Verapamil Hydrochloride Injection
» Verapamil Hydrochloride Injection is a sterile solution of Verapamil Hydrochloride in Water for Injection. It contains not less than 90.0 percent and not more than 110.0 percent of the labeled amount of verapamil hydrochloride (C27H38N2O4·HCl).
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in single-dose containers, preferably of Type I glass, protected from light.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
USP Endotoxin RS
USP Verapamil Related Compound A RS 
3,4-Dimethoxy-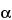 -[3-(methylamino)propyl]-
-[3-(methylamino)propyl]-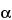 -(1-methylethyl)-benzeneacetonitrile monohydrochloride.
-(1-methylethyl)-benzeneacetonitrile monohydrochloride.
C17H26N2O2·HCl 326.87

3,4-Dimethoxy-
C17H26N2O2·HCl 326.87
Identification—
A:
It meets the requirements under Identification—Organic Nitrogenous Bases  181
181 , a volume of Injection equivalent to 100 mg of verapamil hydrochloride being used, chloroform being used in place of carbon disulfide, and a 0.1-mm cell being used in place of a 1-mm cell.
, a volume of Injection equivalent to 100 mg of verapamil hydrochloride being used, chloroform being used in place of carbon disulfide, and a 0.1-mm cell being used in place of a 1-mm cell.
B:
The chromatogram of the Assay preparation obtained as directed in the Assay exhibits a major peak for verapamil hydrochloride, the retention time of which corresponds to that exhibited in the chromatogram of the Standard preparation, obtained as directed in the Assay.
C:
It responds to the tests for Chloride  191
191 .
.
Bacterial endotoxins  85
85 —
It contains not more than 16.7 USP Endotoxin Units per mg of verapamil hydrochloride.
—
It contains not more than 16.7 USP Endotoxin Units per mg of verapamil hydrochloride.
pH  791
791 :
between 4.0 and 6.5.
:
between 4.0 and 6.5.
Particulate matter  788
788 :
meets the requirements for small-volume injections.
:
meets the requirements for small-volume injections.
Related compounds—
Aqueous solvent mixture, Mobile phase, System suitability solution, and Chromatographic system
—Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Standard solution—
Dissolve accurately weighed quantities of USP Verapamil Hydrochloride RS, USP Verapamil Related Compound A RS, USP Verapamil Related Compound E RS, and USP Verapamil Related Compound F RS in Mobile phase to obtain a solution having known concentrations of about 2.5 mg of USP Verapamil Hydrochloride RS per mL and 0.0075 mg each of USP Verapamil Related Compound A RS, USP Verapamil Related Compound E RS, and USP Verapamil Related Compound F RS per mL.
Test solution—
Use the Assay preparation.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 10 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, and allow the Test solution to elute for not less than four times the retention time for verapamil hydrochloride. Record the chromatograms, and measure all of the peak responses. The retention times are about 0.4 for verapamil related compound F, 0.5 for verapamil related compound A, 0.7 for verapamil related compound E, and 1.0 for verapamil. Calculate the quantity, in mg, of each individual impurity in each mL of the Injection taken by the formula:
C(L/D)(rU / rS)
in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, verapamil related compound A, verapamil related compound E, or verapamil related compound F in the Standard solution [note—For calculating any other unspecified impurity, C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Verapamil Hydrochloride RS in the Standard solution. ] ; L is the labeled quantity, in mg per mL, of verapamil hydrochloride in the Injection; D is the concentration, in mg per mL, of verapamil hydrochloride in the Test solution, on the basis of the labeled quantity in each mL and the extent of dilution; and rU and rS are the peak responses of the appropriate impurity in the Test solution and the Standard solution, respectively: not more than 0.3% of any specified impurity is found, and the sum of all impurities is not greater than 1.0%.
Other requirements—
It meets the requirements under Injections  1
1 .
.
Assay—
Aqueous solvent mixture—
Prepare a 0.015 N sodium acetate solution containing about 33 mL of glacial acetic acid per L.
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of Aqueous solvent mixture, acetonitrile, and 2-aminoheptane (70:30:0.5). Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Standard preparation—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Verapamil Hydrochloride RS in Mobile phase to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 2.5 mg per mL.
Assay preparation—
Dilute the Injection quantitatively, if necessary, with Mobile phase to obtain a solution having a concentration of not more than 2.5 mg of verapamil hydrochloride per mL.
System suitability solution—
Dissolve suitable quantities of USP Verapamil Hydrochloride RS and USP Verapamil Related Compound B RS in Mobile phase to obtain a solution having known concentrations of about 1.9 mg per mL and 1.5 mg per mL, respectively.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 278-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 12.5- to 15-cm column that contains packing L1. The flow rate is about 0.9 mL per minute. Chromatograph the System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative retention times are about 0.88 for verapamil related compound B and 1.0 for verapamil; the resolution, R, between the verapamil related compound B and verapamil peaks is not less than 1.5; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 278-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 12.5- to 15-cm column that contains packing L1. The flow rate is about 0.9 mL per minute. Chromatograph the System suitability solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative retention times are about 0.88 for verapamil related compound B and 1.0 for verapamil; the resolution, R, between the verapamil related compound B and verapamil peaks is not less than 1.5; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 10 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, and allow the Assay preparation to elute for not less than four times the retention time for verapamil. Record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for all of the major peaks. Calculate the quantity, in mg, of verapamil hydrochloride (C27H38N2O4·HCl) in each mL of the Injection taken by the formula:
C(L/D)(rU / rS)
in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Verapamil Hydrochloride RS in the Standard preparation; L is the labeled quantity, in mg per mL, of verapamil hydrochloride in the Injection; D is the concentration, in mg per mL, of verapamil hydrochloride in the Assay preparation, on the basis of the labeled quantity in each mL and the extent of dilution; and rU and rS are the peak responses obtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Sujatha Ramakrishna, Ph.D.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8349 |
(SM22010) Monographs - Small Molecules 2 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
|
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology |
USP35–NF30 Page 5011
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 32(6) Page 1762