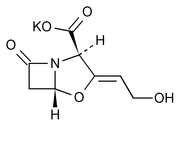
Clavulanate Potassium
C8H8KNO5 237.25
4-Oxa-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 3-(2-hydroxyethylidene)-7-oxo-, monopotassium salt, 2R-(2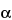 ,3Z,5
,3Z,5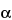 )-;
)-;
Potassium (Z)-(2R,5R)-3-(2-hydroxyethylidene)-7-oxo-4-oxa-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate

 [61177-45-5].
[61177-45-5].
(klav'' ue lan' ate poe tas' ee um).
C8H8KNO5 237.25
4-Oxa-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 3-(2-hydroxyethylidene)-7-oxo-, monopotassium salt, 2R-(2
Potassium (Z)-(2R,5R)-3-(2-hydroxyethylidene)-7-oxo-4-oxa-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylate
DEFINITION
Clavulanate Potassium contains the equivalent of NLT 75.5% and NMT 92.0% of clavulanic acid (C8H9NO5), calculated on the anhydrous basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• A.
The retention time of the major peak for clavulanic acid in the Sample solution corresponds to that in the Standard solution, as obtained in the Assay.
• B. Identification Tests—General, Potassium  191
191 :
Meets the requirements
:
Meets the requirements
ASSAY
• Procedure
Solution A:
7.8 mg/mL of monobasic sodium phosphate in water. Adjust with phosphoric acid or 10 N sodium hydroxide to a pH of 4.4 ± 0.1 before final dilution.
Mobile phase:
Methanol and Solution A (1:19)
Standard solution:
0.25 mg/mL of USP Clavulanate Lithium RS in water
System suitability solution:
0.5 mg/ml of amoxicillin dissolved in Standard solution
Sample solution:
0.25 mg/mL of Clavulanate Potassium in water
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 220 nm
Column:
4-mm × 30-cm; 3- to 10-µm packing L1
Flow rate:
2 mL/min
Injection size:
20 µL
System suitability
Samples:
Standard solution and System suitability solution
[Note—The relative retention times for clavulanic acid and amoxicillin are about 0.5 and 1.0, respectively. ]
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 3.5 between the amoxicillin and clavulanic acid peaks, System suitability solution
Column efficiency:
NLT 550 theoretical plates, Standard solution
Tailing factor:
NMT 1.5, Standard solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 2.0%, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of C8H9NO5 in each mg of Clavulanate Potassium taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × P × F × 100
| rU | = | = peak response from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Clavulanate Lithium RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of Clavulanate Potassium in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
| P | = | = designated potency of USP Clavulanate Lithium RS, in µg/mg of clavulanic acid |
| F | = | = unit conversion factor, 0.001 mg/µg |
Acceptance criteria:
75.5%–92.0% on the anhydrous basis
IMPURITIES
Organic Impurities
• Procedure 1
Solution A:
0.05 M monobasic sodium phosphate. Adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 4.0 ± 0.1.
Solution B:
Methanol and Solution A (1:1)
Mobile phase:
See the gradient table below.
