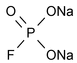Sodium Monofluorophosphate
(soe' dee um mon'' oh floor'' oh fos' fate).
» Sodium Monofluorophosphate contains not less than 91.7 percent and not more than 100.5 percent of Na2PFO3, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed containers.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
USP Sodium Fluoride RS
Identification—
A:
Place about 1 g in a platinum crucible in a well-ventilated hood, and add 15 mL of sulfuric acid. Cover the crucible with a piece of clear, polished glass, and heat on a steam bath for 1 hour. Remove the glass cover, rinse it in water, and dry: the glass surface exposed to vapors from the crucible is etched.
B:
A solution (1 in 10) with silver nitrate TS yields a white precipitate, which is soluble in diluted nitric acid and in dilute ammonium hydroxide (1 in 2).
C:
A solution responds to the tests for Sodium  191
191 .
.
pH  791
791 :
between 6.5 and 8.0, in a solution (1 in 50).
:
between 6.5 and 8.0, in a solution (1 in 50).
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 105
—
Dry it at 105 to constant weight: it loses not more than 0.2% of its weight.
to constant weight: it loses not more than 0.2% of its weight.
Arsenic, Method I  211
211 :
3 ppm.
:
3 ppm.
Heavy metals, Method I  231
231 —
Dissolve 400 mg in 25 mL of water: the limit is 0.005%.
—
Dissolve 400 mg in 25 mL of water: the limit is 0.005%.
Limit of fluoride ion—
[note—Use plasticware throughout this test. ]
Buffer solution—
To 55 g of sodium chloride in a 1000-mL volumetric flask add 500 mg of sodium citrate, 255 g of sodium acetate, and 300 mL of water. Shake to dissolve, and cautiously add 115 mL of glacial acetic acid with mixing. Cool to room temperature, add 300 mL of isopropyl alcohol, dilute with water to volume, and mix: the pH of this solution is between 5.0 and 5.5.
Standard stock solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Sodium Fluoride RS quantitatively in water to obtain a solution containing 1105 µg per mL. Each mL of this solution contains 500 µg of fluoride ion. Store in a tightly closed, plastic container.
Standard preparations—
To four 100-mL volumetric flasks transfer, respectively, 2.0-, 4.0-, 10.0-, and 20.0-mL portions of the Standard stock solution, dilute each with Buffer solution to volume, and mix to obtain solutions having fluoride ion concentrations of 10, 20, 50, and 100 µg per mL, respectively.
Test preparation—
Transfer about 1.8 g, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask, add water to dissolve, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Transfer 20.0 mL of this solution to a second 100-mL volumetric flask, dilute with Buffer solution to volume, and mix.
Procedure—
Concomitantly measure the potential (see pH  791
791 ), in mV, of the Standard preparations and of the Test preparation with a pH meter capable of a minimum reproducibility of ±0.2 mV, equipped with a glass-sleeved calomel-fluoride specific-ion electrode system. [note—When taking measurements, immerse the electrodes in the solution, which has been transferred to a 150-mL plastic beaker containing a plastic-coated stirring bar. Allow to stir on a magnetic stirrer having an insulated top until equilibrium is attained (1 to 2 minutes), and record the potential. Rinse and dry the electrodes between measurements, taking care to avoid damaging the crystal of the specific-ion electrode. ] Plot the logarithm of the fluoride-ion concentrations, in µg per mL, of each Standard preparation versus potential, in mV. From the measured potential of the Test preparation and the standard curve, determine the concentration, in µg per mL, of fluoride ion in the Test preparation: not more than 1.2% is found.
), in mV, of the Standard preparations and of the Test preparation with a pH meter capable of a minimum reproducibility of ±0.2 mV, equipped with a glass-sleeved calomel-fluoride specific-ion electrode system. [note—When taking measurements, immerse the electrodes in the solution, which has been transferred to a 150-mL plastic beaker containing a plastic-coated stirring bar. Allow to stir on a magnetic stirrer having an insulated top until equilibrium is attained (1 to 2 minutes), and record the potential. Rinse and dry the electrodes between measurements, taking care to avoid damaging the crystal of the specific-ion electrode. ] Plot the logarithm of the fluoride-ion concentrations, in µg per mL, of each Standard preparation versus potential, in mV. From the measured potential of the Test preparation and the standard curve, determine the concentration, in µg per mL, of fluoride ion in the Test preparation: not more than 1.2% is found.
Assay—
Monochloroacetate buffer—
Dissolve 189 g of monochloroacetic acid and 55 g of sodium hydroxide in about 1500 mL of water. Cool, dilute with water to 2000 mL, and mix.
