Talc
 that Talc is not derived from deposits that are known to contain associated asbestos, and
that Talc is not derived from deposits that are known to contain associated asbestos, and (RB 1-Aug-2011) which method specified in the test for Absence of Asbestos was used for analysis.
(RB 1-Aug-2011) which method specified in the test for Absence of Asbestos was used for analysis.
 (Postponed indefinitely)
(Postponed indefinitely) (RB 1-Aug-2011)
(RB 1-Aug-2011)
(talk).
DEFINITION
Talc is a powdered, selected, natural, hydrated magnesium silicate. Pure talc has the formula Mg3Si4O10(OH)2. It may contain variable amounts of associated minerals among which chlorites (hydrated aluminum and magnesium silicates), magnesite (magnesium carbonate), calcite (calcium carbonate), and dolomite (calcium and magnesium carbonate) are predominant.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Infrared Absorption:
The IR spectrum of a potassium bromide dispersion of it exhibits maxima at 3677 ± 2 cm–1, at 1018 ± 2 cm–1, and at 669 ± 2 cm–1.
• B. Procedure
Sample:
100 mg
Analysis:
Mix about 200 mg of anhydrous sodium carbonate and 2 g of anhydrous potassium carbonate, and melt in a platinum crucible. To the melt add the Sample, and continue heating until fusion is complete. Cool, and transfer the fused mixture to a dish or beaker with the aid of about 50 mL of hot water. Add hydrochloric acid to the liquid until effervescence ceases, then add 10 mL more of the acid, and evaporate the mixture on a steam bath to dryness. Cool, add 20 mL of water, boil, and filter the mixture. Save the insoluble residue for use in Identification test C.
To 5 mL of the filtrate add 1 mL of 6 N ammonium hydroxide and 1 mL of ammonium chloride TS. Filter, if necessary, and add 1 mL of dibasic sodium phosphate TS to the filtrate.
Acceptance criteria:
A white, crystalline precipitate of magnesium ammonium phosphate is formed.
• C. Procedure
Sample:
100 mg of the insoluble residue from Identification test B
Analysis:
In a lead or platinum crucible and using a copper wire, mix the Sample with about 10 mg of sodium fluoride and a few drops of sulfuric acid to give a thin slurry. Cover the crucible with a thin transparent plate of plastic under which a drop of water is suspended, and warm gently.
Acceptance criteria:
Within a short time, a white ring is rapidly formed around the drop of water.
ASSAY
• Content of Magnesium
Lanthanum chloride solution:
To 5.9 g of lanthanum oxide slowly add 10 mL of hydrochloric acid, and heat to boiling. Allow to cool, and dilute with water to 100 mL.
Magnesium standard stock solution:
10 µg/mL of magnesium, prepared by diluting an 8.365 mg/mL solution of magnesium chloride in diluted hydrochloric acid with water (1 in 100)
Magnesium standard solutions:
Into four identical 100-mL volumetric flasks, each containing 10.0 mL of hydrochloric acid and 10 mL of Lanthanum chloride solution, transfer respectively 2.5, 3.0, 4.0, and 5.0 mL of Magnesium standard stock solution, and dilute with water to volume.
Sample stock solution:
[Caution—Perchlorates mixed with heavy metals are known to be explosive. Take proper precautions while performing this analysis.
]
Weigh 500 mg of Talc in a 100-mL polytetrafluoroethylene dish. Add 5 mL of hydrochloric acid, 5 mL of lead-free nitric acid, and 5 mL of perchloric acid. Stir gently, then add 35 mL of hydrofluoric acid, and evaporate slowly on a hot plate to moist dryness (until about 0.5 mL remains). To the residue, add 5 mL of hydrochloric acid, cover with a watch glass, heat to boiling, and allow to cool. Rinse the watch glass and the dish with water, transfer to a 50-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume.
Sample solution:
Dilute the Sample stock solution with water (1 in 200). Transfer 4.0 mL of this solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 10.0 mL of hydrochloric acid and 10 mL of Lanthanum chloride solution, and dilute with water to volume.
Instrumental conditions
Mode:
Atomic absorption spectrophotometry
Analytical wavelength:
Magnesium emission line at 285.2 nm
Lamp:
Magnesium hollow-cathode
Flame:
Air–acetylene
Analysis
Samples:
Magnesium standard solutions and Sample solution
Concomitantly determine the absorbance of the solutions.
Acceptance criteria:
17.0%–19.5%
IMPURITIES
• Water-Soluble Substances
Sample:
10.0 g
Analysis:
To the Sample add 50 mL of carbon dioxide-free water, heat to boiling, and boil under a reflux condenser for 30 min. Allow to cool, filter, and dilute with carbon dioxide-free water to 50.0 mL. Test with litmus paper. Evaporate 25.0 mL of the filtrate to dryness, dry at 105 for 1 h, and weigh the residue.
for 1 h, and weigh the residue.
Acceptance criteria:
The filtrate is neutral to litmus paper, and the weight of the residue is NMT 5 mg (0.1%).
