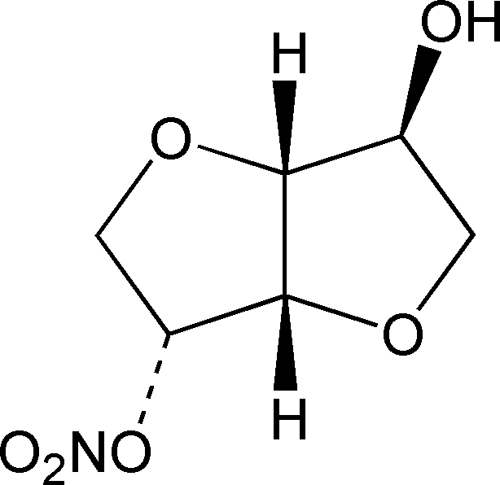
Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate
d-Glucitol, 1,4:3,6-dianhydro-, 5-nitrate.
1,4:3,6-Dianhydro-d-glucitol 5-nitrate
» Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate is a dry mixture of isosorbide mononitrate (C6H9NO6) with lactose or other suitable excipients to permit safe handling. It contains not less than 95.0 percent and not more than 105.0 percent of the labeled amount of isosorbide mononitrate (C6H9NO6).
[Caution—Exercise proper precautions in handling undiluted isosorbide mononitrate, which is a powerful explosive and can be exploded by percussion or excessive heat. Only exceedingly small amounts should be isolated.
]
Packaging and storage—
Preserve in tight containers. Store at a temperature between 20 and 30
and 30 .
.
USP Reference standards  11
11 —
—
Identification—
A:
Shake a quantity of it, equivalent to about 25 mg of isosorbide mononitrate, with 10 mL of acetone for 5 minutes. Filter, evaporate to dryness at a temperature below 40 , and dry the residue in a vacuum over phosphorus pentoxide for 16 hours: the IR absorption spectrum of a potassium bromide dispersion prepared from the residue so obtained exhibits maxima only at the same wavelengths as that of a similar preparation from the residue obtained from USP Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate RS.
, and dry the residue in a vacuum over phosphorus pentoxide for 16 hours: the IR absorption spectrum of a potassium bromide dispersion prepared from the residue so obtained exhibits maxima only at the same wavelengths as that of a similar preparation from the residue obtained from USP Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate RS.
B:
The retention time of the major peak in the chromatogram of the Assay preparation corresponds to that in the chromatogram of the Standard preparation, as obtained in the Assay.
Heavy metals, Method I  231
231 :
not more than 10 µg per g.
:
not more than 10 µg per g.
Related compounds—
test 1—
Adsorbent:
0.25-mm layer of chromatographic silica gel mixture.
Standard solution 1—
Weigh accurately a quantity of USP Isosorbide RS, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with absolute alcohol to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.0125 mg of isosorbide per mL.
Standard solution 2—
Weigh accurately a quantity of USP Isosorbide RS, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with absolute alcohol to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.025 mg of isosorbide per mL.
Standard solution 3—
Weigh accurately a quantity of USP Isosorbide RS, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with absolute alcohol to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.05 mg of isosorbide per mL.
Test solution—
Transfer a portion of Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate, equivalent to about 200 mg of isosorbide mononitrate, accurately weighed, to a suitable container, add 20.0 mL of absolute alcohol, sonicate for 10 minutes, and then centrifuge. Use the supernatant.
Application volume:
20 µL.
Developing solvent system:
a mixture of absolute alcohol and toluene (8:2).
Procedure—
Proceed as directed for Thin-Layer Chromatography under Chromatography  621
621 . After developing, dry the plate with warm air for about 10 minutes, dip the plate in a solution prepared by dissolving 1.25 g of potassium permanganate and 10.0 g of sodium hydroxide in 500 mL of water (prepared fresh for each plate), and heat at 105
. After developing, dry the plate with warm air for about 10 minutes, dip the plate in a solution prepared by dissolving 1.25 g of potassium permanganate and 10.0 g of sodium hydroxide in 500 mL of water (prepared fresh for each plate), and heat at 105 for 5 minutes. Any spot in the chromatogram obtained from the Test solution and corresponding to the RF value of the spots obtained from the Standard solutions is not more intense than the spot in the chromatogram obtained from Standard solution 3: not more than 0.5% of any individual impurity is found. If the spot in the chromatogram obtained from the Test solution is nearly as intense as the spot obtained from Standard solution 3, further dilute the Test solution with absolute alcohol (1:1), repeat the test, and compare the intensity of the isosorbide spot in the diluted Test solution with the intensity of the spots obtained from the Standard solutions, correcting the percentage level for the additional dilution of the Test solution.
for 5 minutes. Any spot in the chromatogram obtained from the Test solution and corresponding to the RF value of the spots obtained from the Standard solutions is not more intense than the spot in the chromatogram obtained from Standard solution 3: not more than 0.5% of any individual impurity is found. If the spot in the chromatogram obtained from the Test solution is nearly as intense as the spot obtained from Standard solution 3, further dilute the Test solution with absolute alcohol (1:1), repeat the test, and compare the intensity of the isosorbide spot in the diluted Test solution with the intensity of the spots obtained from the Standard solutions, correcting the percentage level for the additional dilution of the Test solution.
test 2—
Mobile phase, Resolution solution, and Chromatographic system—
Proceed as directed in the Assay.
Isosorbide mononitrate related compound A standard solution—
Prepare as directed for Isosorbide mononitrate related compound A standard preparation in the Assay.
Isosorbide dinitrate standard stock solution—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Diluted Isosorbide Dinitrate RS in methanol, sonicate and warm if necessary, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with methanol to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.125 mg of isosorbide dinitrate per mL.
