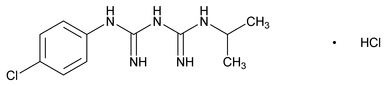
Proguanil Hydrochloride
(proe gwahn' il hye'' droe klor' ide).
Biguanide, 1-(4-chlorophenyl)-5-isopropyl, hydrochloride.
1-(p-Chlorophenyl)-5-isopropylbiguanide hydrochloride
» Proguanil Hydrochloride contains not less than 98.5 percent and not more than 101.0 percent of C11H16ClN5·HCl, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed, light-resistant containers, and store at room temperature.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
USP Proguanil Hydrochloride RS
USP Proguanil Related Compound C RS
1,5-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)biguanide.
C14H13Cl2N5 322.19
1,5-Bis(4-chlorophenyl)biguanide.
C14H13Cl2N5 322.19
USP Proguanil Related Compound D RS
1,5-Bis(1-methylethyl)biguanide, or 1,5-diisopropylbiguanide.
C8H19N5 185.27
1,5-Bis(1-methylethyl)biguanide, or 1,5-diisopropylbiguanide.
C8H19N5 185.27
Identification—
B:
It meets the requirements of the test for Chloride  191
191 .
.
Acidity or alkalinity—
To 35 mL of water maintained at 60 to 65
to 65 , add 0.4 mL of methyl red–methylene blue TS. Neutralize to a gray color with either 0.01 N sodium hydroxide or 0.01 N hydrochloric acid. Add 400 mg of Proguanil Hydrochloride, and stir until completely dissolved. The solution is gray or green. Not more than 0.2 mL of 0.01 N hydrochloric acid is required to change the color of the solution to reddish-violet.
, add 0.4 mL of methyl red–methylene blue TS. Neutralize to a gray color with either 0.01 N sodium hydroxide or 0.01 N hydrochloric acid. Add 400 mg of Proguanil Hydrochloride, and stir until completely dissolved. The solution is gray or green. Not more than 0.2 mL of 0.01 N hydrochloric acid is required to change the color of the solution to reddish-violet.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 105
—
Dry it at 105 for 2 hours: it loses not more than 0.5% of its weight.
for 2 hours: it loses not more than 0.5% of its weight.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.1%.
:
not more than 0.1%.
Limit of chloroaniline—
Naphthylethylenediamine dihydrochloride solution—
Dissolve 0.1 g of naphthylethylenediamine dihydrochloride in water and dilute with the same solvent to 100 mL. [note—Prepare immediately before use. ]
Procedure—
Dissolve 100 mg in 1 mL of 2 N hydrochloric acid, and dilute with water to 20 mL. Cool to 5 . Add 1 mL of a 3.45 g per L solution of sodium nitrite, and allow to stand at 5
. Add 1 mL of a 3.45 g per L solution of sodium nitrite, and allow to stand at 5 for 5 minutes. Add 2 mL of a 50 g per L solution of ammonium sulfamate, and allow to stand for 10 minutes. Add 2 mL of Naphthylethylenediamine dihydrochloride solution, dilute with water to 50 mL, and allow to stand for 30 minutes. Any red color produced is not more intense than that of a standard prepared at the same time and in the same manner, using 20 mL of a 1.25 mg per L solution of chloroaniline (250 ppm).
for 5 minutes. Add 2 mL of a 50 g per L solution of ammonium sulfamate, and allow to stand for 10 minutes. Add 2 mL of Naphthylethylenediamine dihydrochloride solution, dilute with water to 50 mL, and allow to stand for 30 minutes. Any red color produced is not more intense than that of a standard prepared at the same time and in the same manner, using 20 mL of a 1.25 mg per L solution of chloroaniline (250 ppm).
Related compounds—
Mobile phase—
Dissolve 3.78 g of sodium hexanesulfonate in a mixture of 1200 mL of methanol, 800 mL of water, and 10 mL of glacial acetic acid.
Standard stock solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Proguanil Hydrochloride RS in Mobile phase to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.1 mg per mL.
Standard solution—
Quantitatively dilute a suitable portion of the Standard stock solution with Mobile phase to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.2 µg per mL.
