Fludeoxyglucose F 18 Injection
» Fludeoxyglucose F 18 Injection is a sterile, aqueous solution, suitable for intravenous administration, of 2-deoxy-2-[18F]fluoro-d-glucose in which a portion of the molecules are labeled with radioactive 18F (see Radiopharmaceuticals for Positron Emission Tomography—Compounding  823
823 ). It contains not less than 90.0 percent and not more than 110.0 percent of the labeled amount of 18F expressed in MBq (mCi) per mL at the time indicated in the labeling. It may contain suitable preservatives and/or stabilizing agents.
). It contains not less than 90.0 percent and not more than 110.0 percent of the labeled amount of 18F expressed in MBq (mCi) per mL at the time indicated in the labeling. It may contain suitable preservatives and/or stabilizing agents.
Specific activity:
no carrier added.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in single-dose or multiple-dose containers that are adequately shielded.
Labeling—
Label it to include the following, in addition to the information specified for Labeling under Injection  1
1 : the time and date of calibration; the amount of 18F as fludeoxyglucose expressed as total MBq (mCi) per mL, at time of calibration; the expiration time and date; the name and quantity of any added preservative or stabilizer; and the statement “Caution—Radioactive Material.” The labeling indicates, that in making dosage calculations, correction is to be made for radioactive decay. The radioactive half-life of 18F is 109.7 minutes. The label indicates “Do not use if cloudy or if it contains particulate matter.”
: the time and date of calibration; the amount of 18F as fludeoxyglucose expressed as total MBq (mCi) per mL, at time of calibration; the expiration time and date; the name and quantity of any added preservative or stabilizer; and the statement “Caution—Radioactive Material.” The labeling indicates, that in making dosage calculations, correction is to be made for radioactive decay. The radioactive half-life of 18F is 109.7 minutes. The label indicates “Do not use if cloudy or if it contains particulate matter.”
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
USP Endotoxin RS.
USP Fludeoxyglucose RS.
USP Fludeoxyglucose Related Compound A RS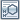 .
.
USP Fludeoxyglucose Related Compound B RS .
.
USP Endotoxin RS.
USP Fludeoxyglucose RS.
USP Fludeoxyglucose Related Compound A RS
 .
.
USP Fludeoxyglucose Related Compound B RS
 .
.
Identification—
A:
Radionuclidic identity—Its half-life, determined using a suitable detector system (see Radioactivity  821
821 ), is between 105 and 115 minutes.
), is between 105 and 115 minutes.
B:
Radiochemical identity—The RF value of Fludeoxyglucose F 18 in the chromatogram of the Test solution corresponds to that in the chromatogram of the Standard solution, as obtained in the Radiochemical purity test.
Bacterial endotoxins  85
85 (see Sterilization and Sterility Assurance under Radiopharmaceuticals for Positron Emission Tomography—Compounding
(see Sterilization and Sterility Assurance under Radiopharmaceuticals for Positron Emission Tomography—Compounding  823
823 )—
It contains not more than 175/V USP Endotoxin Unit per mL of the Injection, in which V is the maximum administered total dose, in mL, at the expiration time.
)—
It contains not more than 175/V USP Endotoxin Unit per mL of the Injection, in which V is the maximum administered total dose, in mL, at the expiration time.
pH  791
791 :
between 4.5 and 7.5.
:
between 4.5 and 7.5.
Radiochemical purity—
Standard solution—
Dissolve 10 mg of USP Fludeoxyglucose RS in 100 mL of acetonitrile and water (95:5). (The USP Fludeoxyglucose RS that is specified in this test is nonradioactive 2-deoxy-2-fluoro-d-glucose [molecular weight 182.15].)
Test solution—
Use the Injection.