Standard solution—
Transfer a quantity of USP Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate RS, accurately weighed, to a suitable volumetric flask. Dissolve in water, quantitatively add a volume of Isosorbide mononitrate related compound A standard solution and a volume of Isosorbide dinitrate standard stock solution, and dilute with water to volume to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 2.0 mg of isosorbide mononitrate per mL, 0.005 mg of isosorbide mononitrate related compound A per mL, and 0.005 mg of isosorbide dinitrate per mL. Filter a portion of the solution, discarding the first few mL of the filtrate.
Test solution—
Use the Assay preparation, prepared as directed in the Assay.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 50 µL) of the Standard solution and the Test solution into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the areas for the major peaks. Calculate the percentage of isosorbide mononitrate related compound A and isosorbide dinitrate relative to the amount of isosorbide mononitrate in the portion of Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate taken by the formula:
100(CV/W )(rU / rS)
in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of isosorbide mononitrate related compound A or isosorbide dinitrate, as appropriate, in the Standard solution; V is the volume, in mL, of the Test solution; W is the amount, in mg, of isosorbide mononitrate in the portion of Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate used to prepare the Test solution, based on the label claim; and rU and rS are the peak areas of the corresponding components obtained from the Test solution and the Standard solution, respectively: not more than 0.25% of isosorbide mononitrate related compound A is found; and not more than 0.25% of isosorbide dinitrate is found. Calculate the percentage of each other impurity (other than isosorbide mononitrate related compound A or isosorbide dinitrate) in the portion of Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate taken by the formula:
100(ri / rs)
in which ri is the peak area for each other impurity obtained from the Test solution; and rs is the sum of the areas of all the peaks: not more than 0.5% of total impurities is found, including isosorbide mononitrate related compound A and isosorbide dinitrate; and not more than 0.5% of total impurities is found, the results for Test 1 and Test 2 being considered.
Assay—
Mobile phase—
Prepare a filtered and degassed mixture of water and methanol (95:5). Make adjustments if necessary (see System Suitability under Chromatography  621
621 ).
).
Standard preparation—
Transfer an accurately weighed quantity of USP Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate RS to a suitable volumetric flask, dissolve in water, add a volume of methanol equivalent to 4% of the flask volume, and dilute with water to volume to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 2.0 mg of isosorbide mononitrate per mL.
Isosorbide mononitrate related compound A standard preparation—
Dissolve an accurately weighed quantity of USP Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate Related Compound A RS in methanol, and dilute quantitatively, and stepwise if necessary, with methanol to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 1.0 mg of isosorbide mononitrate related compound A per mL. Quantitatively dilute a portion of this solution with water to obtain a solution having a known concentration of about 0.05 mg per mL.
Resolution solution—
Transfer 10.0 mL of Isosorbide mononitrate related compound A standard preparation, 1.0 mL of the Standard preparation, and 4.0 mL of methanol to a 100-mL volumetric flask, and dilute with water to volume. Filter a portion of the solution, discarding the first few mL of the filtrate.
Assay preparation—
Transfer an accurately weighed amount of Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate, equivalent to 100 mg of isosorbide mononitrate, to a 50-mL volumetric flask, dissolve in about 25 mL of water, add 2 mL of methanol, dilute with water to volume, and mix. Filter a portion of the solution, discarding the first few mL of the filtrate.
Chromatographic system (see Chromatography  621
621 )—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 220-nm detector and a 4-mm × 12.5-cm column that contains packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute, increasing to 3.0 mL per minute at about 8.5 minutes to ensure that the isosorbide mononitrate peak has completely eluted. Chromatograph the Resolution solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative retention times are about 0.8 for isosorbide mononitrate related compound A, 1.0 for isosorbide mononitrate, and 4.1 for isosorbide dinitrate; and the resolution, R, between isosorbide mononitrate related compound A and isosorbide mononitrate is not less than 2.0. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
)—
The liquid chromatograph is equipped with a 220-nm detector and a 4-mm × 12.5-cm column that contains packing L1. The flow rate is about 1.5 mL per minute, increasing to 3.0 mL per minute at about 8.5 minutes to ensure that the isosorbide mononitrate peak has completely eluted. Chromatograph the Resolution solution, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative retention times are about 0.8 for isosorbide mononitrate related compound A, 1.0 for isosorbide mononitrate, and 4.1 for isosorbide dinitrate; and the resolution, R, between isosorbide mononitrate related compound A and isosorbide mononitrate is not less than 2.0. Chromatograph the Standard preparation, and record the peak responses as directed for Procedure: the relative standard deviation for replicate injections is not more than 2.0%.
Procedure—
Separately inject equal volumes (about 50 µL) of the Standard preparation and the Assay preparation into the chromatograph, record the chromatograms, and measure the areas for the isosorbide mononitrate peaks. Calculate the quantity, in mg, of isosorbide mononitrate (C6H9NO6) in the portion of Diluted Isosorbide Mononitrate taken by the formula:
CV(rU / rS)
in which C is the concentration, in mg per mL, of isosorbide mononitrate in the Standard preparation; V is the volume, in mL, of the Assay preparation; and rU and rS are the peak areas obtained from the Assay preparation and the Standard preparation, respectively.
Auxiliary Information—
Please check for your question in the FAQs before contacting USP.
| Topic/Question | Contact | Expert Committee |
|---|---|---|
| Monograph | Sujatha Ramakrishna, Ph.D.
Senior Scientific Liaison 1-301-816-8349 |
(SM22010) Monographs - Small Molecules 2 |
| Reference Standards | RS Technical Services 1-301-816-8129 rstech@usp.org |
USP35–NF30 Page 3591
Pharmacopeial Forum: Volume No. 32(6) Page 1699