Krill Oil
DEFINITION
Krill Oil is the fixed oil extracted from Antarctic krill (Euphausia superba Dana) biomass using appropriate food grade organic solvents. Krill Oil contains NLT 28% (w/w) and NMT 52% (w/w) of total phospholipids, of which 60% to 90% is phosphatidylcholine. It contains NLT 10% (w/w) of eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA) and NLT 5.0% (w/w) of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in the form of phospholipids. It also contains NLT 0.01% of astaxanthin.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Fatty Acid Profile
Antioxidant solution, System suitability solution 1, and Chromatographic system:
Proceed as directed in Fats and Fixed Oils  401
401 , Omega-3 Fatty Acids Determination and Profile.
, Omega-3 Fatty Acids Determination and Profile.
Standard solution:
Prepare as directed in Test Solution 1 in Fats and Fixed Oils  401
401 , Omega-3 Fatty Acids Determination and Profile, except use 250 mg of USP Krill Oil RS.
, Omega-3 Fatty Acids Determination and Profile, except use 250 mg of USP Krill Oil RS.
Sample solution:
Prepare as directed in the Standard solution, except replace USP Krill Oil RS with Krill Oil.
System suitability
Samples:
System suitability solution 1 and Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Chromatogram similarity:
The chromatogram obtained from the Standard solution is similar to the reference chromatogram provided with the lot of USP Krill Oil RS being used.
Resolution:
NLT 1.0 between the methyl oleate and methyl cis-vaccinate peaks, Standard solution
Theoretical area percentages:
Meets the requirements for System suitability solution 1
Analysis
Sample:
Sample solution
Identify the retention times of the relevant fatty acid methyl esters in the Sample solution by comparing the chromatogram of the Sample solution with that of the Standard solution and the USP reference chromatogram.
Calculate the area percentage for each fatty acid as methyl esters in the portion of Krill Oil taken:
Result = (rA/rB) × 100
| rA | = | = peak area of each individual fatty acid from the Sample solution |
| rB | = | = total area from all peaks, except the solvent and butylated hydroxytoluene peaks, from the Sample solution |
Acceptance criteria:
The fatty acids obtained from the Sample solution meet the limit requirements in Table 1.
Table 1
| Fatty Acid
|
Shorthand Notation |
Lower Limit (Area %) |
Upper Limit (Area %) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monounsaturated fatty acids | |||
| Palmitoleic acid | 16:1 n-7 | 2.5 | 9.0 |
| cis-Vaccenic acid | 18:1 n-7 | 4.7 | 7.0 |
| Oleic acid | 18:1 n-9 | 7.0 | 14.5 |
| Eicosenic acid | 20:1 n-9 | 0.1 | 1.2 |
| Erucic acid | 22:1 n-9 | 0.0 | 0.9 |
| Polyunsaturated fatty acids | |||
| Linoleic acid | 18:2 n-6 | 1.4 | 3.0 |
| 18:3 n-3 | 0.5 | 3.5 | |
| Moroctic acid | 18:4 n-3 | 1.8 | 7.2 |
| Eicosapentaenoic acid | 20:5 n-3 | 14.0 | 22.1 |
| Docosapentaenoic acid | 22:5 n-3 | 0.0 | 0.7 |
| Docosahexaenoic acid | 22:6 n-3 | 7.5 | 13.2 |
• B. Phospholipid Profile
Solution A, Line shape standard (1H), Sensitivity standard (1H), Sensitivity standard (31P), Internal standard, Sample solution, Standard solution, Instrumental conditions, System suitability, and Analysis:
Proceed as directed in the test for Content of Total Phospholipids.
Acceptance criteria:
The Sample solution contains all of the following phospholipids: phosphatidylcholine [60%–90% (w/w) of the total phospholipids content], lysophosphatidylcholine (as a mixture of 1-lysophosphatidylcholine and 2-lysophosphatidylcholine), and phosphatidylethanolamine.
COMPOSITION
• Content of EPA and DHA
Standard solution 1a, Standard solution 1b, Standard solution 2a, Standard solution 2b, System suitability solution 1, and Chromatographic system:
Proceed as directed in Fats and Fixed Oils  401
401 , Omega-3 Fatty Acids Determination and Profile.
, Omega-3 Fatty Acids Determination and Profile.