Procedure—
Apply a volume of Injection, appropriately diluted such that it provides a count rate suitable for the radioactivity detection system being utilized, to an activated silica gel thin-layer chromatographic plate (see Chromatography  621
621 ). Apply about 10 µL of the Standard solution to the same chromatographic plate. Develop the chromatogram in a solvent system consisting of a mixture of acetonitrile and water (95:5) until the solvent has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate, and allow the chromatogram to dry. Determine the radioactivity distribution by scanning the chromatogram with a suitable collimated radiation detector. Determine the location of the Fludeoxyglucose by spraying the developed chromatographic plate with 2 N sulfuric acid and heating the plate at 110
). Apply about 10 µL of the Standard solution to the same chromatographic plate. Develop the chromatogram in a solvent system consisting of a mixture of acetonitrile and water (95:5) until the solvent has moved about three-fourths of the length of the plate. Remove the plate, and allow the chromatogram to dry. Determine the radioactivity distribution by scanning the chromatogram with a suitable collimated radiation detector. Determine the location of the Fludeoxyglucose by spraying the developed chromatographic plate with 2 N sulfuric acid and heating the plate at 110 for 10 minutes: the RF value of Fludeoxyglucose F 18 (determined by radiochromatogram scanning) corresponds to that of the Standard solution (about 0.4); the radioactivity of Fludeoxyglucose F 18 is not less than 90% of the total radioactivity.
for 10 minutes: the RF value of Fludeoxyglucose F 18 (determined by radiochromatogram scanning) corresponds to that of the Standard solution (about 0.4); the radioactivity of Fludeoxyglucose F 18 is not less than 90% of the total radioactivity.
Radionuclidic purity—
Using a suitable gamma-ray spectrometer (see Selection of a Counting Assembly under Radioactivity  821
821 ), count an appropriate aliquot of the Injection for a period of time sufficient to collect a gamma spectrum. The resultant gamma spectrum should be analyzed for the presence of identifiable photopeaks which are not characteristic of 18F emissions. Not less than 99.5% of the observed gamma emissions should correspond to the 0.511 MeV, 1.022 MeV, or Compton scatter peaks of 18F.
), count an appropriate aliquot of the Injection for a period of time sufficient to collect a gamma spectrum. The resultant gamma spectrum should be analyzed for the presence of identifiable photopeaks which are not characteristic of 18F emissions. Not less than 99.5% of the observed gamma emissions should correspond to the 0.511 MeV, 1.022 MeV, or Compton scatter peaks of 18F.
Change to read:
Chemical purity—
[Note—The methods and limits described in this section relate to potential impurities associated with the acid-hydrolysis method of synthesis for the Injection. Specific examples include aminopolyether (KryptofixR) and 2-chloro-2-deoxy-d-glucose. If methods of synthesis that may result in different impurities are used, the presence of unlabeled ingredients, reagents, and by-products specific to the process must be controlled, and their potential for physiological or pharmacological effects must be considered (see Radiopharmaceuticals for Positron Emission Tomography—Compounding
limit of aminopolyether—
[Note—This test must be performed for Fludeoxyglucose F 18 produced by any route of synthesis that uses this reagent.]
Absorbent:
0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel.1
Test solution—
Use the Injection.
Standard solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Fludeoxyglucose Related Compound A RS in saline TS to obtain a solution having a known concentration of 50 µg per mL.
Application volume:
about 1 µL.
Developing solvent system:
a mixture of methanol and 30% ammonium hydroxide (9:1).
Procedure—
Proceed as directed for Thin-Layer Chromatography under Chromatography  621
621 . Place the plate in a chamber containing iodine crystals. Develop the plate until a spot is visible on the chromatogram of the Standard solution: the size and intensity of the spot obtained from the Test solution does not exceed that obtained from the Standard solution.
. Place the plate in a chamber containing iodine crystals. Develop the plate until a spot is visible on the chromatogram of the Standard solution: the size and intensity of the spot obtained from the Test solution does not exceed that obtained from the Standard solution.
limit of 2-chloro-2-deoxy-d-glucose—
[Note—This test is performed when the nucleophilic synthesis includes hydrolysis with hydrochloric acid or the use of anionic exchange resins in the chloride form to trap fluoride 18F released from the target prior to its use in the synthesis of Fludeoxyglucose F 18.]
Mobile phase—
Dissolve about 16 g of 50% sodium hydroxide solution in 1000 mL of water, filter, and degas by sparging with helium.
System suitability solution—
Dissolve accurately weighed quantities of USP Fludeoxyglucose RS and USP Fludeoxyglucose Related Compound B RS in Mobile phase to obtain a solution having known concentrations of 1.0 mg per mL and 0.1 mg per mL, respectively.
Standard solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Fludeoxyglucose Related Compound B RS in water to obtain a solution having a known concentration of 0.1 mg per mL.
