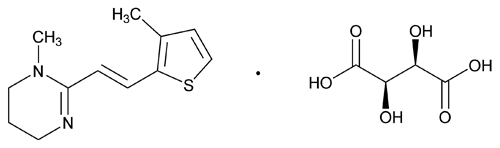
Morantel Tartrate
(moe ran' tel tar' trate).
Pyrimidine, 1,4,5,6-tetrahydro-1-methyl-2-[2-(3-methyl-2-thienyl)ethenyl]-, (E)-,[R-(R*,R*)]-2,3-dihydroxybutanedioate (1:1).
(E)-1,4,5,6-Tetrahydro-1-methyl-2-[2-(3-methyl-2-thienyl)vinyl]pyrimidine tartrate (1:1)
Morantel
» Morantel Tartrate contains not less than 96.4 percent and not more than 101.5 percent of C12H16N2S · C4H6O6, calculated on the dried basis.
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in well-closed, light-resistant containers. Store at 25 , excursions permitted between 15
, excursions permitted between 15 and 30
and 30 .
.
Labeling—
Label it to indicate it is for veterinary use only.
Clarity and color of solution—
Dissolve and dilute 0.25 g to 25.0 mL in carbon dioxide-free water. The solution is clear and yellow to greenish yellow in color.
Identification—
B:
It meets the requirements of the test for Tartrate  191
191 .
.
C:
The retention time of the morantel peak in the chromatogram of the Test solution corresponds to that in the chromatogram of Standard solution 1, as obtained in the test for Related compounds.
Melting temperature  741
741 :
167
:
167 to 172
to 172 .
.
pH  791
791 :
between 2.8 and 3.9.
:
between 2.8 and 3.9.
Solution—
Dissolve and dilute 0.25 g to 25.0 mL in carbon dioxide-free water.
Loss on drying  731
731 —
Dry it at 100
—
Dry it at 100 to 105
to 105 to constant weight: it loses not more than 1.5% of its weight.
to constant weight: it loses not more than 1.5% of its weight.
Residue on ignition  281
281 :
not more than 0.1%.
:
not more than 0.1%.
Heavy metals, Method II  231
231 —
not more than 20 ppm.
—
not more than 20 ppm.
Related compounds—
[note—Conduct this test without exposure to daylight, and with the minimum necessary exposure to artificial light. ]
Mobile phase—
Mix 3.5 mL of triethylamine and 850 mL of water. Adjust with phosphoric acid to a pH of 2.5. Add 50 mL of tetrahydrofuran and 100 mL of methanol, and mix.
Tartrate solution—
Prepare a solution containing about 0.15 mg of tartaric acid per mL in Mobile phase.
Standard solution 1—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Morantel Tartrate RS in Mobile phase to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 5.0 µg per mL.
Standard solution 2—
Dilute 2.0 mL of Standard solution 1 to 100.0 mL with Mobile phase.
System suitability solution—
Expose 10 mL of Standard solution 1 to daylight for 15 minutes before injection.
Test solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of Morantel Tartrate in Mobile phase to obtain a solution having a concentration of about 0.5 mg per mL.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 226-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 0.75 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Tartrate solution, Standard solution 1, and the System suitability solution, and record the peak areas as directed for Procedure: using the System suitability solution, the resolution, R, between morantel and its preceding peak ((Z)-isomer) is not less than 2. The relative retention times are about 0.8, 1.0, and 1.2 for the morantel (Z)-isomer, morantel, and the morantel 4-methyl isomer (1-methyl-2-[(E)-2-(4-methylthiophen-2-yl)ethenyl]-1,4,5,6 tetrahydropyrimidine), respectively.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 226-nm detector and a 4.6-mm × 25-cm column that contains 5-µm packing L1. The flow rate is about 0.75 mL per minute. Chromatograph the Tartrate solution, Standard solution 1, and the System suitability solution, and record the peak areas as directed for Procedure: using the System suitability solution, the resolution, R, between morantel and its preceding peak ((Z)-isomer) is not less than 2. The relative retention times are about 0.8, 1.0, and 1.2 for the morantel (Z)-isomer, morantel, and the morantel 4-methyl isomer (1-methyl-2-[(E)-2-(4-methylthiophen-2-yl)ethenyl]-1,4,5,6 tetrahydropyrimidine), respectively.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 20 µL) of the Tartrate solution, Standard solution 1, Standard solution 2, and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the areas for the major peaks. Disregarding the tartrate peak and any peak in the chromatogram of the Test solution less than the area of the principal peak in the chromatogram of Standard solution 2, calculate the area percentage of each impurity, relative to morantel, in the portion of Morantel Tartrate taken by the formula:
100(CS / CU)(ri / rS)
in which CS and CU are the concentrations of morantel tartrate, in mg per mL, of Standard solution 1 and the Test solution, respectively; and ri and rS are the peak areas of each individual impurity and morantel obtained from the Test solution and Standard solution 1, respectively: not more than 3% of the morantel 4-methyl isomer is found; not more than 0.5% of any other individual impurity is found; and not more than 1% of total other individual impurities is found.
Assay—
Dissolve 0.280 g in 40 mL of anhydrous acetic acid. Titrate with 0.1 N perchloric acid VS, determining the endpoint potentiometrically (see Titrimetry  541
541 ). One mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 37.04 mg of C12H16N2S · C4H6O6.
). One mL of 0.1 N perchloric acid is equivalent to 37.04 mg of C12H16N2S · C4H6O6.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Morgan Puderbaugh, B.S.
Associate Scientific Liaison 1-301-998-6833 |
(SM32010) Monographs - Small Molecules 3 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 3952
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 32(6) Page 1735