Test solution 1:
Prepare as directed in Test Solution 1 in Fats and Fixed Oils  401
401 , Omega-3 Fatty Acids Determination and Profile, except use 250 mg of Krill Oil.
, Omega-3 Fatty Acids Determination and Profile, except use 250 mg of Krill Oil.
Test solution 2:
Prepare as directed in Test Solution 2 in Fats and Fixed Oils  401
401 , Omega-3 Fatty Acids Determination and Profile, except use 250 mg of Krill Oil.
, Omega-3 Fatty Acids Determination and Profile, except use 250 mg of Krill Oil.
Analysis:
Proceed as directed in the Analysis (for triglycerides) in Fats and Fixed Oils  401
401 , Omega-3 Fatty Acids Determination and Profile.
, Omega-3 Fatty Acids Determination and Profile.
Acceptance criteria:
NLT 10.0% (w/w) of EPA and NLT 5.0% (w/w) of DHA
• Content of Total Phospholipids
[Note—All deuterated solvents used in this method should be NLT 99.8 atom % D. Whenever water is used in this method, it should be of sufficient quality to ensure that no trace metals or other contaminants that may affect the analysis are present. ]
Solution A:
0.2 M EDTA, adjusted with a 1 M cesium carbonate solution to a pH of 7.2–7.5. Document the final pH and the amount of 1 M cesium carbonate solution necessary to attain the desired pH. [Note—Use cesium carbonate of a sufficient grade for trace metals analysis. ]
Line shape standard (1H):
1% chloroform in acetone-d6
Sensitivity standard (1H):
0.1% ethylbenzene in chloroform-d
Sensitivity standard (31P):
0.0485 M triphenyl phosphate in acetone-d6
Internal standard:
Use a suitable triphenyl phosphate NMR analytical standard with purity NLT 99.0%.
Sample solution:
[Note—NMR solvents containing tetramethylsilane (TMS) are readily available. If the solvents used do not contain TMS, it must be added to the Sample solution at an approximate concentration of 0.05% (v/v) for use as a chemical shift scale reference. ] Transfer 300–350 mg of Krill Oil to a 5-mL sealable glass vial. Add 25.0 mg of the Internal standard to the vial. Add 1 mL each of deuterated chloroform (chloroform-d) and deuterated methanol (methanol-d4) of a grade suitable for NMR analysis to the vial to dissolve the sample. Once dissolution is complete, add 1 mL of Solution A, seal the vial, and shake the solution for 10–20 min, then centrifuge the contents of the vial. Transfer the lower organic phase to an appropriate NMR tube. It is critical to collect the entire organic phase and transfer it to the NMR tube. It may be unavoidable to also transfer small amounts of the aqueous phase when collecting the organic phase in the NMR tube. This is acceptable practice, so long as the aqueous phase remains completely separated and atop the organic phase in the NMR tube. The entire amount of aqueous phase must be above the probe's radio frequency (RF) coil (outside the analysis area of the tube). Should the organic phase contain undissolved materials, they must remain suspended at the aqueous-organic interface and be outside the analysis area of the tube as well. The organic phase must be free of bubbles and suspended materials that may interfere with NMR data acquisition.
Standard solution:
Prepare as directed in the Sample solution, using 300–350 mg of USP Krill Oil RS in place of the sample.
Instrumental conditions
Magnetic field strength:
NLT 300 MHz for 1H frequency
Probe:
Direct observe probe capable of tuning to the resonance frequency of 31P (dependent on the specific magnetic field strength used)
Instrument performance qualification
[Note—Testing for sensitivity and line shape should be performed on the interval specified by the manufacturer of the instrument used. Performing these tests on a minimum of a monthly basis is required for this method, but may be done more often, as required. Resolution testing is to be performed during each analysis and documented as a part of the analytical results. ]
1H Line shape test:
Using the Line shape standard (1H) and the protocol recommended by the instrument manufacturer, the instrument must achieve the line shape specifications for the probe in use, as required by the instrument manufacturer. [Note—A different standard solution may be required or recommended by the manufacturer of the instrument; 1% chloroform in acetone-d6 is most commonly used. ]
1H Sensitivity test:
Using the Sensitivity standard (1H) and the protocol recommended by the instrument manufacturer, the instrument must achieve the sensitivity specifications required by the instrument manufacturer. [Note—A different standard solution may be required or recommended by the manufacturer of the instrument; 0.1% ethylbenzene in chloroform-d is most commonly used. ]
31P Sensitivity test:
Using the Sensitivity standard (31P) and the protocol recommended by the instrument manufacturer, the instrument must achieve the sensitivity specifications required by the instrument manufacturer. [Note—A different standard solution may be required or recommended by the manufacturer of the instrument; 0.0485 M triphenyl phosphate in acetone-d6 is most commonly used. ]
1H Resolution test:
The resolution is demonstrated by the ability to detect both of the 29Si satellite signals of TMS. The satellites must be resolved from the TMS signal in the spectrum with a line broadening factor of NMT 0.5 ppm.