| Time (min) |
Solution A (%) |
Solution B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 100 | 0 |
| 4 | 100 | 0 |
| 15 | 50 | 50 |
| 18 | 50 | 50 |
| 24 | 100 | 0 |
Standard solution:
0.1 mg/mL of USP Clavulanate Lithium RS in Solution A
Sample solution:
10.0 mg/mL of Clavulanate Potassium in Solution A
System suitability solution:
0.1 mg/mL each of USP Clavulanate Lithium RS and amoxicillin in Solution A
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 230 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 10-cm; 5-µm packing L1
Temperature:
40
Flow rate:
1 mL/min
[Note—The system is equilibrated for 15 min with 100% Solution A. ]
Injection size:
20 µL
System suitability
Samples:
Standard solution and System suitability solution
[Note—The relative retention times for clavulanic acid and amoxicillin are about 1.0 and 2.5, respectively. ]
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 13 between the clavulanic acid peak and the amoxicillin peak, System suitability solution
Column efficiency:
NLT 2000 theoretical plates from the clavulanic acid peak, System suitability solution
Tailing factor:
NMT 2.0 for the clavulanic acid peak, System suitability solution
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 2%, Standard solution
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage, in terms of clavulanate potassium equivalent, of each impurity in the Clavulanate Potassium taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × (Mr1/Mr2) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of an individual impurity peak from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of clavulanic acid from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of Clavulanate Potassium from the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
| Mr1 | = | = molecular weight of clavulanate potassium, 237.3 |
| Mr2 | = | = molecular weight of clavulanate lithium, 205.1 |
Acceptance criteria
Total impurities:
NMT 2%
• Procedure 2: Limit of Clavam-2-Carboxylate Potassium
Mobile phase:
0.1 M monobasic sodium phosphate. Adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 4.0 ± 0.1.
Standard solution:
5 µg/mL of USP Clavam-2-Carboxylate Potassium RS in water
Sample solution:
10 mg/mL of Clavulanate Potassium in water
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 210 nm
Column:
4-mm × 30-cm; 3- to 10-µm packing L1
Flow rate:
0.5 mL/min
Injection size:
20 µL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
[Note—The relative retention times for clavam-2-carboxylic acid and clavulanic acid are about 0.7 and 1.0, respectively. ]
Suitability requirements
Column efficiency:
NLT 4000 theoretical plates
Tailing factor:
NMT 1.5
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 5%
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of clavam-2-carboxylate potassium in the sample taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × F × 100
| rU | = | = peak response from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of the Standard solution (µg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of Clavulanate Potassium in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
| F | = | = unit conversion factor, 0.001 mg/µg |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.01%
• Procedure 3: Limit of Aliphatic Amines
Internal standard solution:
50 µL of 3-methyl-2-pentanone in water to 100 mL
Standard solution:
Dissolve 80.0 mg of each of the following amines in 2 N hydrochloric acid: 1,1-dimethylethylamine, diethylamine, tetramethylethylenediamine, 1,1,3,3-tetramethylbutylamine, and N,N¢-diisopropylethylenediamine. Dilute with 2 N hydrochloric acid to 200.0 mL. Transfer 5.0 mL of this solution to a centrifuge tube. Add 5.0 mL of Internal standard solution, 10.0 mL of 2 N sodium hydroxide, 5.0 mL of isopropyl alcohol, and 5 g of sodium chloride. Shake for 1 min, and centrifuge to separate the layers. Use the upper layer.
Sample solution:
Transfer 1.0 g of Clavulanate Potassium to a centrifuge tube, add 5.0 mL of Internal standard solution, 5.0 mL of 2 N sodium hydroxide, 10.0 mL of water, 5.0 mL of isopropyl alcohol, and 5 g of sodium chloride. Shake for 1 min, and centrifuge to separate the layers. Use the upper layer.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
GC
Detector:
Flame ionization
Column:
0.53-mm × 50-m capillary fused silica column that contains a 5-µm film coating of stationary phase G41
Temperature
Injector:
200
Detector:
250
Column:
See the temperature program table below.
| Initial Temperature ( |
Temperature Ramp ( |
Final Temperature ( |
Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 35 | — | 35 | 7 |
| 35 | 30 | 150 | 15 |
Carrier gas:
Helium
Flow rate:
8 mL/min
Split ratio:
1:10
Injection size:
1 µL
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
[Note—See the table below for relative retention times. ]
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
|---|---|
| 1,1-Dimethylethylamine | 0.55 |
| Diethylamine | 0.76 |
| 3-Methyl-2-pentanone (internal standard) | 1.0 |
| Tetramethylethylenediamine | 1.07 |
| 1,1,3,3-Tetramethylbutylamine | 1.13 |
| N,N¢-Diisopropylethylenediamine | 1.33 |
| Bis(2-methylamino)ethyl ethera | 1.57 |
|
a
The relative retention time for this compound is provided for information only; bis(2-methylamino)ethyl ether is not a component of the Standard solution.
|
|
Calculate the percentage of each impurity in the Clavulanate Potassium taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response for an individual impurity from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response for the relevant analyte from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of the relevant analyte in the Standard solution |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of Clavulanate Potassium in the Standard solution |
Calculate the percentage of any individual impurity for which no relevant reference compound is provided in the Standard solution by the same formula, except for rS use the peak response corresponding to the 1,1-dimethylethylamine peak.