Related compound C solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Proguanil Related Compound C RS in Mobile phase to obtain a solution having a concentration of about 0.5 µg per mL. [note—USP Proguanil Related Compound C RS is 1,5-bis(4-chlorophenyl)biguanide. ]
Related compound D solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Proguanil Related Compound D RS in Mobile phase to obtain a solution having a concentration of about 0.5 µg per mL. [note—USP Proguanil Related Compound D RS is 1,5-bis(1-methylethyl)biguanide. ]
System suitability solution—
Dilute 1 mL of the Standard stock solution with Mobile phase to 200 mL. To 1 mL of the resulting solution, add 1 mL of Related compound D solution, and mix.
Test solution—
Dissolve 10.0 mg of Proguanil Hydrochloride in Mobile phase, and dilute with Mobile phase to 100.0 mL.
Chromatographic system
(see Chromatography  621
621 )—The liquid chromatograph is equipped with either a programmable variable wavelength detector or two separate detectors capable of monitoring at 230 nm and at 254 nm, and a 4.6-mm × 12.5-cm or 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. Chromatograph the System suitability solution at 230 nm, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between proguanil related compound D and proguanil peaks is not less than 5. Chromatograph the Standard solution at 230 nm, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 10.0%.
)—The liquid chromatograph is equipped with either a programmable variable wavelength detector or two separate detectors capable of monitoring at 230 nm and at 254 nm, and a 4.6-mm × 12.5-cm or 4.6-mm × 15-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 1 mL per minute. Chromatograph the System suitability solution at 230 nm, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the resolution, R, between proguanil related compound D and proguanil peaks is not less than 5. Chromatograph the Standard solution at 230 nm, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 10.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Related compound C solution, Related compound D solution, Standard solution, and the Test solution into a chromatograph and record the chromatograms at both wavelengths for at least five times the retention time of the proguanil peak. Identify the components based on their relative retention times, which are about 0.46 for proguanil related compound D, 1.0 for proguanil, and about 2.5 for proguanil related compound C, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Calculate the percentage of proguanil related compounds C and D, as detected at 230 nm, in the portion of Proguanil Hydrochloride taken by the formula:
100(CS / CT)(rU / rS)
in which CS and CT are the concentrations, in mg per mL, of proguanil hydrochloride in the Standard solution and the Test solution, respectively; rU is the peak response for proguanil related compounds C and D, respectively, obtained from the Test solution at 230 nm; and rS is the peak response for the proguanil peak obtained from the Standard solution at 230 nm: not more than 0.2% of proguanil related compound C and not more than 0.2% of proguanil related compound D is found.
Calculate the percentage of any other impurity, as detected at 230 nm and at 254 nm, in the portion of Proguanil Hydrochloride taken by the formula:
100(CS / CT)(rU / rS)
in which CS and CT are the concentrations, in mg per mL, of proguanil hydrochloride in the Standard solution and the Test solution, respectively; rU is the peak response for each impurity, obtained from the Test solution at 230 nm or at 254 nm, respectively; and rS is the peak response for the proguanil peak obtained from the Standard solution at 230 nm or at 254 nm, respectively: not more than 0.1% of any other impurity is found. Calculate the percentage of total impurities as the sum of the calculated percentage contents of known and unknown impurities, considering each peak at the wavelength at which the peak shows the higher value: not more than 0.5% is found. Disregard any peak below 0.05%.
Assay—
Suspend 100 mg of Proguanil Hydrochloride in 20 mL of glacial acetic acid, shake, and heat at 50 for 5 minutes. Cool to room temperature, and add 40 mL of acetic anhydride. Titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid, determining the endpoint potentiometrically. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 14.51 mg of C11H16ClN5·HCl.
for 5 minutes. Cool to room temperature, and add 40 mL of acetic anhydride. Titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid, determining the endpoint potentiometrically. Each mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 14.51 mg of C11H16ClN5·HCl.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Leonel M. Santos, Ph.D.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8168 |
(SM12010) Monographs - Small Molecules 1 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 4436
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 34(2) Page 296