• Limit of Iron
Iron standard stock solution:
250 µg/mL of iron from 4.840 g ferric chloride in a 150 g/L solution of hydrochloric acid in water. Prepare immediately before use.
Iron standard solutions:
Into four 100-mL volumetric flasks, each containing 50.0 mL of 0.5 N hydrochloric acid, transfer respectively 2.0, 2.5, 3.0, and 4.0 mL of the Standard iron stock solution, and dilute each flask with water to volume.
Sample stock solution:
Transfer 10.0 g of Talc to a conical flask fitted with a reflux condenser. Gradually add 50 mL of 0.5 N hydrochloric acid while stirring, and heat on a water bath for 30 min. Allow to cool. Transfer the mixture to a beaker, and allow the undissolved material to settle. Filter the supernatant into a 100-mL volumetric flask, retaining as much as possible of the insoluble material in the beaker. Wash the residue and the beaker with three 10-mL portions of hot water. Wash the filter with 15 mL of hot water, allow the filtrate to cool, and dilute with water to 100.0 mL.
Sample solution:
Transfer 2.5 mL of the Sample stock solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 50.0 mL of 0.5 N hydrochloric acid, and dilute with water to volume.
Instrumental conditions
Mode:
Atomic absorption spectrophotometry
Analytical wavelength:
Iron emission line at 248.3 nm
Lamp:
Iron hollow-cathode
Flame:
Air–acetylene
Analysis
Samples:
Iron standard solutions and Sample solution
Concomitantly determine the absorbance of the solutions. Make any correction using a deuterium lamp.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.25%
• Limit of Lead
Sample solution:
Use the Sample stock solution as directed in the test for Limit of Iron.
Diluent:
Nitric acid in water (1 in 100)
Lead standard stock solution:
10 µg/mL of lead prepared as follows. Dissolve 160 mg of lead nitrate in 100 mL of Diluent, and dilute with water to 1000 mL. Dilute this solution with water (1 in 10).
Lead standard solutions:
Into four identical 100-mL volumetric flasks, each containing 50.0 mL of 0.5 N hydrochloric acid, transfer respectively 5.0, 7.5, 10.0, and 12.5 mL of Lead standard stock solution, and dilute with water to volume.
Instrumental conditions
Mode:
Atomic absorption spectrophotometry
Analytical wavelength:
Lead emission line at 217.0 nm
Lamp:
Lead hollow-cathode
Flame:
Air–acetylene
Analysis
Samples:
Lead standard solutions and Sample solution
Concomitantly determine the absorbance of the solutions.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 10 ppm
• Limit of Calcium
Lanthanum chloride solution:
Prepare as directed in the Assay.
Calcium standard stock solution:
100 µg/mL of calcium, prepared immediately before use by diluting a 3.67 mg/mL solution of calcium chloride dihydrate in diluted hydrochloric acid with water (1 in 10)
Calcium standard solutions:
Into four identical 100-mL volumetric flasks, each containing 10.0 mL of hydrochloric acid and 10 mL of Lanthanum chloride solution, transfer respectively 1.0, 2.0, 3.0, and 4.0 mL of Calcium standard stock solution, and dilute each solution with water to volume.
Sample stock solution:
Prepare as directed in the Assay.
Sample solution:
Transfer 5.0 mL of the Sample stock solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 10.0 mL of hydrochloric acid and 10 mL of Lanthanum chloride solution, and dilute with water to volume.
Instrumental conditions
Mode:
Atomic absorption spectrophotometry
Analytical wavelength:
Calcium emission line at 422.7 nm
Lamp:
Calcium hollow-cathode
Flame:
Nitrous oxide–acetylene
Analysis
Samples:
Calcium standard solutions and Sample solution
Concomitantly determine the absorbance of the solutions.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.9%
• Limit of Aluminum
Cesium chloride solution:
25.3 mg/mL of cesium chloride in water.
Aluminum standard stock solution:
100 µg/mL of aluminum, prepared immediately before use by diluting an 8.947 mg/mL solution of aluminum chloride in water with water (1 in 10)
Aluminum standard solutions:
Into four identical 100-mL volumetric flasks, each containing 10.0 mL of hydrochloric acid and 10 mL of Cesium chloride solution, transfer respectively 5.0, 10.0, 15.0, and 20.0 mL of Aluminum standard stock solution, and dilute with water to volume.
Sample stock solution:
Proceed as directed in the Assay. Transfer 5 mL of the Cesium chloride solution to the 50-mL flask prior to transfer of the residue, and dilute with water to volume.
Sample solution:
Transfer 5.0 mL of the Sample stock solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask, add 10 mL of the Cesium chloride solution and 10.0 mL of hydrochloric acid, and dilute with water to volume.
