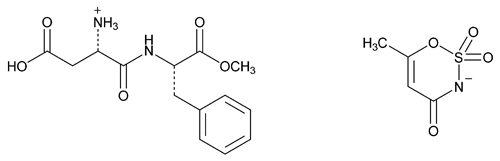
Aspartame Acesulfame
C18H23O9N3S 457.46
Aspartame acesulfame salt;
[2-Carboxy- -(N-b-methoxycarbonyl-2-phenyl)ethylcarbamoyl)]ethanaminium 6-methyl-4-oxo-1,2,3-oxathiazin-3-ide-2,2-dioxide;
-(N-b-methoxycarbonyl-2-phenyl)ethylcarbamoyl)]ethanaminium 6-methyl-4-oxo-1,2,3-oxathiazin-3-ide-2,2-dioxide;
l-Phenylalanine, l- -aspartyl-2-methyl ester compound with 6-methyl-1,2,3-oxathiazin-4(3H)-one 2,2-dioxide (1:1)
-aspartyl-2-methyl ester compound with 6-methyl-1,2,3-oxathiazin-4(3H)-one 2,2-dioxide (1:1)


 [106372-55-8].
[106372-55-8].
(as' par tame a'' se sul' fame).
C18H23O9N3S 457.46
Aspartame acesulfame salt;
[2-Carboxy-
l-Phenylalanine, l-
DEFINITION
Aspartame Acesulfame contains NLT 63.0% and NMT 66.0% of aspartame, calculated on the dried basis. It contains NLT 34.0% and NMT 37.0% of acesulfame, calculated as the acid form on the dried basis.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Infrared Absorption  197K
197K
[Note—Do not dry specimens. ]
ASSAY
• Procedure
Sample:
0.150 g
Analysis:
Dissolve the Sample in 50 mL of dehydrated alcohol. Titrate with 0.1 N tetrabutylammonium hydroxide in methanol/isopropyl alcohol VS. Potentiometrically determine the volumes of titrant, in mL, at the first equivalence point (V1) and at the second equivalence point (V2). Perform a blank titration with 50 mL of dehydrated alcohol, and designate the volume of titrant, in mL, as VB.
Calculate the percentage of acesulfame (Result 1) and aspartame (Result 2) in the portion of Aspartame Acesulfame taken:
Result 1 = 163N(V1  VB)/10W
VB)/10W
Result 2 = 294N(V2  V1)/10W
V1)/10W
| N | = | = normality of the titrant |
| W | = | = weight of Aspartame Acesulfame taken (g) |
Acceptance criteria:
Aspartame, 63.0%–66.0% on the dried basis; acesulfame, 34.0%–37.0% as the acid form on the dried basis
IMPURITIES
• Residue on Ignition  281
281 :
NMT 1.1%
:
NMT 1.1%
• Heavy Metals, Method II  231
231 :
NMT 10 ppm
:
NMT 10 ppm
• Limit of Potassium
Potassium stock solution:
19.0 µg/mL of potassium chloride, previously dried at 105 for 2 h, in water. This solution contains 10 µg of potassium/mL.
for 2 h, in water. This solution contains 10 µg of potassium/mL.
Standard solution A:
Transfer 10.0 mL of Potassium stock solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 2.0 mL of sodium chloride solution (1 in 5) and 1.0 mL of hydrochloric acid, and dilute with water to volume (1.0 µg/mL of potassium).
Standard solution B:
Transfer 15.0 mL of Potassium stock solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 2.0 mL of sodium chloride solution (1 in 5) and 1.0 mL of hydrochloric acid, and dilute with water to volume (1.5 µg/mL of potassium).
Standard solution C:
Transfer 20.0 mL of Potassium stock solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 2.0 mL of sodium chloride solution (1 in 5) and 1.0 mL of hydrochloric acid, and dilute with water to volume (2.0 µg/mL of potassium).
Sample stock solution:
3.0 mg/mL of Aspartame Acesulfame
Sample solution:
Transfer 10 mL of Sample stock solution to a 100-mL volumetric flask. Add 2.0 mL of sodium chloride solution (1 in 5) and 1.0 mL of hydrochloric acid, and dilute with water to volume. Filter the solution.
