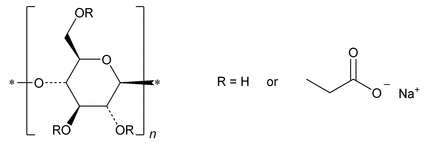Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium
Sodium salts of polymers containing substituted anhydroglucose units with the general formula:
[C6H7O2(OH)x(OCH2COONa)y]n
where n is the degree of polymerization;
y is the degree of substitution;
x is between 1.50 and 2.80;
y is between 0.20 and 1.50;
and x + y = 3.0
Carboxymethyl cellulose, sodium, partially hydrolyzed enzymatically.
Sodium salts of polymers containing substituted anhydroglucose units with the general formula:
[C6H7O2(OH)x(OCH2COONa)y]n
where n is the degree of polymerization;
y is the degree of substitution;
x is between 1.50 and 2.80;
y is between 0.20 and 1.50;
and x + y = 3.0
Carboxymethyl cellulose, sodium, partially hydrolyzed enzymatically.
DEFINITION
Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium is the sodium salt of a polycarboxymethyl ether of cellulose, which has been partially hydrolyzed by enzymatic treatment with food grade Trichoderma reesei cellulase. Its degree of substitution is NLT 0.20 and NMT 1.50, corresponding to a sodium (Na) content of NLT 2.6% and NMT 12.2%, calculated on the dried basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• A.
Vigorously shake a 0.1% solution of Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium: no layer of foam appears.
• B.
To 5 mL of a 0.5% solution of Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium add 5 mL of a 5% solution of copper or aluminium sulfate: a precipitate appears.
• C.
Add 0.5 g of Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium to 50 mL of water, while stirring, to produce a uniform dispersion. Continue stirring until a clear solution of 1% is produced. Dilute 1 mL of this solution with 1 mL of water in a small test tube. Add 5 drops of 1-naphthol TS. Incline the tube, and carefully introduce down the side of the tube 2 mL of sulfuric acid, so that it forms a lower layer: a red-purple color develops at the interface.
• D. Identification Tests—General, Sodium  191
191 :
A portion of the 1% solution obtained from Identification test C meets the requirements.
:
A portion of the 1% solution obtained from Identification test C meets the requirements.
• E.
It meets the requirements of the test for Viscosity.
ASSAY
• Degree of Substitution
Sample:
2.0 g of Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium
Analysis:
Ignite a clean and dry quartz crucible with a Bunsen burner, cool to room temperature in a desiccator, and weigh the crucible accurately. Transfer the Sample to the crucible. Carefully ignite on a small flame for about 10 min, and make sure that the Sample does not burn or excessively glow. Cool, and moisten the residue with 3–5 mL of sulfuric acid. Heat the crucible cautiously until the fuming is complete, and heat further until the Sample turns grayish white. Place the crucible in an oven at about 600 , until no black spots are visible. Cool the crucible in a desiccator to room temperature, and weigh. Place the crucible again in an oven at about 600
, until no black spots are visible. Cool the crucible in a desiccator to room temperature, and weigh. Place the crucible again in an oven at about 600 for 1 h, cool the crucible to room temperature in a desiccator, and weigh. This last step is repeated until a constant weight is achieved.
for 1 h, cool the crucible to room temperature in a desiccator, and weigh. This last step is repeated until a constant weight is achieved.
Calculate the percentage of sodium, PNa, in the portion of Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium taken:
Result = 100 × NNa × ANa × (W2 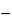 W1)/{Mr × W[(100
W1)/{Mr × W[(100 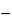 LOD)/100]}
LOD)/100]}
| NNa | = | = number of sodium atoms/molecule of sodium sulfate, 2 |
| ANa | = | = atomic weight of sodium, 22.99 |
| W2 | = | = weight of the crucible with ash residue (g) |
| W1 | = | = weight of the crucible (g) |
| Mr | = | = molecular weight of sodium sulfate, 142.04 |
| W | = | = weight of Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium taken (g) |
| LOD | = | = Loss on Drying value of Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium (%) |
Calculate the Degree of Substitution (DS):
Result = Mr1 × (PNa 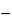 PNaCl
PNaCl 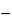 PNaG)/{100 × ANa
PNaG)/{100 × ANa 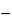 [(Mr2
[(Mr2 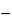 AH) × (PNa
AH) × (PNa 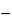 PNaCl
PNaCl 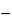 PNaG)]}
PNaG)]}
| Mr1 | = | = molar mass of one glucose unit, 162.14 |
| PNaCl | = | = percentage of sodium chloride obtained in the test for Limit of Sodium Chloride and Sodium Glycolate |
| PNaG | = | = percentage of sodium glycolate obtained in the test for Limit of Sodium Chloride and Sodium Glycolate |
| ANa | = | = atomic weight of sodium, 22.99 |
| Mr2 | = | = molar mass of one sodium carboxymethyl unit (CH2COONa), 81.03 |
| AH | = | = atomic weight of hydrogen, 1.01 |
Acceptance criteria:
NLT 0.20 and NMT 1.50 carboxymethyl groups (CH2COOH)/anhydroglucose unit on the dried basis
IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
• Limit of Lead
Nitric acid solution:
Dilute 10 mL of nitric acid with 20 mL of water. Boil this solution to remove nitrous fumes, and allow it to cool to room temperature.