31P Resolution test:
The resolution is demonstrated using the phosphatidylcholine ether peak and the phosphatidylcholine peak. The separation of these peaks (with line broadening factor of 1.0) must be demonstrated as follows. Using the baseline as a reference, determine the total peak height of the phosphatidylcholine ether peak, and draw a line at 30% of that total peak height (intensity). The phosphatidylcholine ether peak and the neighboring phosphatidylcholine peak must be fully resolved at a point that is NMT 30% of the peak height of the phosphatidylcholine ether peak.
Data collection:
Use the parameters specified in Table 2. Use 90 degree pulses, and calibrate pulses before use according to the recommendations supplied by the instrument manufacturer.
Table 2
| Parameter | 31P NMR Quantitative Measurement |
1H NMR Qualitative Measurement |
|---|---|---|
| Pulse program |
1H-decoupled 31P | Single pulse 1H |
| Spectral width | 50 ppm (25 ppm to |
20 ppm ( |
| Transmitter offset | Center of spectral width, 0 ppm | Center of spectral width, 7 ppm |
| Relaxation delay | 2–5 s | 2–5 s |
| Acquisition time | 1–6 s | 1–6 s |
| Sum of relaxation delay and acquisition time |
NLT 15 s | NLT 15 s |
| Size of data set | NLT 64k (32k with zero-filling) |
NLT 64k (32k with zero-filling) |
[Note—The acquisition time is dependent upon the field strength and the time domain. The number of scans acquired using a 300 MHz instrument must be NLT 512. ]
System suitability:
Under the conditions outlined in Data collection, the 31P NMR signal of triphenyl phosphate should be observed at 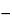 17.80 ppm, and the 1H NMR spectrum should be referenced to the 1H signal of TMS (0 ppm) for all spectra acquired in the Analysis. For quantitative analysis, a sufficient number of scans should be acquired such that the signal-to-noise ratio for the phosphatidylcholine signal in the 31P spectrum of the Sample solution acquired in the Analysis is NLT 2000.
17.80 ppm, and the 1H NMR spectrum should be referenced to the 1H signal of TMS (0 ppm) for all spectra acquired in the Analysis. For quantitative analysis, a sufficient number of scans should be acquired such that the signal-to-noise ratio for the phosphatidylcholine signal in the 31P spectrum of the Sample solution acquired in the Analysis is NLT 2000.
Analysis:
Acquire the data outlined in Data collection. Minimally acquire the 1H spectrum (fingerprint) of the Sample solution and the Standard solution as well as the quantitative 31P spectrum of the Sample solution and the Standard solution. Record the resulting spectra, and perform integration by hand or automated means on the quantitative 31P NMR spectrum of the Sample solution. Integration of the peaks contained in the spectrum of the Sample solution must be performed such that the complete set of phospholipid peaks (as identified by comparison to the spectrum of the Standard solution and its reference spectrum) is included in the integration. The integration region for each signal must extend ±0.05 ppm on either side of the 31P signal. Quantify the total phospholipids present, the phosphatidylcholine ether content, and the phosphatidylcholine content in the Sample solution using comparison to the concentration of the Internal standard.
Compare the 1H spectrum of the Sample solution to that of the Standard solution to determine the similarity of fingerprints according to which phospholipids identified in the reference spectrum of the Standard solution are present in the spectrum of the Sample solution.
