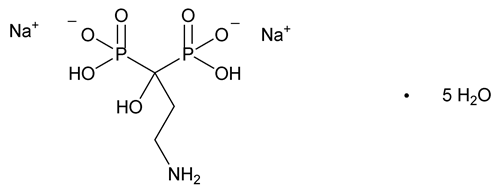
Pamidronate Disodium
(pam'' i droe' nate dye soe' dee um).
Phosphonic acid, (3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene)bis-, disodium salt, pentahydrate.
Disodium dihydrogen (3-amino-1-hydroxypropylidene)diphosphonate, pentahydrate
Anhydrous 279.06
» Pamidronate Disodium contains not less than 98.0 percent and not more than 102.0 percent of C3H9NNa2O7P2, calculated on the anhydrous basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers. Store at a temperature not exceeding 30 .
.
Clarity and color of solution—
Test preparation 1—
Dissolve 1.0 g in 50 mL of water with gentle warming. Cool to room temperature.
Test preparation 2—
Dissolve 1.0 g in 25 mL of 2 N sodium hydroxide solution with gentle warming. Cool to room temperature.
Procedure—
Examine Test preparation 1 and Test preparation 2: the solutions are clear. Separately measure the absorbance of each of these solutions at 420 nm in 4-cm cells, using water as the blank for Test preparation 1 and using 2 N sodium hydroxide solution as the blank for Test preparation 2: the absorbance of each solution is not more than 0.10.
Identification—
B:
The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation corresponds to that in the chromatogram of the Standard preparation, as obtained in the Assay.
C:
It meets the requirements of the pyroantimonate precipitate test for Sodium  191
191 .
.
Microbial enumeration tests  61
61 and Tests for specified microorganisms
and Tests for specified microorganisms  62
62 —
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 1000 cfu per g, and the total combined yeasts and molds count does not exceed 100 cfu per g.
—
The total aerobic microbial count does not exceed 1000 cfu per g, and the total combined yeasts and molds count does not exceed 100 cfu per g.
pH  791
791 :
between 7.8 and 8.8, in a solution (1 in 100).
:
between 7.8 and 8.8, in a solution (1 in 100).
Water, Method I  921
921 :
between 23.0% and 25.5%.
:
between 23.0% and 25.5%.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 :
20 µg per g.
:
20 µg per g.
Related compounds—
test 1—
Adsorbent:
0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel mixture.
Test solution—
Transfer 30 mg of Pamidronate Disodium to a 10-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Standard solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Beta Alanine RS in water, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with water to obtain a solution containing 0.006 mg of beta alanine per mL.
Application volume:
10 µL.
Developing solvent system:
a mixture of methanol, diisopropyl ether, and 25% ammonia (9:8:4).
Spray reagent—
Dissolve 0.2 g of ninhydrin in 100 mL of a mixture of butyl alcohol and 2 N acetic acid (95:5).
Procedure—
Proceed as directed for Thin-Layer Chromatography under Chromatography  621
621 . Dry the plate between 100
. Dry the plate between 100 and 105
and 105 until the ammonia disappears completely. Spray with Spray reagent, and heat between 100
until the ammonia disappears completely. Spray with Spray reagent, and heat between 100 and 105
and 105 for about 15 minutes. Examine the plate under white light. The spot obtained from the Test solution having an RF value of about 0.5 is not greater in size or intensity than the corresponding spot obtained from the Standard solution: not more than 0.2% of beta alanine is found. Evaluate any other additional spot in the chromatogram of the Test solution, and determine the percentage of total other impurities (excluding beta alanine).
for about 15 minutes. Examine the plate under white light. The spot obtained from the Test solution having an RF value of about 0.5 is not greater in size or intensity than the corresponding spot obtained from the Standard solution: not more than 0.2% of beta alanine is found. Evaluate any other additional spot in the chromatogram of the Test solution, and determine the percentage of total other impurities (excluding beta alanine).