Lead standard stock solution:
Dissolve 1.60 g of lead nitrate (Pb(NO3)2) in about 30 mL of Nitric acid solution in a 1000-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix. At 20 , transfer 10.0 mL of this lead solution to a 500-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. The Lead standard stock solution contains 20 µg/mL of Pb.
, transfer 10.0 mL of this lead solution to a 500-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. The Lead standard stock solution contains 20 µg/mL of Pb.
Standard solutions:
Transfer 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5 mL of the Lead standard stock solution to six identical 100-mL volumetric flasks, and add 50 mL of water to each flask. To each flask, add 8 mL of sulfuric acid and 10 mL of hydrochloric acid, and mix well. After complete dissolution, dilute each flask with water to volume, and mix. Transfer 1 mL of each solution to a separate 50-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to a final concentration of 0, 4, 8, 12, 16, and 20 µg/L of Pb, respectively.
Sample solution:
Transfer 1 g of Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium to a 100-mL beaker, and add 5 mL of 30% hydrogen peroxide. While stirring, add 50 mL of water to the solution, and heat the beaker on a hot plate at 50 , until all solids are dissolved. Quantitatively transfer this solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 300 µL of nitric acid, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
, until all solids are dissolved. Quantitatively transfer this solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 300 µL of nitric acid, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Blank solution:
Prepare as directed in the Sample solution, but omit the test specimen.
Spectrometric conditions
Mode:
Graphite furnace atomic absorption spectrophotometer, equipped with a lead hollow-cathode lamp and an adequate means of background correction.
Analytical wavelength:
Lead emission line of 283.3 nm
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solutions, Sample solution, and Blank solution
Concomitantly determine the absorbances of the Samples. Optimize the instrument program for lead as recommended by the manufacturer. The strongest Standard solution is aspirated to optimize the instrument settings to give a full-scale reading on the detector. Correct the area responses of all Sample solution and Standard solutions for the Blank solution area response. Generate the appropriate lead calibration curve, and determine the lead concentration, C, in µg/L, in the Sample solution.
Calculate the content of lead, in µg, in each g of Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium taken:
Result = (V × C)/W
| V | = | = volume of the Sample solution, 0.1 L |
| W | = | = weight of Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium taken to prepare the Sample solution (g) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 3 µg/g of lead.
• Limit of Sodium Chloride and Sodium Glycolate
Sodium Chloride
Ferric solution:
Dissolve 20 g of ferric ammonium sulfate (FeNH4(SO4)2·12H2O) in a 100-mL volumetric flask containing 80 mL of water, add 0.3 mL of 10 N nitric acid (dilute 600 mL of nitric acid with water to 1000 mL), dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Analysis:
Transfer an accurate quantity of Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium, equivalent to 5.0 g on the dried basis, to a platinum or porcelain crucible. Heat the test specimen first with a small flame so that the test specimen does not ignite. When the charring is complete, heat further in an electric oven at about 600 for 15 min. After cooling, pulverize the ashes thus obtained and extract several times with water. Filter the extracts into a 500-mL volumetric flask, add 5 mL of 10 N nitric acid, and dilute with water to volume. Transfer 100 mL of this extract to a suitable flask, add 2.0 mL of 0.2 N silver nitrate and 3 g of potassium nitrate, and mix. [Note—Silver chloride precipitate may develop. The potassium nitrate will prevent the silver chloride from interfering with the indication reaction. ] After complete dissolution of the potassium nitrate, titrate this mixture with 0.02 N ammonium thiocyanate VS by adding 3 mL of Ferric solution as an indicator. Titrate until a red color develops and persists for at least 30 s. Each mL of 0.02 N silver nitrate is equivalent to 1.169 mg of sodium chloride.
for 15 min. After cooling, pulverize the ashes thus obtained and extract several times with water. Filter the extracts into a 500-mL volumetric flask, add 5 mL of 10 N nitric acid, and dilute with water to volume. Transfer 100 mL of this extract to a suitable flask, add 2.0 mL of 0.2 N silver nitrate and 3 g of potassium nitrate, and mix. [Note—Silver chloride precipitate may develop. The potassium nitrate will prevent the silver chloride from interfering with the indication reaction. ] After complete dissolution of the potassium nitrate, titrate this mixture with 0.02 N ammonium thiocyanate VS by adding 3 mL of Ferric solution as an indicator. Titrate until a red color develops and persists for at least 30 s. Each mL of 0.02 N silver nitrate is equivalent to 1.169 mg of sodium chloride.
