosaminylazithromycin and N-demethylazithromycin is not less than 1.5; the tailing factor of the peaks for desosaminylazithromycin, N-demethylazithromycin, and azithromycin is not more than 1.5; the column efficiency is not less than 1500 theoretical plates for the azithromycin peak; and the relative standard deviation of the desosaminylazithromycin, N-demethylazithromycin, and azithromycin peaks for replicate injections is not more than 5%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 25 µL) of the Standard solution, the Blank, and the Test solution into the chromatograph, and measure the responses for all the peaks. Calculate the percentage of desosaminylazithromycin in the portion of Azithromycin for Injection taken by the formula:
(P)(CS / CU)(ri / rS)(100)
in which P is the potency, in mg per mg, of USP Desosaminylazithromycin RS; CS is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Desosaminylazithromycin RS in the Standard solution; CU is the concentration, in mg per mL, of azithromycin in the Test solution; ri is the response of the desosaminylazithromycin peak obtained from the Test solution; and rS is the response for the desosaminylazithromycin peak in the Standard solution. Calculate the percentage of N-demethylazithromycin in the portion of Azithromycin for Injection taken by the formula:
(P)(CS / CU)(ri / rS)(100)
in which P is the potency, in mg per mg, of USP N-Demethylazithromycin RS; CS is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP N-Demethylazithromycin RS in the Standard solution; CU is the concentration, in mg per mL, of azithromycin in the Test solution; ri is the response of the N-demethylazithromycin peak obtained from the Test solution; and rS is the response for the N-demethylazithromycin peak in the Standard solution. Calculate the percentage of each of the other related compounds, including unspecified impurities, in the portion of Azithromycin for Injection taken by the formula:
(P/1000)(CS / CU)(ri / rS)(100)
in which (P / 1000) is the potency, converted from µg per mg to mg per mg, of USP Azithromycin RS; CS is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Azithromycin RS in the Standard solution; CU is the concentration, in mg per mL, of azithromycin in the Test solution; ri is the response of the impurity peak obtained from the Test solution; and rS is the response for the azithromycin peak in the Standard solution. The specified and unspecified impurities meet the limits specified in Table 1. Disregard any peaks corresponding to those obtained with the Blank.
Table 1
| Peak Identification |
Relative Retention Time |
Limit (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 3¢-(N,N-Didemethyl)azithromycin (aminoazithromycin) + 3¢-(N,N-didemethyl)-3¢-N-formylazithromycin | 0.25 | 1.0 |
| Desosaminylazithromycin | 0.31 | 0.3 |
| 3¢-N-Demethyl-3¢-N- formylazithromycin |
0.32 | 1.0 |
| N-Demethylazithromycin | 0.35 | 1.0 |
| 3¢-De(dimethylamino)-3¢-oxoazithromycin | 0.72 | 1.0 |
| Azithromycin | 1.00 | — |
| Any other unspecified impurity |
— | 0.2 |
| Total impurities | — | 3.0 |
Other requirements—
It meets the requirements specified under Injections  1
1 .
.
Assay—
Potassium phosphate buffer—
Dissolve about 6.7 g of dibasic potassium phosphate in 1000 mL of water, and mix. Prior to use, pass through a filter having a porosity of 0.45 µm.
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of acetonitrile and Potassium phosphate buffer (52 : 48). Adjust with 10 N potassium hydroxide to a pH of 11.0 ± 0.1. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Diluent:
a mixture of acetonitrile and water (52 : 48).
Resolution solution—
Transfer accurately weighed quantities of USP Azaerythromycin A RS and USP Azithromycin RS to a suitable volumetric flask. Dissolve in acetonitrile, using 52% of the final volume. Dilute with water to volume, and mix to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 1 mg each of azaerythromycin and azithromycin per mL.
Standard preparation—
Transfer an accurately weighed quantity of USP Azithromycin RS to a suitable volumetric flask. Dissolve in acetonitrile, using about 52% of the final volume. Dilute with water to volume, and mix to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 1 mg of azithromycin per mL.
Assay preparation—
Reconstitute 3 vials individually as directed in the labeling. Mix the contents of all the reconstituted vials. Dilute a portion of the mixture quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with Diluent to obtain a solution having a nominal concentration of about 1 mg azithromycin per mL, based on the label claim.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 215-nm detector, a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L67, and a 4.6-mm × 1-cm guard column that contains 5-µm packing L67. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. The column is maintained at about 40
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 215-nm detector, a 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L67, and a 4.6-mm × 1-cm guard column that contains 5-µm packing L67. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. The column is maintained at about 40 . The autosampler temperature is maintained at 15
. The autosampler temperature is maintained at 15 . Chromatograph the Resolution solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative retention times are about 0.68 and 1.0, respectively, for the azaerithromycin A and azithromycin peaks; and the resolution, R, between the peaks due to azaerythromycin A and azithromycin is not less than 2.5. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the column efficiency is not less than 1500 theoretical plates; the tailing factor is not less than 0.9 and not more than 1.5; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2%.
. Chromatograph the Resolution solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative retention times are about 0.68 and 1.0, respectively, for the azaerithromycin A and azithromycin peaks; and the resolution, R, between the peaks due to azaerythromycin A and azithromycin is not less than 2.5. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the column efficiency is not less than 1500 theoretical plates; the tailing factor is not less than 0.9 and not more than 1.5; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 15 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, and measure the area responses for the major peaks. Calculate the percentage of the label claim of azithromycin (C38H72N2O12) in the portion of Azithromycin for Injection taken by the formula:
(P/1000)(CS / CU)(rU / rS)(100)
in which (P/1000) is the potency, converted from µg per mg to mg per mg, of USP Azithromycin RS; CS is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Azithromycin RS in the Standard preparation; CU is the nominal concentration, in mg per mL, of azithromycin in the Assay preparation; and rU and rS are the peak area responses for azithromycin obtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Ahalya Wise, M.S.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8161 |
(SM12010) Monographs - Small Molecules 1 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
|
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology |
USP35–NF30 Page 2284
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 37(3)