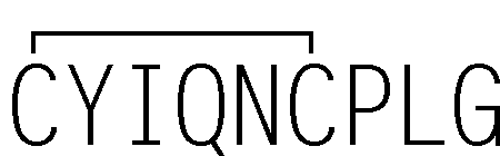
Oxytocin
(ox'' i toe' sin).
» Oxytocin is a nonapeptide hormone having the property of causing the contraction of uterine smooth muscle and of the myoepithelial cells within the mammary gland. It is prepared by synthesis. Its oxytocic activity is not less than 400 USP Oxytocin Units per mg.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers, preferably of Type I glass, in a refrigerator.
Microbial enumeration tests  61
61 and Tests for specified microorganisms
and Tests for specified microorganisms  62
62 —
The total bacterial count does not exceed 200 cfu per g. For products of animal origin, it meets also the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli.
—
The total bacterial count does not exceed 200 cfu per g. For products of animal origin, it meets also the requirements of the tests for absence of Salmonella species and Escherichia coli.
Identification—
A:
The retention time of the oxytocin peak in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation corresponds to that in the chromatogram of the Standard preparation as obtained in the Assay.
Perform one of the following two tests:
B: Nuclear Magnetic Resonance—
[note—Concentrations of Oxytocin in both the Standard solution and the Test solution must be the same (within 5% of each other) but can be adjusted based on the quality of the spectrum obtained. The spectra must be acquired under the same conditions for both the Standard solution and the Test solution. The spectra obtained are of sufficient quality to allow quantification of the integrals of the resonances specified below to be obtained. Integrals and spectra of both the Standard solution and the Test solution can be repeated and averaged. ]
pH 5.0 Sodium phosphate buffer—
Dissolve 27.6 g of monobasic sodium phosphate in 900 mL of water, adjust with phosphoric acid or 10 N sodium hydroxide to a pH of 5.0 ± 0.1, dilute with water to 1000 mL, and mix.
Standard solution—
Prepare a 10 mg per mL solution (approximately 1 mL) of USP Oxytocin Identification RS in pH 5.0 Sodium phosphate buffer. Lyophilize to dryness, redissolve in deuterium oxide, lyophilize again, redissolve in deuterium oxide, and lyophilize once again (to replace exchangeable hydrogens with deuterium). Dissolve in 1 mL of deuterium oxide containing 0.5% v/v (2,2,3,3-(d4)-3-(trimethylsilyl) propionic acid sodium salt (TSP) as a chemical shift reference.
Test solution—
Prepare a 10 mg per mL solution (approximately 1 mL) of Oxytocin in pH 5.0 Sodium phosphate buffer. Proceed as directed for the Standard solution.
Procedure—
Obtain a proton NMR spectrum of both the Standard solution and the Test solution. The spectra from both solutions are qualitatively and quantitatively similar, and all the resonances from the spectrum of the Standard solution are present in the spectrum of the Test solution and have the same chemical shift values (±0.1 ppm). Identify any other resonances in the spectrum of the Test solution that are not present in the spectrum of the Standard solution. The integrals of the acetate and deuterium oxide peaks at 1.9 ppm and 4.9 ppm can differ quantitatively in the spectra of the Standard solution and the Test solution.
C: Amino acid content—
Use a suitable, validated procedure (see Biotechnology-Derived Articles—Amino Acid Analysis  1052
1052 ).
).
Standard solutions—
Prepare a solution having known equimolar amounts of l-alanine, l-arginine, l-aspartic acid, l-glutamic acid, glycine, l-histidine, l-isoleucine, l-leucine, l-lysine, l-methionine, l-phenylalanine, l-proline, l-serine, l-threonine, l-tyrosine, and l-valine with half the equimolar amount of l-cystine. For the validation of the method, use an appropriate internal standard, such as norleucine. Prepare a separate, equimolar solution of l-tryptophan.
Test solution—
[note—The following hydrolysis conditions and concentrations can be modified depending on the method of analysis chosen. ] Transfer about 64 mg of Oxytocin, accurately weighed, to a suitable vessel, and dissolve in 1.0 mL of water. Transfer 0.10 mL of this solution to a vacuum hydrolysis tube, add 2.0 mL of 6 N hydrochloric acid, evacuate the tube, and heat for 16 hours at 120 . Transfer 0.10 mL of the hydrolysate so obtained to a suitable vessel, add 1 mL of water, and lyophilize. Dissolve in and dilute to a suitable volume in a buffer solution suitable for amino acid analysis.