Test solution—
Use the Injection.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a pulsed amperometric detector and a 4.0-mm × 25-cm column that contains 10-µm packing L46. The flow rate is adjusted to about 0.5 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Standard solution and the System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between fludeoxyglucose and fludeoxyglucose related compound B is not less than 1.5; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 5%.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a pulsed amperometric detector and a 4.0-mm × 25-cm column that contains 10-µm packing L46. The flow rate is adjusted to about 0.5 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Standard solution and the System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between fludeoxyglucose and fludeoxyglucose related compound B is not less than 1.5; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 5%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 100 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the areas for the major peaks. Calculate the quantity, in mg, of 2-chloro-2-deoxy-d-glucose in each mL of the Injection taken by the formula:
 per dose
per dose 4 is found.
4 is found. 
 4
4
C(rU / rS)
in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Fludeoxyglucose Related Compound B RS in the Standard solution; and rU and rS are the 2-chloro-2-deoxy-d-glucose peak areas obtained from the Test solution and the Standard solution, respectively: not more than 1 mg
Residual solvents—
Standard solutions—
Prepare separate aqueous solutions of ether, acetonitrile, and dehydrated alcohol having known concentrations of 0.1%, 0.01%, and 0.1%, respectively.
Test solutions—
Use the Injection.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector, a splitless injector system, and a 0.53-mm × 30-m fused-silica column coated with a 0.25-µm, chemically cross-linked G16 stationary phase. The carrier gas is helium, flowing at a rate of 10 mL per minute. (Nitrogen may be used as a makeup gas.) The chromatograph is programmed as follows. Initially the temperature is maintained at 40
)—
The gas chromatograph is equipped with a flame-ionization detector, a splitless injector system, and a 0.53-mm × 30-m fused-silica column coated with a 0.25-µm, chemically cross-linked G16 stationary phase. The carrier gas is helium, flowing at a rate of 10 mL per minute. (Nitrogen may be used as a makeup gas.) The chromatograph is programmed as follows. Initially the temperature is maintained at 40 for 2 minutes, then the temperature is increased at a rate of 20
for 2 minutes, then the temperature is increased at a rate of 20 per minute to 130
per minute to 130 , and maintained at 130
, and maintained at 130 for 5.5 minutes. The injection port and detector temperatures are maintained at 250
for 5.5 minutes. The injection port and detector temperatures are maintained at 250 and 300
and 300 , respectively. Inject the Standard solutions, and record the identity peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between any two components is not less than 1.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 5%.
, respectively. Inject the Standard solutions, and record the identity peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between any two components is not less than 1.0; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 5%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 1 µL) of the Standard solutions and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the peak responses. Calculate the percentage of acetonitrile, ether, and alcohol in the Injection by the formula:
C(ri / rS)
in which C is the percentage of the relevant analyte in the Standard solution; and ri and rS are the peak responses of the relevant analyte obtained from the Test solution, if any, and the Standard solution, respectively: not more than 0.04% of acetonitrile is found; not more than 0.5% of ether is found; and not more than 0.5% of alcohol is found.
Other requirements—
It meets the requirements under Injections  1
1 , except that the Injection may be distributed or dispensed prior to completion of the test for Sterility
, except that the Injection may be distributed or dispensed prior to completion of the test for Sterility  71
71 , the latter test being started within 24 hours of final manufacture, and except that it is not subject to the recommendation of Volume in Container.
, the latter test being started within 24 hours of final manufacture, and except that it is not subject to the recommendation of Volume in Container.
Assay for radioactivity—
Using a suitable calibrated system as directed under Radioactivity  821
821 , determine the radioactivity in MBq (or mCi) per mL, of the Injection.
, determine the radioactivity in MBq (or mCi) per mL, of the Injection.
1
Available from Alltech Associates, Inc., 2051 Waukegan Rd., Deerfield, IL 60015 as Machery Nagel SILG/UV 254 4 × 8 cm, Alltech catalog No. 805021.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
Chromatographic Column—
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
| Monograph | Ian DeVeau, Ph.D.
Director, Veterinary Drugs and Radiopharmaceuticals 1-301-816-8178 |
(RMI05) Radiopharmaceuticals and Medical Imaging Agents 05 |
| Reference Standards | Lili Wang, Technical Services Scientist 1-301-816-8129 RSTech@usp.org |
|
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Senior Scientist 1-301-816-8339 |
(MSA05) Microbiology and Sterility Assurance |
USP32–NF27 Page 2406
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 33(6) Page 1176
Chromatographic columns text is not derived from, and not part of, USP 32 or NF 27.