Methylcellulose
Cellulose, methyl ether;
Cellulose methyl ether

 [9004-67-5].
[9004-67-5].
(meth'' il sel' ue lose).
| Attributes | EP | JP | USP |
|---|---|---|---|
| Definition | + | + | + |
| Labeling | + | + | + |
| Identification A | + | + | + |
| Identification B | + | + | + |
| Identification C | + | + | + |
| Identification D | + | + | + |
| Identification E | + | + | + |
| Apparent Viscosity, Method 1 | + | + | + |
| Apparent Viscosity, Method 2 | + | + | + |
| pH | + | + | + |
| Heavy Metals | + | + | + |
| Loss on Drying | + | + | + |
| Residue on Ignition | + | + | + |
| Assay | + | + | + |
Legend: + will adopt and implement;  will not stipulate.
will not stipulate.
In EP, Viscosity and Assay will be dealt with in the non-mandatory Functionality-Related Characteristics section. The assay limits will not be included in the Definition (EP).
Nonharmonized attributes: Packaging and Storage
Specific local attributes: Appearance of solution (EP), Description (JP), Limit of glyoxal (EP).
Cellulose, methyl ether;
Cellulose methyl ether
DEFINITION
Methylcellulose is a methyl ether of cellulose. When dried at 105 for 1 h, it contains NLT 26.0% and NMT 33.0% of methoxy (OCH3) groups.
for 1 h, it contains NLT 26.0% and NMT 33.0% of methoxy (OCH3) groups.
IDENTIFICATION
• A. Procedure
Analysis:
Evenly distribute 1.0 g onto the surface of 100 mL of water in a beaker, tapping the top of the beaker gently, if necessary, to ensure a uniform layer on the surface, and allow to stand for 1–2 min.
Acceptance criteria:
The powdered material aggregates on the surface.
• B. Procedure
Analysis:
Evenly distribute 1.0 g into 100 mL of boiling water, and stir the mixture using a magnetic stirrer with a 25-mm long bar: a slurry is formed and the particles do not dissolve. Allow the slurry to cool to 5 and stir using a magnetic stirrer.
and stir using a magnetic stirrer.
Acceptance criteria:
A clear or slightly turbid solution occurs with its thickness dependent on the viscosity grade.
• C. Procedure
Analysis:
To 0.1 mL of the sample solution obtained in Identification test B add 9 mL of diluted sulfuric acid (9 in 10), shake, heat in a water bath for exactly 3 min, immediately cool in an ice bath, add carefully 0.6 mL of ninhydrin TS, shake, and allow to stand at 25 .
.
Acceptance criteria:
A red color develops immediately, and it does not change to purple within 100 min.
• D. Procedure
Analysis:
Add 2–3 mL of the solution obtained in Identification test B onto a glass slide as a thin film and allow the water to evaporate.
Acceptance criteria:
A coherent, clear film forms on the glass slide.
• E. Procedure
Analysis:
Add exactly 50 mL of the sample solution obtained in Identification test B to exactly 50 mL of water in a beaker. Insert a thermometer into the solution. Stir the solution on a magnetic stirrer/hot plate and begin heating at a rate of 2 /min to 5
/min to 5 /min. Determine the temperature at which a turbidity increase begins to occur and designate the temperature as the flocculation temperature.
/min. Determine the temperature at which a turbidity increase begins to occur and designate the temperature as the flocculation temperature.
Acceptance criteria:
The flocculation temperature is higher than 50 .
.
ASSAY
• Procedure
[Caution—Perform all steps involving Hydriodic acid carefully, in a well-ventilated hood. Use goggles, acid-resistant gloves, and other appropriate safety equipment. Be exceedingly careful when handling the hot vials, because they are under pressure. In the event of hydriodic exposure, wash with copious amounts of water, and seek medical attention at once.
]
Apparatus
Reaction vial:
A 5-mL pressure-tight serum vial, 20 mm in outside diameter, 50 mm in height, and 20 mm in outside diameter and 13 mm in inside diameter at the mouth, equipped with a pressure-tight septum having a polytetrafluoroethylene-faced butyl rubber and an air-tight seal using an aluminum crimp or any sealing system that provides sufficient air tightness.
