Anhydrous Lactose
| Attribute | JP | EP | USP |
| Definition | + | + | + |
| Clarity and color of solution | + | + | + |
| Specific rotation | + | + | + |
| Acidity or alkalinity | + | + | + |
| Loss on drying | – | + | + |
| Water | + | + | + |
| Content of alpha and beta anomers | + | + | + |
| Residue on ignition | + | + | + |
| Protein and light-absorbing impurities | + | + | + |
Legend: + will adopt and implement; – will not stipulate.
Nonharmonized attributes: Characters, Labeling, Microbial limits, Heavy metals, Packaging and storage, Identification (IR).
Specific local attributes: Identification B and C (USP), Particle size distribution (USP), Particle size distribution EP (FRC).
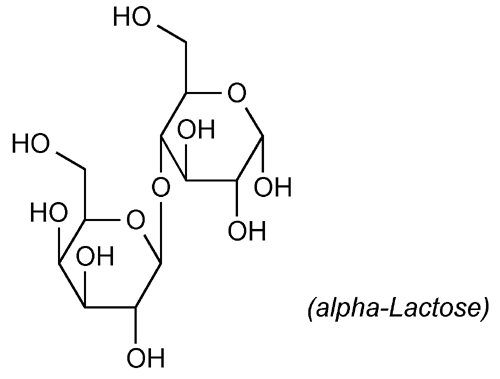
» Anhydrous Lactose is O-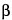 -d-galactopyranosyl-(1®4)-
-d-galactopyranosyl-(1®4)-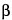 -d-glucopyranose (
-d-glucopyranose (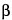 -lactose) or a mixture of O-
-lactose) or a mixture of O-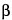 -d-galactopyranosyl-(1®4)-
-d-galactopyranosyl-(1®4)-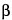 -d-glucopyranose and O-
-d-glucopyranose and O-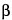 -d-galactopyranosyl-(1®4)-
-d-galactopyranosyl-(1®4)-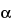 -d-glucopyranose (
-d-glucopyranose (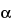 -lactose).
-lactose).
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers.
Labeling—
Where the labeling indicates the relative quantities of alpha and beta lactose, determine compliance using Content of alpha and beta anomers. Where the labeling states the particle size distribution, it also indicates the d10, d50, and d90 values and the range for each.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
USP Anhydrous Lactose RS.
USP Sucrose RS.
USP Fructose RS.
USP Dextrose RS.
USP Anhydrous Lactose RS.
USP Sucrose RS.
USP Fructose RS.
USP Dextrose RS.
Clarity and color of solution—
A solution of 1 g in 10 mL of boiling water is clear and nearly colorless. Determine the absorbance of this solution at a wavelength of 400 nm. The absorbance divided by the path length, in cm, is not more than 0.04.
Identification—
B:
Proceed as directed in Identification test B under Lactose Monohydrate, except to use USP Anhydrous Lactose RS instead of USP Lactose Monohydrate RS in Standard solution A and B and to use Anhydrous Lactose in the Test solution.
Specific rotation  781
781 —
Dissolve 10 g by heating in 80 mL of water to 50
—
Dissolve 10 g by heating in 80 mL of water to 50 . Allow to cool, and add 0.2 mL of 6 N ammonium hydroxide. Allow to stand for 30 minutes, and dilute with water to 100 mL: the specific rotation, calculated on the anhydrous basis, determined at 20
. Allow to cool, and add 0.2 mL of 6 N ammonium hydroxide. Allow to stand for 30 minutes, and dilute with water to 100 mL: the specific rotation, calculated on the anhydrous basis, determined at 20 , is between +54.4
, is between +54.4 and +55.9
and +55.9 .
.
Microbial enumeration tests  61
61 and Tests for specified microorganisms
and Tests for specified microorganisms  62
62 —
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 100 cfu per g, the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 50 cfu per g, and it meets the requirements of the test for absence of Escherichia coli.
—
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 100 cfu per g, the total combined molds and yeasts count does not exceed 50 cfu per g, and it meets the requirements of the test for absence of Escherichia coli.