Calculate the percentage of sodium chloride, PNaCl, in the portion of Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium taken:
Result = (0.001169 × D × V/W) × 100
| D | = | = dilution factor, 5 |
| V | = | = volume of the 0.02 N silver nitrate consumed (mL) |
| W | = | = weight of Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium taken, calculated on the dried basis (g) |
Sodium Glycolate
Mobile phase:
Prepare a filtered and degassed solution of 0.05% phosphoric acid in water.
Standard stock solution:
Transfer 100 mg of glycolic acid, previously dried overnight in a vacuum desiccator over phosphorus pentoxide, and accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with Mobile phase to volume, and mix.
Standard solutions:
Transfer 0.5-, 1.0-, 1.5-, 2.0-, and 2.5-mL portions of the Standard stock solution, respectively, into five identical 100-mL volumetric flasks. To each flask, dilute with Mobile phase to volume, and mix. The Standard solutions have concentrations of 5.0, 10.0, 15.0, 20.0, and 25.0 mg/L, respectively.
Sample solution:
Transfer an accurate quantity of Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium, equivalent to 200 mg on the dried basis, to a flask. Dissolve in and dilute with Mobile phase to 20 mL.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 205 nm
Column:
7.8-mm × 30-cm; packing L22. [Note—Two 7.8-mm × 15-cm columns can be used in place of one 7.8-mm × 30-cm column, provided that the System suitability requirements are met. ]
Flow rate:
0.5 mL/min
Injection size:
50 µL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution with the concentration of 15 mg/L
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 5.0%
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solutions and Sample solution
Separately inject equal volumes of the Standard solutions and the Sample solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Plot the peak areas from the Standard solutions versus the concentration of glycolic acid, in mg/L, in the Standard solutions. From the standard curve and the peak area from the Sample solution, determine the concentration of glycolic acid, C, in mg/L, in the Sample solution.
Calculate the percentage of sodium glycolate, PNaG, in the portion of Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium taken:
Result = {[V × (Mr1/Mr2) × C]/W} × 100
| V | = | = volume of the Sample solution, 0.02 L |
| Mr1 | = | = molecular weight of sodium glycolate, 98.03 |
| Mr2 | = | = molecular weight of glycolic acid, 76.05 |
| W | = | = weight of Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium taken to prepare the Sample solution, calculated on the dried basis (mg) |
Acceptance criteria:
The sum of the percentages from the tests for sodium chloride and sodium glycolate (PNaCl + PNaG) is NMT 0.5%.
Organic Impurities
• Procedure: Limit of Residual Enzyme
Sample:
20.0 g of the dry Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium
Analysis:
Transfer the Sample to a 2000-mL beaker. Add 100 mL of sulfuric acid, and mix using a stirring plate, until all particles are wetted. Prevent excessive foam formation during mixing. Add some glass beads to prevent boiling delay, and slowly heat the solution to a temperature not exceeding 150 . Stir for 30 min, and carefully add 5 mL of hydrogen peroxide dropwise at interval steps. After each step, allow the reaction to subside, and ensure that the solution does not contain any particulates. [Note—It takes up to approximately 125 mL of hydrogen peroxide. ] The temperature is gradually increased to about 300
. Stir for 30 min, and carefully add 5 mL of hydrogen peroxide dropwise at interval steps. After each step, allow the reaction to subside, and ensure that the solution does not contain any particulates. [Note—It takes up to approximately 125 mL of hydrogen peroxide. ] The temperature is gradually increased to about 300 , until strong fumes of sulfur trioxide appear. Stop the heating. If the solution darkens again during heating, carefully add some drops of hydrogen peroxide until a clear solution is obtained. Allow the solution to cool down, add 10 mL of water, and heat again until strong fumes of sulfur trioxide appear. After the solution becomes clear and is cooled down, flush the sides with water, and transfer the solution quantitatively to a 4000-mL round-bottom flask. Dilute with water to a volume of approximately 500 mL, and place the round-bottom flask under the distillation unit. Pipet 10 mL of 0.1 N sulfuric acid into a 300-mL conical flask, and dilute with water to 100 mL. Place the conical flask at the end of the distillation unit, taking care that the end of the distillation unit is below the surface of the liquid. Through a dropping funnel add 500 mL of a 32% sodium hydroxide solution to the round-bottom flask with heavy stirring. Slowly heat until the solution boils. Boil, and collect the distillate for 20 min. Remove the conical flask, and stop the heating. Flush the inside of the condenser with water into the conical flask. Titrate the solution with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide. Perform a blank determination.