Heater:
A heating module with a square-shaped aluminum block having holes 20 mm in diameter and 32 mm in depth, so that the reaction vial fits. The heating module is also equipped with a magnetic stirrer capable of mixing the contents of the vial, or use a reciprocal shaker that performs a reciprocating motion of approximately 100 times/min.
Hydriodic acid:
Use a reagent having a specific gravity of at least 1.69, equivalent to 55%–57% HI.
Internal standard solution:
30 mg/mL of n-octane in o-xylene
Standard solution:
Into a suitable serum vial, weigh 60–100 mg of adipic acid, add 2.0 mL of Hydriodic acid, then pipet 2.0 mL of Internal standard solution into the vial, and close the vial securely with a suitable septum stopper. Weigh the vial and contents, add 45 µL of methyl iodide with a syringe through the septum, weigh again, and calculate the weight of methyl iodide added, by difference. Shake, and allow the layers to separate. Use the upper layer as the Standard solution.
Sample solution:
Transfer 0.065 g of Methylcellulose to a 5-mL thick-walled reaction vial equipped with a pressure-tight septum closure, add 60–100 mg of adipic acid, and pipet 2.0 mL of Internal standard solution into the vial. Cautiously pipet 2.0 mL of Hydriodic acid into the mixture, immediately secure the closure, and weigh it. Using a magnetic stirrer equipped in the heating module, or using a reciprocal shaker, mix the contents of the vial continuously for 60 min while heating the block so that the temperature of the contents is maintained at 130 ± 2 . If a reciprocal shaker or magnetic stirrer cannot be used, shake the vial well by hand at 5-min intervals during the initial 30 min of the heating time. Allow the vial to cool, and again weigh. If the weight loss is less than 0.50% of the contents and there is no evidence of a leak, use the upper layer of the mixture as the Sample solution.
. If a reciprocal shaker or magnetic stirrer cannot be used, shake the vial well by hand at 5-min intervals during the initial 30 min of the heating time. Allow the vial to cool, and again weigh. If the weight loss is less than 0.50% of the contents and there is no evidence of a leak, use the upper layer of the mixture as the Sample solution.
Chromatographic system
Mode:
GC
Detector:
Thermal conductivity or hydrogen flame ionization
Column:
3- to 4-mm × 1.8- to 3-m column packed with 10%–20% liquid phase G1, 125–150 µm in diameter on 100- to 120-mesh support S1A
Column temperature:
100
Carrier gas:
Helium for the thermal conductivity detector, and helium or nitrogen for the hydrogen flame ionization detector
Flow rate:
Adjust so that the retention time of the internal standard is about 10 min.
Injection size:
1 or 2 µL
Analysis
Samples:
Standard solution and Sample solution
Calculate the percentage of methoxy in the Methylcellulose taken:
Result = 21.864 × (RU/RS) × (WS/W)
| 21.864 | = | = ratio of the formula weights of methoxy to methyl iodide times 100% |
| RU | = | = ratio of the peak area of methyl iodide to that of the internal standard from the Sample solution |
| RS | = | = ratio of the peak area of methyl iodide to that of the internal standard from the Standard solution |
| WS | = | = weight of methyl iodide in the Standard solution (mg) |
| W | = | = weight of Methylcellulose calculated on the dried basis taken for the Assay (mg) |
Acceptance criteria:
26.0%–33.0%
IMPURITIES
Inorganic Impurities
• Residue on Ignition  281
281 :
NMT 1.5%
:
NMT 1.5%
• Heavy Metals, Method III  231
231 :
For the Standard Preparation, add the Standard Lead Solution prior to digestion. Omit the Monitor Preparation.
:
For the Standard Preparation, add the Standard Lead Solution prior to digestion. Omit the Monitor Preparation.
Acceptance criteria:
The color of the test solution is not darker than that of the control solution (NMT 20 ppm).
SPECIFIC TESTS
• Loss on Drying  731
731 :
Dry a sample at 105
:
Dry a sample at 105 for 1 h: it loses NMT 5.0% of its weight.
for 1 h: it loses NMT 5.0% of its weight.