0.025 M Thorium nitrate—
Dissolve 13.8 g of thorium nitrate in about 800 mL of water, and filter the solution into a 1000-mL volumetric flask. Dilute with water to volume, and mix. Standardize this solution as follows. Transfer 20.0 mL of Standard stock solution, prepared as directed in the test for Limit of fluoride ion, to a 150-mL beaker containing 50 mL of water. Add 3 drops of sodium alizarinsulfonate TS, mix, and adjust the acidity by the careful addition, successively, of sodium hydroxide solution (1 in 50) and dilute hydrochloric acid (1 in 160), until the pink color has just been discharged. Add 1 mL of Monochloroacetate buffer, and titrate with 0.025 M Thorium nitrate to a permanent pink color. Calculate the molarity of the thorium nitrate titrant taken by the equation:
M = (S) / [(4)(41.99V)]
in which S is the weight, in mg, of USP Sodium Fluoride RS in the portion of Standard stock solution taken, 41.99 is the molecular weight of sodium fluoride, and V is the volume, in mL, of titrant consumed.
Procedure—
Transfer about 1.8 g of Sodium Monofluorophosphate, accurately weighed, to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add about 50 mL of water, mix to effect solution, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Transfer 20.0 mL of this solution to the reaction flask of a suitable fluoride steam distilling apparatus containing 10 lime-glass beads measuring 5 mm in diameter and 70 mL of dilute sulfuric acid (1 in 2). Distill, by passing steam through the solution in the reaction flask and applying heat to the flask, collecting the distillate in a 250-mL volumetric flask. Control the temperature of the solution in the reaction flask so that it does not exceed 140 . Change receivers when the flask is filled to volume with distillate, and continue distilling into a 400-mL beaker until an additional 150 mL to 200 mL of distillate tailing has been collected. Mix the solution in the 250-mL volumetric flask, and transfer 50.0 mL to a 150-mL beaker. To the 150-mL beaker add 50 mL of water and 3 drops of sodium alizarinsulfonate TS, and mix. Adjust the acidity of this solution by the careful addition, successively, of sodium hydroxide solution (1 in 50) and dilute hydrochloric acid (1 in 160), until the pink color has just been discharged. Add 1 mL of Monochloroacetate buffer, titrate with 0.025 M Thorium nitrate to a permanent pink color, and record the volume, in mL, of titrant consumed as VA. Add 3 drops of sodium alizarinsulfonate TS to the distillation tail in the 400-mL beaker, proceed as directed previously with the adjustment of the acidity, the addition of Monochloroacetate buffer, and the titration with 0.025 M Thorium nitrate, and record the volume, in mL, of titrant consumed as VB. Calculate the percentage of Na2PFO3 in the Sodium Monofluorophosphate taken by the formula:
. Change receivers when the flask is filled to volume with distillate, and continue distilling into a 400-mL beaker until an additional 150 mL to 200 mL of distillate tailing has been collected. Mix the solution in the 250-mL volumetric flask, and transfer 50.0 mL to a 150-mL beaker. To the 150-mL beaker add 50 mL of water and 3 drops of sodium alizarinsulfonate TS, and mix. Adjust the acidity of this solution by the careful addition, successively, of sodium hydroxide solution (1 in 50) and dilute hydrochloric acid (1 in 160), until the pink color has just been discharged. Add 1 mL of Monochloroacetate buffer, titrate with 0.025 M Thorium nitrate to a permanent pink color, and record the volume, in mL, of titrant consumed as VA. Add 3 drops of sodium alizarinsulfonate TS to the distillation tail in the 400-mL beaker, proceed as directed previously with the adjustment of the acidity, the addition of Monochloroacetate buffer, and the titration with 0.025 M Thorium nitrate, and record the volume, in mL, of titrant consumed as VB. Calculate the percentage of Na2PFO3 in the Sodium Monofluorophosphate taken by the formula:
[(2)(143.95)(5VA + VB)(M) / (W)]  (143.95 / 18.9984)(F)
(143.95 / 18.9984)(F)
in which M is the molarity of 0.025 M Thorium nitrate; W is the weight, in g, of the Sodium Monofluorophosphate taken; F is the percentage of fluoride ions determined as directed in the test for Limit of fluoride ion; 143.95 is the molecular weight of sodium monofluorophosphate; 18.9984 is the atomic weight of fluorine; and the other terms are as defined therein.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Elena Gonikberg, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8251 |
(SM32010) Monographs - Small Molecules 3 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 4664