. Transfer 0.10 mL of the hydrolysate so obtained to a suitable vessel, add 1 mL of water, and lyophilize. Dissolve in and dilute to a suitable volume in a buffer solution suitable for amino acid analysis.
Procedure—
Inject equal volumes of the Standard solutions and the Test solution into the amino acid analyzer, and measure and record the responses for each amino acid peak. Express the content of each amino acid in moles. Calculate the relative proportions of the amino acids, taking1/6 of the sum of the number of moles of aspartic acid, glutamic acid, proline, glycine, isoleucine, and leucine as equal to 1. The values fall within the following limits: aspartic acid: 0.90 to 1.10; glutamic acid: 0.90 to 1.10; proline: 0.90 to 1.10; glycine: 0.90 to 1.10; leucine: 0.90 to 1.10; isoleucine: 0.90 to 1.10; tyrosine: 0.7 to 1.05; half-cystine: 1.4 to 2.1. Not more than traces of other amino acids are present.
Acetic acid content  503
503 :
between 6% and 10%.
:
between 6% and 10%.
Test Solution—
Transfer about 15 mg of Oxytocin, accurately weighed, to a 10-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in and dilute with Diluent to volume, and mix.
Ordinary impurities—
The sum of the responses of impurities in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation obtained in the Assay is not more than 5% of the area of the oxytocin peak.
Assay—
Mobile phase A—
Prepare a buffer solution of 0.1 M monobasic sodium phosphate.
Mobile phase B—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of acetonitrile in water (1:1). Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Diluent—
Dissolve 5.0 g of chlorobutanol in 5.0 mL of glacial acetic acid, add 5.0 g of alcohol, 1.1 g of sodium acetate, and 1000 mL of water, and mix.
Standard preparation—
Dissolve the entire contents of a vial of USP Oxytocin RS in a known volume of Diluent. [note—The solution may be diluted as necessary to a working concentration range for the assay. ]
Assay preparation—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of Oxytocin in Diluent to obtain a solution containing about 10 USP Oxytocin Units per mL.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a variable wavelength detector set at 220 nm and a 12.0-cm × 4.6-mm column that contains 5-µm packing L1, and is programmed to provide variable mixtures of Mobile phase A and Mobile phase B. The column is maintained at room temperature, and the flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. The system is equilibrated with a mixture of 70% Mobile phase A and 30% Mobile phase B. After each injection of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation, the composition of the mobile phase is changed linearly over the next 20 minutes so that it consists of a mixture of 50% Mobile phase A and 50% Mobile phase B. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the chromatograms as directed for Procedure. Adjust the flow rate or the composition of the Mobile phase such that the retention time of oxytocin is approximately 10 minutes and between 15 and 17 minutes for chlorobutanol. The resolution, R, between oxytocin and the nearest adjacent peak is not less than 1.5, and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0% for oxytocin.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a variable wavelength detector set at 220 nm and a 12.0-cm × 4.6-mm column that contains 5-µm packing L1, and is programmed to provide variable mixtures of Mobile phase A and Mobile phase B. The column is maintained at room temperature, and the flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute. The system is equilibrated with a mixture of 70% Mobile phase A and 30% Mobile phase B. After each injection of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation, the composition of the mobile phase is changed linearly over the next 20 minutes so that it consists of a mixture of 50% Mobile phase A and 50% Mobile phase B. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the chromatograms as directed for Procedure. Adjust the flow rate or the composition of the Mobile phase such that the retention time of oxytocin is approximately 10 minutes and between 15 and 17 minutes for chlorobutanol. The resolution, R, between oxytocin and the nearest adjacent peak is not less than 1.5, and the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0% for oxytocin.
Procedure—
Separately inject three equal volumes (about 100 µL) of the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation into the chromatograph, and record the chromatograms as described under Chromatographic system. Identify the peaks, and determine the area of the oxytocin peak. Calculate the potency of oxytocin in USP Oxytocin Units per mg by the formula:
C(rU / rS)(V / W)
in which C is the concentration, in USP Oxytocin Units per mL, of the Standard preparation; and rU and rS are the mean peak responses obtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively; V is the volume of sample solution in which the sample was dissolved; and W is the amount, in mg, of oxytocin dissolved in the sample solution.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Thomas A. Sigambris, M.S.
Scientific Liaison 1-301-998-6789 |
(BIO12010) Monographs - Biologics and Biotechnology 1 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
|
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology | |
| Radhakrishna S Tirumalai, Ph.D.
Principal Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8339 |
(GCM2010) General Chapters - Microbiology |
USP35–NF30 Page 4192
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 34(3) Page 647