Acidity or alkalinity—
Dissolve 6 g by heating in 25 mL of carbon dioxide-free water, cool, and add 0.3 mL of phenolphthalein TS: the solution is colorless, and not more than 0.4 mL of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide is required to produce a red color.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 80
—
Dry it at 80 for 2 hours: it loses not more than 0.5% of its weight.
for 2 hours: it loses not more than 0.5% of its weight.
Water, Method I  921
921 :
not more than 1.0%, determined on a preparation containing anhydrous lactose in a mixture of methanol and formamide (2:1).
:
not more than 1.0%, determined on a preparation containing anhydrous lactose in a mixture of methanol and formamide (2:1).
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.1%, determined on a specimen ignited at a temperature of 600 ± 50
:
not more than 0.1%, determined on a specimen ignited at a temperature of 600 ± 50 .
.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
5 µg per g.
:
5 µg per g.
Protein and light-absorbing impurities  851
851 —
Measure the light absorption of a 1% (w/v) solution in the range of 210 nm to 300 nm. The absorbance divided by the path length, in cm, is not more than 0.25 in the range of 210 nm to 220 nm and is not more than 0.07 in the range of 270 nm to 300 nm.
—
Measure the light absorption of a 1% (w/v) solution in the range of 210 nm to 300 nm. The absorbance divided by the path length, in cm, is not more than 0.25 in the range of 210 nm to 220 nm and is not more than 0.07 in the range of 270 nm to 300 nm.
Content of alpha and beta anomers—
Silylation reagent—
Prepare a mixture of pyridine and trimethylsilylimidazole (72:28).
Resolution mixture—
Prepare a mixture of alpha lactose monohydrate and beta lactose having an anomeric ratio of about 1:1 based on the labeled anomeric contents of the alpha lactose monohydrate and the beta lactose.
Chromatographic system
(see Chromatography  621
621 )—The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector and a 4-mm × 0.9-m glass column packed with 3% liquid phase G19 on support S1A. The column temperature is maintained at about 215
)—The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector and a 4-mm × 0.9-m glass column packed with 3% liquid phase G19 on support S1A. The column temperature is maintained at about 215 , and the injection port and the detector temperatures are maintained at about 275
, and the injection port and the detector temperatures are maintained at about 275 . The carrier gas is helium, flowing at a rate of about 40 mL per minute.
. The carrier gas is helium, flowing at a rate of about 40 mL per minute.
Derivatization procedure—
Transfer about 1 mg of Anhydrous Lactose to a 5-mL reaction vial equipped with a screw cap, add 0.45 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide, seal the vial tightly with a screw cap, and mix on a vortex mixer to dissolve. Add 1.8 mL of Silylation reagent, seal the vial tightly with a screw cap, and mix gently. Transfer about 1 mg of Resolution mixture to a second 5-mL reaction vial equipped with a screw cap, add 0.45 mL of dimethyl sulfoxide, seal the vial tightly with a screw cap, and mix on a vortex mixer to dissolve. Add 1.8 mL of Silylation reagent, seal the vial tightly with a screw cap, and mix gently. Maintain both vials at room temperature for 20 minutes before using.
Procedure—
Inject a 2.0-µL portion of the derivatized Resolution mixture into the chromatograph, and record the peak areas for the major peaks: the relative retention times are about 0.7 for the silyl derivative of alpha lactose and 1.0 for the silyl derivative of beta lactose, and the resolution, R, between the two peaks is not less than 3.0. Similarly inject a 2.0-µL portion of the derivatized Anhydrous Lactose into the chromatograph, and record the peak areas for the major peaks. Determine the percentage of alpha anomer in the Anhydrous Lactose by the formula:
100ra / (ra + rb)
in which ra is the response of the alpha anomer silyl derivative peak and rb is the response of the beta anomer silyl derivative peak. Determine the percentage of beta anomer in the Anhydrous Lactose by the formula:
100rb / (ra + rb)
in which the terms are as defined above.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
Chromatographic Column—
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Kevin T. Moore, Ph.D.
Scientist 1-301-816-8369 |
(EM105) Excipient Monographs 1 |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
|
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance |
USP32–NF27 Page 1263
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 32(6) Page 1847
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 32 or NF 27.