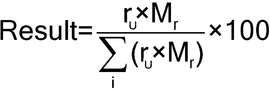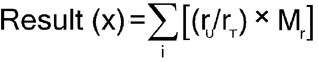Benzalkonium Chloride
Ammonium, alkyldimethyl(phenylmethyl)-, chloride;
Alkylbenzyldimethylammonium chloride

 [8001-54-5].
[8001-54-5].
(ben'' zal koe' nee um klor' ide).
Ammonium, alkyldimethyl(phenylmethyl)-, chloride;
Alkylbenzyldimethylammonium chloride
DEFINITION
Benzalkonium Chloride is a mixture of alkylbenzyldimethylammonium chlorides of the general formula:
[C6H5CH2N(CH3)2R]Cl
in which R represents a mixture of alkyls, including all or some of the group beginning with n-C8H17 and extending through higher homologs, with n-C12H25, n-C14H29, and n-C16H33 composing the major portion. On the anhydrous basis, the content of the n-C12H25 homolog is NLT 40.0%, and the content of the n-C14H29 homolog is NLT 20.0% of the total alkylbenzyldimethylammonium chloride content. The amount of the n-C12H25 and n-C14H29 homolog components together is NLT 70.0% of the total alkylbenzyldimethylammonium chloride content. The total alkylbenzyldimethylammonium chloride content, calculated on the anhydrous basis, with allowance made for the amount of residue on ignition, is NLT 97.0% and NMT 103.0% of [C6H5CH2N(CH3)2R]Cl.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Procedure
Analysis:
To 2 mL of a solution (1 in 100) add 1 mL of 2 N nitric acid.
Acceptance criteria:
A white precipitate is formed, and it is dissolved after adding 5 mL of alcohol.
• B. Procedure
Analysis:
Dissolve 200 mg in 1 mL of sulfuric acid, add 100 mg of sodium nitrate, and heat on a steam bath for 5 min. Cool, dilute with water to 10 mL, add 500 mg of zinc dust, and warm for 5 min on a steam bath. To 2 mL of the clear supernatant, add 1 mL of sodium nitrite solution (1 in 20), cool in ice water, and then add 3 mL of a solution of 500 mg of 2-naphthol in 10 mL of 6 N ammonium hydroxide.
Acceptance criteria:
An orange-red color is produced.
• C. Identification Tests—General, Chloride  191
191 :
The solution in a mixture of equal volumes of water and alcohol meets the requirements of the tests.
:
The solution in a mixture of equal volumes of water and alcohol meets the requirements of the tests.
• D.
The retention times of the major peaks for benzalkonium chloride in the Sample solution correspond to those of the Standard solution, as obtained in the test for Ratio of Alkyl Components.
ASSAY
• Ratio of Alkyl Components
Solution A:
Adjust a 0.1 M solution of sodium acetate with glacial acetic acid to a pH of 5.0.
Mobile phase:
Acetonitrile and Solution A (9:11). Acetonitrile and Solution A may be adjusted from (2:3) to (3:2) to meet system suitability requirements.
Standard solution:
4 mg/mL of Benzalkonium Chloride, prepared from USP Benzalkonium Chloride RS and water.
Sample solution:
4 mg/mL of Benzalkonium Chloride
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 254 nm
Column:
3.9-mm × 30-cm; packing L10, or 4.6-mm × 25-cm; 10-µm packing L10
Flow rate:
2 mL/min
Injection size:
20 µL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
[Note—See the relative retention times in the table below. Relative retention times are provided for information only, and the standard should be used to ensure appropriate peak identification. ]
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
|---|---|
| C10 homolog | 0.9 |
| C12 homolog | 1.0 |
| C14 homolog | 1.3 |
| C16 homolog | 1.7 |
Suitability requirements
Resolution:
NLT 1.5 between the C12 and C14 peaks
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 2.0% from the C12 peak
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Identify the homolog peaks by comparison of the retention times with those from the Standard solution.
Calculate the percentage of each quaternary ammonium homolog taken:
| rU | = | = area of the peak due to a given homolog in the chromatogram from the Sample solution |
| Mr | = | = molecular weight of a given homolog. The molecular weights of C10, C12, C14, and C16 homologs are 312, 340, 368, and 396, respectively. |
Acceptance criteria:
On the anhydrous basis, the content of the n-C12H25 homolog is NLT 40.0%, and the content of the n-C14H29 homolog is NLT 20.0% of the total alkylbenzyldimethylammonium chloride content. The amount of the n-C12H25 and n-C14H29 homolog components together is NLT 70.0% of the total alkylbenzyldimethylammonium chloride content.
• Total Alkylbenzyldimethylammonium Chlorides
Sample:
Weigh a quantity of Benzalkonium Chloride equivalent to 500 mg of anhydrous benzalkonium chloride.