Acceptance criteria
Total of all aliphatic amines:
NMT 0.2%
• Procedure 4: Limit of 2-Ethylhexanoic Acid
Internal standard solution:
1 mg/mL of 3-cyclohexylpropionic acid in cyclohexane
Standard solution:
1.5 mg/mL of 2-ethylhexanoic acid in Internal standard solution. Transfer 1.0 mL of this solution to a centrifuge tube, and add 4.0 mL of 4 N hydrochloric acid. Shake for 1 min, and allow the phases to separate, centrifuging if necessary. Withdraw the lower phase, and reserve the upper phase. To the lower phase add 1.0 mL of Internal standard solution, and shake for 1 min. Allow the phases to separate, centrifuging if necessary. Withdraw the upper phase, and combine with the reserved upper layer.
Sample solution:
Transfer 300 mg of Clavulanate Potassium to a centrifuge tube. Add 4.0 mL of 4 N hydrochloric acid, and shake with two successive 1.0-mL portions of the Internal standard solution. Allow the phases to separate, centrifuging if necessary. Use the combined upper phases.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
GC
Detector:
Flame ionization
Column:
0.53-mm × 25-m capillary fused silica; 1-µm film coating of stationary phase G35
Temperature
Injector temperature:
200
Detector temperature:
300
Column temperature:
See the temperature program table below.
| Initial Temperature ( |
Temperature Ramp ( |
Final Temperature ( |
Hold Time at Final Temperature (min) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 40 | — | 40 | 2 |
| 40 | 30 | 200 | 3 |
Carrier gas:
Hydrogen
Flow rate:
100 cm/s
Injection size:
1 µL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 2.0 between the 2-ethylhexanoic acid peak and the 3-cyclohexylpropionic acid peak
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of 2-ethylhexanoic acid in the Clavulanate Potassium taken:
Result = (RU/RS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| RU | = | = peak area response ratio of 2-ethylhexanoic acid to 3-cyclohexylpropionic acid from the Sample solution |
| RS | = | = peak area response ratio of 2-ethylhexanoic acid to 3-cyclohexylpropionic acid from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of 2-ethylhexanoic acid in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = nominal concentration of Clavulanate Potassium in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.8%
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Bacterial Endotoxins Test  85
85 :
Where the label states that Clavulanate Potassium is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms, it contains NMT 0.03 USP Endotoxin Unit/mg.
:
Where the label states that Clavulanate Potassium is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms, it contains NMT 0.03 USP Endotoxin Unit/mg.
• Sterility Tests  71
71 :
Where the label states that Clavulanate Potassium is sterile, it meets the requirements when tested as directed under Test for Sterility of the Product to Be Examined, Membrane Filtration.
:
Where the label states that Clavulanate Potassium is sterile, it meets the requirements when tested as directed under Test for Sterility of the Product to Be Examined, Membrane Filtration.
• pH  791
791 :
5.5–8.0, in a 10 mg/mL solution
:
5.5–8.0, in a 10 mg/mL solution
• Water Determination, Method I  921
921 :
NMT 1.5%
:
NMT 1.5%
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight containers.
• Labeling:
Where it is intended for use in preparing injectable dosage forms, the label states that it is sterile or must be subjected to further processing during the preparation of injectable dosage forms.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Ahalya Wise, M.S.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8161 |
(SM12010) Monographs - Small Molecules 1 |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 2696
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 34(6) Page 1441