• Viscosity  911
911
[Note—The density is 1.00 g/mL, so there is no necessity for determining the density at every measurement in the case of having the confirmation data. ]
Method 1:
This method is applied to samples with a viscosity of less than 600 mPa·s. Weigh a quantity of Methylcellulose, equivalent to 4.000 g, calculated on the dried basis, transfer into a wide-mouth bottle, and add hot water to obtain the total weight of the sample and water of 200.0 g. Cap the bottle, and stir by mechanical means at 400 ± 50 rpm for 10 or 20 min until particles are thoroughly dispersed and wetted out. Scrape down the walls of the bottle with a spatula, if necessary, to ensure that there is no undissolved material on the sides of the bottle, and continue the stirring in a cooling water bath equilibrated at a temperature below 5 for another 20–40 min. Adjust the solution weight, if necessary, to 200.0 g using cold water. Centrifuge the solution, if necessary, to expel any entrapped air bubbles. Using a spatula remove any foam, if present. Perform the test with this solution at 20 ± 0.1
for another 20–40 min. Adjust the solution weight, if necessary, to 200.0 g using cold water. Centrifuge the solution, if necessary, to expel any entrapped air bubbles. Using a spatula remove any foam, if present. Perform the test with this solution at 20 ± 0.1 to obtain the kinematic viscosity,
to obtain the kinematic viscosity, 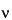 . Separately, determine the density,
. Separately, determine the density, 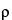 , of the solution, and calculate the viscosity,
, of the solution, and calculate the viscosity, 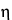 , as
, as 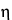 =
= 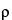
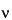 .
.
Method 2:
This method is applied to samples with a viscosity of 600 mPa·s or higher. Weigh a quantity of Methylcellulose, equivalent to 10.00 g, calculated on the dried basis, transfer into a wide-mouth bottle, and add hot water to obtain the total weight of the sample and water of 500.0 g. Capping the bottle, stir by mechanical means at 400 ± 50 rpm for 10–20 min until particles are thoroughly dispersed and wetted out. Scrape down the walls of the bottle with a spatula, if necessary, to ensure that there is no undissolved material on the sides of the bottle, and continue the stirring in a cooling water bath equilibrated at a temperature below 5 for another 20–40 min. Adjust the solution weight, if necessary, to 500.0 g using cold water. Centrifuge the solution, if necessary, to expel any entrapped air bubbles. Using a spatula remove any foam, if present. Determine the viscosity of this solution at 20 ± 0.1
for another 20–40 min. Adjust the solution weight, if necessary, to 500.0 g using cold water. Centrifuge the solution, if necessary, to expel any entrapped air bubbles. Using a spatula remove any foam, if present. Determine the viscosity of this solution at 20 ± 0.1 using a single cylinder type rotational viscometer.
using a single cylinder type rotational viscometer.
Apparatus:
Brookfield type LV model or equivalent. Rotor No., revolution, and calculation multiplier: apply the conditions specified in the following table.
| Labeled Viscositya (mPa·s) | Rotor No. | Revolution (rpm) | Calculation Multiplier |
|---|---|---|---|
| 600 or more and less than 1400 | 3 | 60 | 20 |
| 1400 or more and less than 3500 | 3 | 12 | 100 |
| 3500 or more and less than 9500 | 4 | 60 | 100 |
| 9500 or more and less than 99,500 | 4 | 6 | 1000 |
| 99,500 or more | 4 | 3 | 2000 |
|
a
The labeled viscosity is based on the manufacturer's specifications.
|
|||
Operation of apparatus:
Allow the spindle to rotate for 2 min before taking the measurement. Allow a rest period of 2 min between subsequent measurements. Repeat the operation to rotate the spindle specified above twice and average the three readings.
Acceptance criteria:
80.0%–120.0% of that stated on the label for viscosity types less than 600 mPa·s, and 75.0%–140.0% of that stated on the label for viscosity types 600 mPa·s or higher
• pH:
Measure the pH of the solution prepared in the test for Viscosity at 20 ± 2 . Read the indicated pH value after the probe has been immersed for 5 ± 0.5 min.
. Read the indicated pH value after the probe has been immersed for 5 ± 0.5 min.
Acceptance criteria:
5.0–8.0
ADDITIONAL REQUIREMENTS
•  Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers.
Packaging and Storage:
Preserve in well-closed containers.
• Labeling:
Label it to indicate its nominal viscosity type [viscosity of a solution (1 in 50)] in milli-Pascal second (mPa·s).
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Robert H. Lafaver, M.S.
Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8335 |
(EXC2010) Monographs - Excipients |
USP35–NF30 Page 3868
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 35(3) Page 683