Instrumental conditions
Mode:
Atomic absorption spectrophotometry
Analytical wavelength:
766.5 nm (potassium emission line)
Lamp:
Potassium hollow-cathode
Flame:
Air–acetylene
Blank:
Water
Standard curve
Samples:
Standard solution A, Standard solution B, and Standard solution C
Plot:
Absorbance values versus their corresponding concentration (µg/mL) of potassium
Analysis
Sample:
Sample solution
From the Standard curve, determine the concentration of potassium in the Sample solution.
Calculate the percentage of potassium in the portion of Aspartame Acesulfame taken:
Result = (CS/CU) × 100
| CS | = | = concentration of potassium in the Sample solution from the Standard curve (µg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of aspartame acesulfame in the Sample solution (g/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.5%
• Related Compounds
Diluent:
Methanol and water (1:9)
Mobile phase:
Prepare a solution by dissolving 5.6 g of monobasic potassium phosphate in 820 mL of water in a 1-L volumetric flask, adjusting with phosphoric acid to a pH of 4.3, diluting with methanol to volume, and mixing.
Standard solution:
25 µg/mL of USP Aspartame Related Compound A RS in Diluent
Sample solution:
5 mg/mL in Diluent
[Note—Avoid heat and excessive holding times. ]
Instrumental conditions
Mode:
LC
Detector:
UV 210 nm
Column:
4.6-mm × 25-cm; packing L1
Column temperature:
40
Flow rate:
1.5 mL/min
Injection size:
20 µL
System suitability
Sample:
Standard solution
Suitability requirements
Tailing factor:
NMT 2.0
Relative standard deviation:
NMT 4.0%
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of aspartame related compound A in the portion of Aspartame Acesulfame taken:
Result = (rU/rS) × (CS/CU) × 100
| rU | = | = peak response of aspartame related compound A from the Sample solution |
| rS | = | = peak response of aspartame related compound A from the Standard solution |
| CS | = | = concentration of USP Aspartame Related Compound A RS in the Standard solution (mg/mL) |
| CU | = | = concentration of Aspartame Acesulfame in the Sample solution (mg/mL) |
Acceptance criteria:
NMT 0.5%
• Chromatographic Purity
Diluent, Mobile phase, and Instrumental conditions:
Proceed as directed in Related Compounds.
Acesulfame solution:
2 mg/mL of USP Acesulfame Potassium RS in Diluent
Sample stock solution:
Proceed as directed for Sample solution under Related Compounds.
Sample solution:
75 µg/mL of Aspartame Acesulfame from Sample stock solution in Diluent
Analysis
Samples:
Acesulfame solution, Sample stock solution, and Sample solution
[Note—Continue the elution of the Sample stock solution for twice the retention time of the aspartame peak. ]
Acceptance criteria:
The sum of the responses of all the peaks of the Sample stock solution, excluding the aspartame related compound A, acesulfame, and aspartame peak responses, is not greater than the aspartame peak response from the Sample solution (1.0%).
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Optical Rotation, Specific Rotation  781S
781S
15 N formic acid:
To a 1-L volumetric flask add approximately 300 mL of water, then weigh 719 g of 96% formic acid into this flask, and mix. Cool the solution to 20 . Dilute with water to volume.
. Dilute with water to volume.
Sample solution:
62 mg/mL in 15 N formic acid
Acceptance criteria:
+14.5 to +16.5
to +16.5 , determined at 20
, determined at 20 within 30 min after preparation of the Sample solution. [Note—Divide the calculated specific rotation by 0.646 to correct for the aspartame content in Aspartame Acesulfame. ]
within 30 min after preparation of the Sample solution. [Note—Divide the calculated specific rotation by 0.646 to correct for the aspartame content in Aspartame Acesulfame. ]
• Loss on Drying  731
731 :
Dry a sample at 105
:
Dry a sample at 105 for 4 h: it loses NMT 0.5% of its weight.
for 4 h: it loses NMT 0.5% of its weight.
• Transmittance:
The transmittance of a 1-in-100 solution of Aspartame Acesulfame in distilled water, determined in a 1-cm cell at 430 nm with a suitable spectrophotometer, is NLT 0.95.
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
• Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers, and store in a cool, dry place.
• USP Reference Standards  11
11
USP Aspartame Related Compound A RS
5-Benzyl-3,6-dioxo-2-piperazineacetic acid.
C13H14N2O4 262.27
5-Benzyl-3,6-dioxo-2-piperazineacetic acid.
C13H14N2O4 262.27
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Robert H. Lafaver, M.S.
Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8335 |
(EXC2010) Monographs - Excipients |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 1703
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 29(2) Page 453