test 2—
Mobile phase—
Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Impurity stock solution 1—
Transfer about 300 mg of ortho-phosphoric acid, accurately weighed, to a 1000-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Impurity stock solution 2—
Transfer about 250 mg of phosphorous acid, accurately weighed, to a 1000-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Impurity standard solution—
Transfer 2.0 mL each of Impurity stock solution 1 and Impurity stock solution 2 to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Test solution—
Prepare as directed for the Assay preparation.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
Proceed as directed in the Assay. Chromatograph the Impurity standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the elution order is a phosphate peak followed by the phosphite peak; the resolution, R, between the two peaks is not less than 2.5; the relative standard deviation for replicate injections, determined from the phosphate peak, is not more than 10%; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections, determined from the phosphite peak, is not more than 20%.
)—
Proceed as directed in the Assay. Chromatograph the Impurity standard solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the elution order is a phosphate peak followed by the phosphite peak; the resolution, R, between the two peaks is not less than 2.5; the relative standard deviation for replicate injections, determined from the phosphate peak, is not more than 10%; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections, determined from the phosphite peak, is not more than 20%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 100 µL) of the Impurity standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Calculate the percentage of phosphates as ortho-phosphoric acid in the portion of Pamidronate Disodium taken by the formula:
0.2(W1 / W)(rU / rS)
in which W1 is the weight, in mg, of ortho-phosphoric acid taken to prepare the Impurity stock solution 1; W is the weight, in mg, of Pamidronate Disodium taken to prepare the Test solution; and rU and rS are the phosphate peak responses obtained from the Test solution and the Impurity standard solution, respectively: not more than 0.5% of phosphate, determined as ortho-phosphoric acid, is found.
Calculate the percentages of phosphites as phosphorous acid in the portion of Pamidronate Disodium taken by the formula:
0.2(W2 / W)(rU / rS)
in which W2 is the weight, in mg, of phosphorous acid taken to prepare the Impurity stock solution 2; W is as defined above; and rU and rS are the phosphite peak responses obtained from the Test solution and the Impurity standard solution, respectively: not more than 0.5% of phosphite, determined as phosphorous acid, is found; and not more than 0.5% of total phosphate and phosphite combined is found.
Calculate the percentage of any other impurity in the portion of Pamidronate Disodium taken by the formula:
0.2(W1 / W)(ri / rS)
in which W1 and W are as defined above; ri is the peak response of any other impurity in the Test solution; and rS is the response of the phosphate peak obtained from the Impurity standard solution: not more than 0.5% of total other impurities (excluding beta alanine, phosphate as ortho-phosphoric acid, and phosphite as phosphorous acid) is found, the results for Test 1 and Test 2 being added.
Assay—
Mobile phase—
To 2500 mL of water, add 0.47 mL of anhydrous formic acid, adjust with 2 N sodium hydroxide solution to a pH of 3.5, filter, and degas. Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ). [note—The small amounts of formic acid have a strong influence on the retention times. ]
). [note—The small amounts of formic acid have a strong influence on the retention times. ]
Standard preparation—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Pamidronate Disodium RS in water, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with water to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 2 mg per mL.
Assay preparation—
Transfer about 100 mg of Pamidronate Disodium, accurately weighed, to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with water to volume, and mix.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a refractive index detector and a 4.6-mm ×10-cm column that contains packing L23. The flow rate is about 1.0 mL per minute. The column temperature is maintained at 35
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a refractive index detector and a 4.6-mm ×10-cm column that contains packing L23. The flow rate is about 1.0 mL per minute. The column temperature is maintained at 35 . Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the tailing factor is not less than 0.3 and not more than 1.2; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the tailing factor is not less than 0.3 and not more than 1.2; and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 100 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the responses for the major peaks. Calculate the quantity, in mg, of C3H9NNa2O7P2 in the portion of Pamidronate Disodium taken by the formula:
50C(rU / rS)
in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of USP Pamidronate Disodium RS in the Standard preparation; and rU and rS are the peak responses obtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Elena Gonikberg, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8251 |
(SM32010) Monographs - Small Molecules 3 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
|
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology |
USP35–NF30 Page 4200
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 34(5) Page 1179