Analysis:
Transfer the Sample, with the aid of 35 mL of water, to a glass-stoppered, 250-mL conical separator containing 25 mL of methylene chloride. Add 10 mL of 0.1 N sodium hydroxide, and 10.0 mL of freshly prepared potassium iodide solution (1 in 20), insert the stopper into the separator, shake, allow the layers to separate, and discard the methylene chloride layer. Wash the aqueous layer with three 10-mL portions of methylene chloride, and discard the washings. Transfer the aqueous layer to a glass-stoppered, 250-mL conical flask, and rinse the separator with three 5-mL portions of water, adding the washings to the flask. Add 40 mL of cold hydrochloric acid to the flask, mix, and titrate with 0.05 M potassium iodate VS until the solution becomes light brown in color. Add 5 mL of methylene chloride, insert the stopper into the flask, and shake vigorously. Continue the titration, dropwise, with shaking after each addition, until the methylene chloride layer becomes colorless and the aqueous layer is clear yellow. Record the titrant volume, Vt (mL). Perform a blank determination, using 20 mL of water as the sample, and record the titrant volume, Vb (mL). [Note—Vb > Vt. ] The difference between the two titrations represents the amount of potassium iodate equivalent to the weight of benzalkonium chloride in the sample. Each mL of 0.05 M potassium iodate is equivalent to x/10 mg of benzalkonium chloride, where x represents the average molecular weight of the sample, derived by summing, for all homologs, the products:
| rU | = | = area of the peak produced by a given homolog in the chromatogram from the Ratio of Alkyl Components test |
| rT | = | = sum of the peak areas for all homologs in the chromatogram from the Ratio of Alkyl Components test |
| Mr | = | = molecular weight of a given homolog. The molecular weights of the C10, C12, C14, and C16 homologs are 312, 340, 368, and 396, respectively. |
Acceptance criteria:
97.0%–103.0% on the anhydrous basis
IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
• Residue on Ignition  281
281 :
NMT 2.0%
:
NMT 2.0%
Organic Impurities
• Procedure 1: Limit of Amines and Amine Salts
Sample:
5.0 g of Benzalkonium Chloride
Analysis and Acceptance criteria:
Dissolve the Sample with heating carefully e.g., on top of a steam bath with water as the steam source in 20 mL of a mixture of methanol and 1 N hydrochloric acid VS (97:3). [Note—However, the mixed solution must not reach the boiling point. ] Add 100 mL of isopropyl alcohol. Pass a stream of nitrogen slowly through the solution. Gradually add 12.0 mL of 0.1 N tetrabutylammonium hydroxide VS, while recording the potentiometric titration curve. If the curve shows two inflection points, the volume of titrant added between the two points is NMT 5.0 mL, corresponding to NMT 0.1 mmol/g of amines and amine salts. If the curve shows no point of inflection, the substance being examined does not comply with the test. If the curve shows one point of inflection, repeat the test, but add 3.0 mL of a 25.0 mg/mL solution of dimethyldecylamine in isopropyl alcohol before the titration. If after addition of 12.0 mL of the titrant, the titration curve shows only one point of inflection, the substance being examined does not comply with the test.
• Procedure 2: Limit of Benzyl Alcohol, Benzaldehyde, and (Chloromethyl)benzene
[Note—Prepare the solutions immediately before use. ]
Solution A:
Dissolve 1.09 g of sodium 1-hexanesulfonate and 6.9 g of monobasic sodium phosphate in water in a 1000-mL volumetric flask, adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 3.5, and dilute with water to volume.
Solution B:
Methanol
Mobile phase:
See the gradient table below.
| Time (min) |
Solution A (%) |
Solution B (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | 80 | 20 |
| 10 | 80 | 20 |
| 14 | 50 | 50 |
| 35 | 50 | 50 |
| 36 | 20 | 80 |
| 55 | 20 | 80 |
| 56 | 80 | 20 |
| 65 | 80 | 20 |
Standard solution A:
0.25 mg/mL of USP Benzyl Alcohol RS in methanol
Standard solution B:
0.075 mg/mL of USP Benzaldehyde RS in methanol
Standard solution C:
0.025 mg/mL of USP Benzyl Alcohol RS in methanol, prepared from Standard solution A and methanol
Sample solution:
50 mg/mL of Benzalkonium Chloride in methanol
Chromatographic system
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 210 nm for benzyl alcohol and (chloromethyl)benzene; UV 257 nm for benzaldehyde
Column:
4.6-mm × 15-cm analytical column; 5-µm packing L1
Column temperature:
30
Flow rate:
1.0 mL/min
Injection size:
20 µL
System suitability
Samples:
Standard solution A, Standard solution B, Standard solution C, and Sample solution
[Note—See the relative retention times in the table below. ]
| Name | Relative Retention Time |
|---|---|
| Benzyl alcohol | 1.0 |
| Benzaldehyde | 1.3 |
| (Chloromethyl)benzene | 2.4 |
Suitability requirements
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 5.0% for the benzyl alcohol peak, Standard solution A
Signal-to-noise ratio:
NLT 10 for the principal peak in the chromatogram, Standard solution C
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution A, Standard solution B, Standard solution C, and Sample solution
To calculate the content of (chloromethyl)benzene, multiply the peak area of (chloromethyl)benzene by 1.3. [Note—The correction factor is used due to baseline shift. ]
Acceptance criteria
Benzyl alcohol:
The response of the benzyl alcohol peak from the Sample solution is NMT that of the benzyl alcohol peak from the Standard solution A, corresponding to NMT 0.5%.
Benzaldehyde:
The response of the benzaldehyde peak from the Sample solution is NMT that of the benzaldehyde peak from Standard solution B, corresponding to NMT 0.15%.
(Chloromethyl)benzene:
The response of the (chloromethyl)benzene peak from the Sample solution is NMT 0.1 times that of the principal peak in the chromatogram from Standard solution A, corresponding to NMT 0.05%.
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Acidity or Alkalinity
Sample:
0.5 g of Benzalkonium Chloride
Analysis:
Dissolve the Sample in water, dilute with water to 50 mL, and mix. Add 0.1 mL of bromocresol purple TS.
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.1 mL of 0.1 N hydrochloric acid or 0.1 N sodium hydroxide is required to change the color of the indicator.
• Water Determination, Method I  921
921 :
NMT 15.0%
:
NMT 15.0%
• Water-Insoluble Matter:
A solution (1 in 10) is free from turbidity and insoluble matter.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in tight containers. No storage requirements specified.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Robert H. Lafaver, M.S.
Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8335 |
(EXC2010) Monographs - Excipients |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 1708
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 35(6) Page 1496