Acceptance criteria
Total phospholipids:
28%–52% (w/w)
Phosphatidylcholine:
60%–90% (w/w) of the Total phospholipids content
• Content of Astaxanthin
[Note—Perform this analysis in subdued light, using low-actinic glassware. ]
Sample solution:
0.005 g/mL in chloroform. [Note—If the solution is not clear, centrifuge it with an appropriate centrifuge to obtain a clear supernatant. ]
Instrumental conditions
Analytical wavelength:
486 nm
Cell path:
1 cm
Blank:
Chloroform
Analysis
Sample:
Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of astaxanthin in the portion of Krill Oil taken:
Result = A/(F × C)
| A | = | = absorbance of the Sample solution |
| F | = | = coefficient of extinction (E1%) of pure astaxanthin in chloroform (100 mL·g |
| C | = | = concentration of the Sample solution (g/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
NLT 0.01%
CONTAMINANTS
• Fats and Fixed Oils  401
401 :
NMT 0.1 ppm each of Pb, Cd, inorganic As, and Hg
:
NMT 0.1 ppm each of Pb, Cd, inorganic As, and Hg
• Limit of Dioxins, Furans, and Polychlorinated Biphenyls
Analysis:
Determine the content of polychlorinated dibenzo-para-dioxins (PCDDs) and polychlorinated dibenzofurans (PCDFs) by method No. 1613 revision B of the Environmental Protection Agency. Determine the content of polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs) by method No. 1668 revision A of the Environmental Protection Agency.
Acceptance criteria:
The sum of PCDDs and PCDFs is NMT 2.0 pg/g of WHO toxic equivalents. The sum of PCDDs, PCDFs, and dioxin-like PCBs (polychlorinated biphenyls, non-ortho IUPAC congeners PCB-77, PCB-81, PCB-126, and PCB-169, and mono-ortho IUPAC congeners PCB-105, PCB-114, PCB-118, PCB-123, PCB-156, PCB-157, PCB-167, and PCB-189) is NMT 3.0 pg/g of WHO toxic equivalents.
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Astaxanthin Esterification
Standard solution A:
10 mg/mL of USP Astaxanthin Esters from Haematococcus pluvialis RS in acetone
Standard solution B:
10 mg/mL of USP Astaxanthin (Synthetic) RS in acetone
Sample solution:
250 mg/mL of Krill Oil in acetone
Chromatographic system
Mode:
TLC
Adsorbent:
0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel. [Note—Dry silica gel at 110 for 1 h before use. ]
for 1 h before use. ]
Application volume:
5 µL
Developing solvent system:
Hexane and acetone (70:30)
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution A, Standard solution B, and Sample solution
Develop the chromatogram in the Developing solvent system until the solvent front has moved about 15 cm of the length of the plate. Remove the plate from the chamber, and allow to dry.
Acceptance criteria:
The principal spot from Standard solution B, located in the bottom half of the plate, is free astaxanthin. The Sample solution may exhibit a light, minor spot, in the same location. The principal spots from Standard solution A are from monoesters (primary spot, located slightly above the middle of the plate) and diesters (secondary spot, located in the top third of the plate). The principal spot from the Sample solution should correspond in color and RF value to the diester spot from Standard solution A. The secondary spot from the Sample solution should correspond in color and approximately the same RF value to the monoester spot from Standard solution A. [Note—Slight differences in RF values within monoester spots and within diester spots may exist because of different intensities. ]
• Fats and Fixed Oils, Acid Value  401
401 :
170–190
:
170–190
• Fats and Fixed Oils, Peroxide Value  401
401 :
NMT 5.0 mEq peroxide/kg
:
NMT 5.0 mEq peroxide/kg
• Fats and Fixed Oils, Unsaponifiable Matter  401
401 :
NMT 1.5%
:
NMT 1.5%
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight, light-resistant containers, and store at controlled room temperature. It may be bottled or otherwise packaged in containers from which air has been expelled by production of a vacuum or by an inert gas.
• Labeling:
The label states the average content of DHA and EPA in mg/g. It also states the name and concentration of any added antioxidant.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Astaxanthin Esters from Haematococcus pluvialis RS
USP Krill Oil RS
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Huy T. Dinh, M.S.
Senior Scientific Liaison (301) 816-8594 |
(DS2010) Monographs - Dietary Supplements and Herbal Medicines |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP38–NF33 Page 6115
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 41(2)