Synthetic Paraffin
DEFINITION
Synthetic Paraffin is synthesized by the Fischer-Tropsch process from carbon monoxide and hydrogen, which are catalytically converted to a mixture of paraffin hydrocarbons; the lower molecular weight fractions are removed by distillation, and the residue is hydrogenated and further treated by percolation through activated charcoal. This mixture may be fractionated into its components by a solvent separation method, using a suitable synthetic isoparaffinic petroleum hydrocarbon solvent. It may contain NMT 0.005% of a suitable antioxidant.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Infrared Absorption  197
197 :
A thin film of it, cast from a melt onto a cesium bromide plate, exhibits a pair of very strong IR absorption peaks between 2840 cm
:
A thin film of it, cast from a melt onto a cesium bromide plate, exhibits a pair of very strong IR absorption peaks between 2840 cm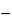 1 and 3000 cm
1 and 3000 cm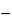 1, a pair of moderately strong peaks between 1430 cm
1, a pair of moderately strong peaks between 1430 cm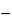 1 and 1490 cm
1 and 1490 cm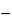 1, a pair of medium peaks between 720 cm
1, a pair of medium peaks between 720 cm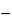 1 and 750 cm
1 and 750 cm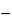 1, and only weak peaks at any other wavenumbers.
1, and only weak peaks at any other wavenumbers.
IMPURITIES
• Heavy Metals, Method II  231
231 :
NMT 20 ppm
:
NMT 20 ppm
• Limit of Oil Content
Analysis:
Follow ASTM Method D721-68, “Standard Test Method for Oil Content of Petroleum Waxes” (Reapproved 1987).1
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.5%
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Absorptivity
Sample solution:
Transfer 50–100 mg to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Dissolve in decahydronaphthalene at 88 , dilute with the same solvent at this temperature to volume, and mix.
, dilute with the same solvent at this temperature to volume, and mix.
Blank:
Decahydronaphthalene
Instrumental conditions
Mode:
UV
Analytical wavelength:
290 nm
Cell:
10 cm (jacketed cells maintained at 88 )
)
Analysis
Samples:
Sample solution and Blank
Determine the absorbance of the Sample solution, and calculate the absorptivity.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.01
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers.
• Labeling:
The labeling indicates its congealing temperature, viscosity, and needle penetration range under the specified conditions.
1
Available from the American Society for Testing and Materials, 1916 Race St., Philadelphia, PA 19103.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Robert H. Lafaver, M.S.
Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8335 |
(EXC2010) Monographs - Excipients |
USP35–NF30 Page 1886