, until strong fumes of sulfur trioxide appear. Stop the heating. If the solution darkens again during heating, carefully add some drops of hydrogen peroxide until a clear solution is obtained. Allow the solution to cool down, add 10 mL of water, and heat again until strong fumes of sulfur trioxide appear. After the solution becomes clear and is cooled down, flush the sides with water, and transfer the solution quantitatively to a 4000-mL round-bottom flask. Dilute with water to a volume of approximately 500 mL, and place the round-bottom flask under the distillation unit. Pipet 10 mL of 0.1 N sulfuric acid into a 300-mL conical flask, and dilute with water to 100 mL. Place the conical flask at the end of the distillation unit, taking care that the end of the distillation unit is below the surface of the liquid. Through a dropping funnel add 500 mL of a 32% sodium hydroxide solution to the round-bottom flask with heavy stirring. Slowly heat until the solution boils. Boil, and collect the distillate for 20 min. Remove the conical flask, and stop the heating. Flush the inside of the condenser with water into the conical flask. Titrate the solution with 0.1 M sodium hydroxide. Perform a blank determination.
Calculate the percentage of protein in the portion of Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium taken:
Result = {F × AN × [VACA 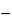 (VTB
(VTB 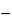 VB) × CTB]/W} × 100
VB) × CTB]/W} × 100
| F | = | = calculation factor for the theoretical amount of nitrogen present in protein, 6.25 |
| AN | = | = atomic weight of nitrogen, 14.01 g/mol |
| VA | = | = volume of 0.1 N sulfuric acid added to the conical flask (mL) |
| CA | = | = exact concentration of sulfuric acid added to the conical flask (N) |
| VTB | = | = volume of the sodium hydroxide solution consumed in the titration for the sample determination (mL) |
| VB | = | = volume of the sodium hydroxide solution consumed in the titration for the blank determination (mL) |
| CTB | = | = concentration of the sodium hydroxide solution used in the titration (N) |
| W | = | = weight of Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium taken (mg) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.1% of protein
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Viscosity  911
911
Analysis:
After determining the Loss on Drying, weigh a quantity of undried Enzymatically-Hydrolyzed Carboxymethylcellulose Sodium, equivalent to 60.0 g on the dried basis. In a 400-mL beaker, transfer about 240 mL of water, minus the amount of water in the test specimen. Over a period of seconds, transfer the test specimen to the 400-mL beaker containing water, while slowly and continuously stirring the solution to make the mixture weigh 300 g. When the specimen is well wetted, increase the rate of stirring, taking care to avoid mixing in excess air. Dissolve the test specimen while stirring rapidly. Equilibrate the mixture in a water bath at 25 for 1 h, until all air bubbles dissipate. Stir the solution in the beaker for 5 min at 300 rpm, making sure that no air bubbles are incorporated. Transfer the solution to a 250-mL beaker of 5 cm in internal diameter and about 12 cm in height, for measurement. Determine its viscosity at 25 ± 0.1
for 1 h, until all air bubbles dissipate. Stir the solution in the beaker for 5 min at 300 rpm, making sure that no air bubbles are incorporated. Transfer the solution to a 250-mL beaker of 5 cm in internal diameter and about 12 cm in height, for measurement. Determine its viscosity at 25 ± 0.1 , using a suitable rotational viscometer with a cylindrical spindle 1.9 cm in diameter and 6.5 cm high, attached to a shaft 0.3 cm in diameter.1 The spindle rotates at 12 rpm at an immersion depth of 8.1 cm. Follow the instrument manufacturer’s directions to measure the apparent viscosity.
, using a suitable rotational viscometer with a cylindrical spindle 1.9 cm in diameter and 6.5 cm high, attached to a shaft 0.3 cm in diameter.1 The spindle rotates at 12 rpm at an immersion depth of 8.1 cm. Follow the instrument manufacturer’s directions to measure the apparent viscosity.
Acceptance criteria:
The viscosity is between 200 and 500 mPa·s.
• pH  791
791 :
6.0–8.5, in a solution prepared in carbon dioxide-free water (1 in 100)
:
6.0–8.5, in a solution prepared in carbon dioxide-free water (1 in 100)
• Loss on Drying  731
731 :
Dry it at 105
:
Dry it at 105 for 3 h: it loses NMT 12.0% of its weight.
for 3 h: it loses NMT 12.0% of its weight.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers, and store in a cool and dry place.
• Labeling:
Label it to indicate the viscosity, giving the viscosity measurement parameters, concentration of the solution, and the type of equipment used. The labeling also indicates the value for Degree of Substitution.
1
A suitable spindle is available from Brookfield as an LV1 spindle, or the equivalent.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Robert H. Lafaver, M.S.
Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8335 |
(EXC2010) Monographs - Excipients |
USP35–NF30 Page 1739
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 34(6) Page 1519