Instrumental conditions
Mode:
Atomic absorption spectrophotometry
Analytical wavelength:
Aluminum emission line at 309.3 nm
Lamp:
Aluminum hollow-cathode
Flame:
Nitrous oxide–acetylene
Analysis
Samples:
Aluminum standard solutions and Sample solution
Concomitantly determine the absorbance of the solutions.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 2.0%
• Absence of Asbestos
[Note—Suppliers of Talc may use one of the following methods to determine the absence of asbestos. ]
Proceed as directed for Procedure 1 or Procedure 2. If either test is positive, perform Procedure 3.
Procedure 1: Infrared Absorption
The IR absorption spectrum of a potassium bromide dispersion of Talc at the absorption band at 758 ± 1 cm–1, using scale expansion, may indicate the presence of tremolite or chlorite. If the absorption band remains after ignition of the substance at 850 for at least 30 min, it indicates the presence of tremolite. In the range 600 cm–1 to 650 cm–1 using scale expansion, any absorption band or shoulder may indicate the presence of serpentines.
for at least 30 min, it indicates the presence of tremolite. In the range 600 cm–1 to 650 cm–1 using scale expansion, any absorption band or shoulder may indicate the presence of serpentines.
Procedure 2:
Use the following conditions (see X-Ray Diffraction  941
941 ):
):
Cu K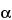 monochromatic 40 kV radiation, 24–30 mA; the incident slit is set at 1
monochromatic 40 kV radiation, 24–30 mA; the incident slit is set at 1 ; the detection slit is set at 0.2
; the detection slit is set at 0.2 ; the goniometer speed is 1/10
; the goniometer speed is 1/10 2
2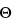 /min; the scanning range is 10
/min; the scanning range is 10 –13
–13 2
2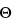 and 24
and 24 –26
–26 2
2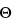 ; the sample is not oriented. Prepare a random sample, and place on the sample holder. Pack and smooth its surface with a polished glass microscope slide. Record the diffractograms: the presence of amphiboles is detected by a diffraction peak at 10.5 ± 0.1
; the sample is not oriented. Prepare a random sample, and place on the sample holder. Pack and smooth its surface with a polished glass microscope slide. Record the diffractograms: the presence of amphiboles is detected by a diffraction peak at 10.5 ± 0.1 2
2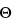 , and the presence of serpentines is detected by diffraction peaks at 24.3 ± 0.1
, and the presence of serpentines is detected by diffraction peaks at 24.3 ± 0.1 2
2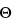 to 12.1 ± 0.1
to 12.1 ± 0.1 2
2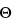 .
.
Procedure 3:
The presence of asbestos (see Optical Microscopy  776
776 ) is shown if there is a range of length to width ratios of 20:1 to 100:1, or higher for fibers longer than 5 µm; if there is a capability of splitting into very thin fibrils; and if there are two or more of the following four criteria: (1) parallel fibers occurring in bundles, (2) fiber bundles displaying frayed ends, (3) fibers in the form of thin needles, and (4) matted masses of individual fibers and/or fibers showing curvature.
) is shown if there is a range of length to width ratios of 20:1 to 100:1, or higher for fibers longer than 5 µm; if there is a capability of splitting into very thin fibrils; and if there are two or more of the following four criteria: (1) parallel fibers occurring in bundles, (2) fiber bundles displaying frayed ends, (3) fibers in the form of thin needles, and (4) matted masses of individual fibers and/or fibers showing curvature.
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Microbial Enumeration Tests  61
61 and Tests for Specified Microorganisms
and Tests for Specified Microorganisms  62
62
Intended for topical administration
Total aerobic microbial count:
NMT 100 cfu/g
Total combined molds and yeasts count:
NMT 50 cfu/g
Intended for oral administration
Total aerobic microbial count:
NMT 1000 cfu/g
Total combined molds and yeasts count:
NMT 100 cfu/g
• Acidity and Alkalinity:
Boil 2.5 g of Talc with 50 mL of carbon dioxide-free water under reflux. Filter under vacuum. To 10 mL of the filtrate, add 0.1 mL of bromothymol blue TS. Add 0.01 N hydrochloric acid until the indicator changes color. To a second 10 mL of the filtrate, add 0.1 mL of phenolphthalein TS. Add 0.01 N sodium hydroxide until the indicator turns pink.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.4 mL of 0.01 N hydrochloric acid is required to change the color of the bromothymol blue indicator. NMT 0.3 mL of 0.01 N sodium hydroxide is required to change the color of the phenolpthalein indicator to pink.
• Loss on Ignition  733
733
Sample:
1 g
Analysis:
Ignite at 1075 ± 25 to constant weight.
to constant weight.
Acceptance criteria:
It loses NMT 7.0% of its weight.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers. No storage requirements specified.
• Labeling:
The label states, where applicable, that the substance is suitable for oral or topical administration. The certificate of analysis states the absence of asbestos. It also indicates which method specified in the test for Absence of Asbestos was used for analysis.
Change to read:
• Labeling:
The label states, where applicable, that the substance is suitable for oral or topical administration. The certificate of analysis states the absence of asbestos. It also indicates
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Robert H. Lafaver, M.S.
Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8335 |
(EXC2010) Monographs - Excipients |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology |
USP35–NF30 Page 4741
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 31(6) Page 1662